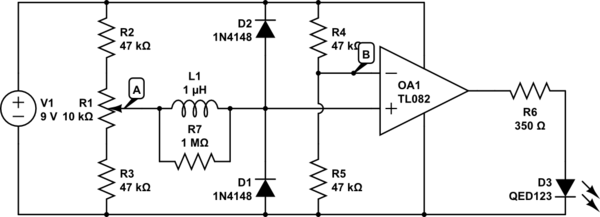
RF oscillator uses current-feedback op amp
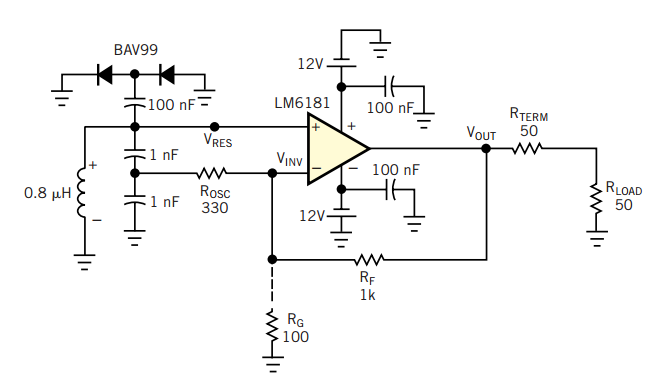
A current-feedback amplifier is a well-known component with many uses. Its basic block diagram shows that its input stage is a voltage follower in practice, a symmetrical emitter follower. The configuration samples the output current, converts it to voltage across a large impedance, and amplifies it to the output using a high-power, low-output-impedance amplifier.
A current-feedback amplifier (CFA) is characterized by its ability to maintain a high bandwidth and fast response time while providing significant gain. The fundamental operation of a CFA relies on the feedback mechanism that adjusts the gain based on the output current rather than the output voltage, which is typical in voltage-feedback amplifiers. This unique feedback approach allows for improved stability and performance in various applications, including audio amplification, signal processing, and instrumentation.
The basic block diagram of a CFA typically includes an input stage that consists of a voltage follower, often implemented with a symmetrical emitter follower configuration. This stage is essential for ensuring that the input signal is buffered effectively, providing high input impedance and low output impedance. The voltage follower configuration allows for minimal loading on the preceding stage while ensuring that the input signal is accurately represented at the output.
The output stage of the CFA is designed to deliver high power with low output impedance, making it suitable for driving loads directly. The output current is sampled and converted into a voltage signal across a large impedance. This conversion is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal while enabling the amplifier to operate efficiently under varying load conditions.
In practical applications, current-feedback amplifiers offer advantages such as reduced distortion, enhanced linearity, and improved transient response. These attributes make CFAs particularly effective in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount. The design considerations for CFAs include selecting appropriate feedback components, ensuring thermal stability, and optimizing power supply configurations to achieve the desired performance metrics.
Overall, the current-feedback amplifier serves as a versatile and efficient solution for a wide range of electronic circuit applications, providing reliable amplification with the ability to handle complex signal processing tasks.A current-feedback amplifier is a well-known component with many uses. Its basic block diagram shows that its input stage is a voltage followerin practice, a symmetrical emitter follower (Figure 1). The configuration samples the output current, converts it to voltage across a large impedance, and amplifies it to the output using a high-power, low-output-impedance amplifier.
🔗 External reference
A current-feedback amplifier (CFA) is characterized by its ability to maintain a high bandwidth and fast response time while providing significant gain. The fundamental operation of a CFA relies on the feedback mechanism that adjusts the gain based on the output current rather than the output voltage, which is typical in voltage-feedback amplifiers. This unique feedback approach allows for improved stability and performance in various applications, including audio amplification, signal processing, and instrumentation.
The basic block diagram of a CFA typically includes an input stage that consists of a voltage follower, often implemented with a symmetrical emitter follower configuration. This stage is essential for ensuring that the input signal is buffered effectively, providing high input impedance and low output impedance. The voltage follower configuration allows for minimal loading on the preceding stage while ensuring that the input signal is accurately represented at the output.
The output stage of the CFA is designed to deliver high power with low output impedance, making it suitable for driving loads directly. The output current is sampled and converted into a voltage signal across a large impedance. This conversion is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal while enabling the amplifier to operate efficiently under varying load conditions.
In practical applications, current-feedback amplifiers offer advantages such as reduced distortion, enhanced linearity, and improved transient response. These attributes make CFAs particularly effective in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount. The design considerations for CFAs include selecting appropriate feedback components, ensuring thermal stability, and optimizing power supply configurations to achieve the desired performance metrics.
Overall, the current-feedback amplifier serves as a versatile and efficient solution for a wide range of electronic circuit applications, providing reliable amplification with the ability to handle complex signal processing tasks.A current-feedback amplifier is a well-known component with many uses. Its basic block diagram shows that its input stage is a voltage followerin practice, a symmetrical emitter follower (Figure 1). The configuration samples the output current, converts it to voltage across a large impedance, and amplifies it to the output using a high-power, low-output-impedance amplifier.
🔗 External reference