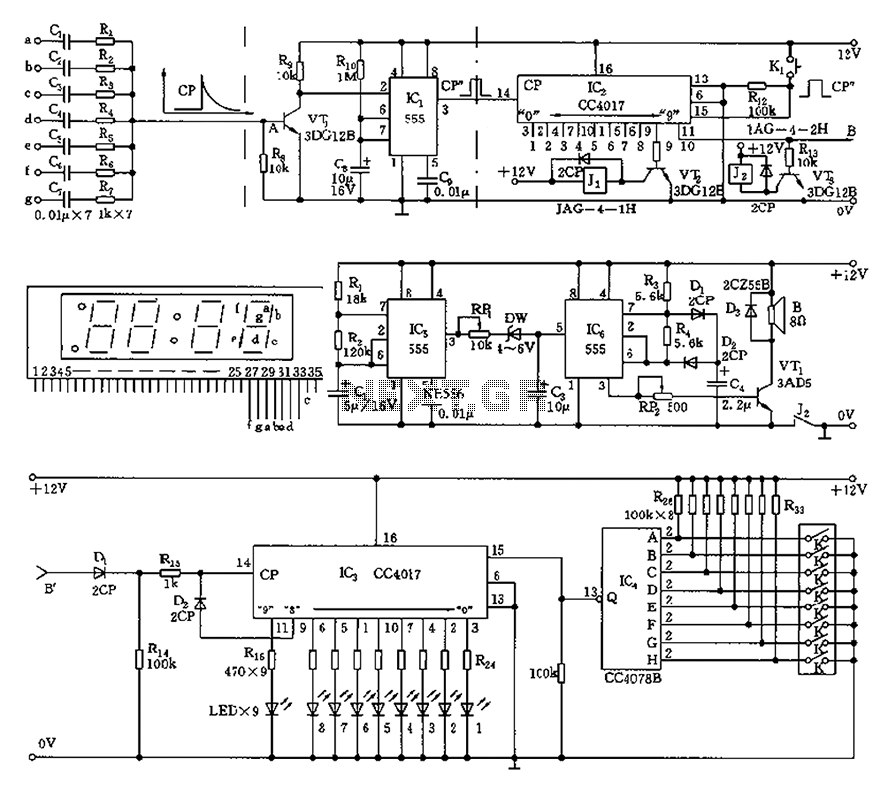
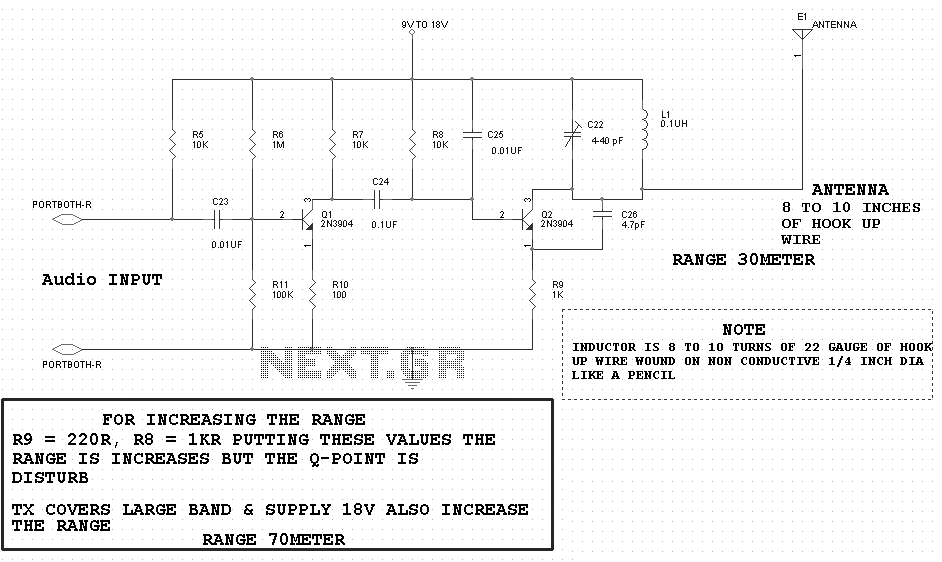
RF Remote Control Encoder and Decoder Chips Explained
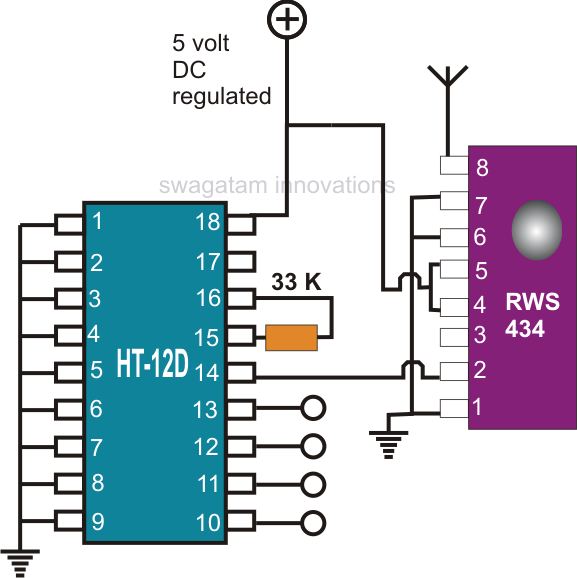
Creating a universal remote control system has become quite straightforward. One can acquire the necessary chips, assemble them, and the high-tech remote control device will be operational. This document discusses specific remote control chips designed for this purpose. The IC TWS-434, along with its encoder chip HT-12E from HOLTEK, forms a high-quality transmitter circuit. In contrast, the chip RWS-434, paired with the decoder IC HT-12D, operates as the receiver module. Both modules can exchange 4 bits of discrete data to control four external loads independently. With the easy accessibility of precise remote control chips, constructing universal remote control modules is now achievable in just a few hours. This document explores compact RF remote control transmitter and receiver modules utilizing the chips HT-12E, HT-12D, TWS-434, and RWS-434. Building a high-end professional remote control system at home has become remarkably simple. The introduction of micro remote control encoder and decoder chips has made creating an RF remote control a task that can be completed in minutes. The applications of remote controls made from these chips are numerous; they can be employed to control virtually any electrical device, with car security systems being a notable application. The TWS-434 and RWS-434 remote control chips complement each other, with the former serving as the transmitter and the latter as the receiver. The TWS-434 is a compact 4-bit transmitter module capable of transmitting four types of coded signals discretely, while the RWS-434 receives these signals and generates four discrete decoded signals at its outputs. Both components primarily function as wireless sender and receiver units and require external encoders and decoders for their operations. The HOLTEK encoder and decoder chips HT-12E and HT-12D work in conjunction with the TWS-434 and RWS-434, respectively, to create the ideal operating parameters for a universal remote control. The IC TWS-434 has a total of six pinouts: pins 1 and 2 are positive inputs, pins 3 and 4 are grounded, pin 6 receives the 4-bit encoded signals, and pin 5 serves as the antenna for radiating the transmitted signals. The antenna of the RWS-434 receives the data sent by the transmitter module and forwards it to the HT-12D for the necessary decoding of the 4-bit data. The decoded information is then output from pins 10, 11, 12, and 13, which is subsequently fed into the output driving circuit to activate the connected devices.
The schematic for this universal remote control system consists of two primary modules: the transmitter module (TWS-434 and HT-12E) and the receiver module (RWS-434 and HT-12D). The transmitter module comprises the TWS-434 chip, which is connected to the HT-12E encoder. The HT-12E encodes the input signals into a 4-bit format, which is then sent to the TWS-434 for transmission. The TWS-434's output pin (pin 5) is connected to an antenna, allowing the encoded signals to be transmitted wirelessly.
In the receiver module, the RWS-434 chip receives the signals transmitted by the TWS-434. Its antenna is connected to the input pin, which captures the incoming RF signals. The RWS-434 then forwards the received signals to the HT-12D decoder chip, which decodes the 4-bit data. The output pins (10, 11, 12, and 13) of the HT-12D are connected to the control circuits that manage the connected loads, enabling them to be activated based on the received commands.
The power supply for both modules should be carefully considered, with appropriate voltage levels provided to ensure optimal performance. Capacitors may be added to stabilize the power supply and filter out noise. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize interference and enhance signal integrity, particularly in the placement of the antennas and the routing of signal paths.
Overall, this universal remote control system offers a versatile solution for controlling various electrical devices, making it an excellent project for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.Making your own universal remote control systems today is very easy. Such procure the relevant chips, assemble them and here goes, your hi-tech remote control device is working for you. Here we explain a couple remote control chips especially designed for the purpose. The IC TWS-434 along with its encoder chip HOLTEK`s HT-12E form a high class tra nsmitter circuit, whereas the chip RWS-434 through its complementing decoder IC HT-12D operates as the receiver module. Both of the above modules are able to exchange 4-bits of discrete data for control four external loads separately.
With the easy availability of accurate remote control chips, making your own universal remote control modules is today just a matter of few hours. We discuss a couple of compact RF remote control transmitter and receiver modules here using the chips: HT-12E, HT-12D, TWS-434, RWS-434 Making a hi-end professional remote control system at home is a child`s play now.
With the advent of micro remote control encoder and decoders chips, making a RF remote control is today a matter of a few hours or rather minutes. Applications of remote controls made from these chips are countless; you may use it for controlling practically any electrical gadget that you can think of, the best application being for car security systems.
A couple of remote control chips, the TWS-434 and the RWS-434 both complement each other, the first one being the transmitter and the later one the receiver. The chip TWS-434 is basically a tiny 4-bit transmitter module, which is able to transmit 4 types of coded signals discretely, whereas the RWS-434 exactly compliments these signals by receiving them and generating 4 discrete decoded signals at its outputs.
However both the above primarily functions just as wireless sender and receiver and therefore require external encoders and decoders to be integrated for the said operations. A couple of HOLTEK`s encoder and decoder chips HT-12E and HT-12D work in conjunction with TWS-434 and RWS-434 respectively to produce the desired ideal universal remote control operating parameters.
The IC TWS-434 has in all 6 pin outs, 1 and 2 are the positive inputs, 3 and 4 are to be grounded, 6 receives the 4-bit encoded signals, pin 5 being the antenna for radiating the received signals. Here, the chip RWS-434, s antenna receive the data transmitted by the above transmitter module and sends it to the IC HT-12D for the necessary decoding of the 4-bit data which ultimately is decoded and produced at the respective outputs for driving the connected loads.
Pin 14 receives the information received by RSW-434 and after decoding the processed data is obtained from the pins 10, 11, 12, 13 respectively, which is further fed to the output driving circuit for activating the connected gadgets. 🔗 External reference
The schematic for this universal remote control system consists of two primary modules: the transmitter module (TWS-434 and HT-12E) and the receiver module (RWS-434 and HT-12D). The transmitter module comprises the TWS-434 chip, which is connected to the HT-12E encoder. The HT-12E encodes the input signals into a 4-bit format, which is then sent to the TWS-434 for transmission. The TWS-434's output pin (pin 5) is connected to an antenna, allowing the encoded signals to be transmitted wirelessly.
In the receiver module, the RWS-434 chip receives the signals transmitted by the TWS-434. Its antenna is connected to the input pin, which captures the incoming RF signals. The RWS-434 then forwards the received signals to the HT-12D decoder chip, which decodes the 4-bit data. The output pins (10, 11, 12, and 13) of the HT-12D are connected to the control circuits that manage the connected loads, enabling them to be activated based on the received commands.
The power supply for both modules should be carefully considered, with appropriate voltage levels provided to ensure optimal performance. Capacitors may be added to stabilize the power supply and filter out noise. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize interference and enhance signal integrity, particularly in the placement of the antennas and the routing of signal paths.
Overall, this universal remote control system offers a versatile solution for controlling various electrical devices, making it an excellent project for both hobbyists and professionals in the field of electronics.Making your own universal remote control systems today is very easy. Such procure the relevant chips, assemble them and here goes, your hi-tech remote control device is working for you. Here we explain a couple remote control chips especially designed for the purpose. The IC TWS-434 along with its encoder chip HOLTEK`s HT-12E form a high class tra nsmitter circuit, whereas the chip RWS-434 through its complementing decoder IC HT-12D operates as the receiver module. Both of the above modules are able to exchange 4-bits of discrete data for control four external loads separately.
With the easy availability of accurate remote control chips, making your own universal remote control modules is today just a matter of few hours. We discuss a couple of compact RF remote control transmitter and receiver modules here using the chips: HT-12E, HT-12D, TWS-434, RWS-434 Making a hi-end professional remote control system at home is a child`s play now.
With the advent of micro remote control encoder and decoders chips, making a RF remote control is today a matter of a few hours or rather minutes. Applications of remote controls made from these chips are countless; you may use it for controlling practically any electrical gadget that you can think of, the best application being for car security systems.
A couple of remote control chips, the TWS-434 and the RWS-434 both complement each other, the first one being the transmitter and the later one the receiver. The chip TWS-434 is basically a tiny 4-bit transmitter module, which is able to transmit 4 types of coded signals discretely, whereas the RWS-434 exactly compliments these signals by receiving them and generating 4 discrete decoded signals at its outputs.
However both the above primarily functions just as wireless sender and receiver and therefore require external encoders and decoders to be integrated for the said operations. A couple of HOLTEK`s encoder and decoder chips HT-12E and HT-12D work in conjunction with TWS-434 and RWS-434 respectively to produce the desired ideal universal remote control operating parameters.
The IC TWS-434 has in all 6 pin outs, 1 and 2 are the positive inputs, 3 and 4 are to be grounded, 6 receives the 4-bit encoded signals, pin 5 being the antenna for radiating the received signals. Here, the chip RWS-434, s antenna receive the data transmitted by the above transmitter module and sends it to the IC HT-12D for the necessary decoding of the 4-bit data which ultimately is decoded and produced at the respective outputs for driving the connected loads.
Pin 14 receives the information received by RSW-434 and after decoding the processed data is obtained from the pins 10, 11, 12, 13 respectively, which is further fed to the output driving circuit for activating the connected gadgets. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713