RS-232 to RS-485 converter circuit usin MAX487
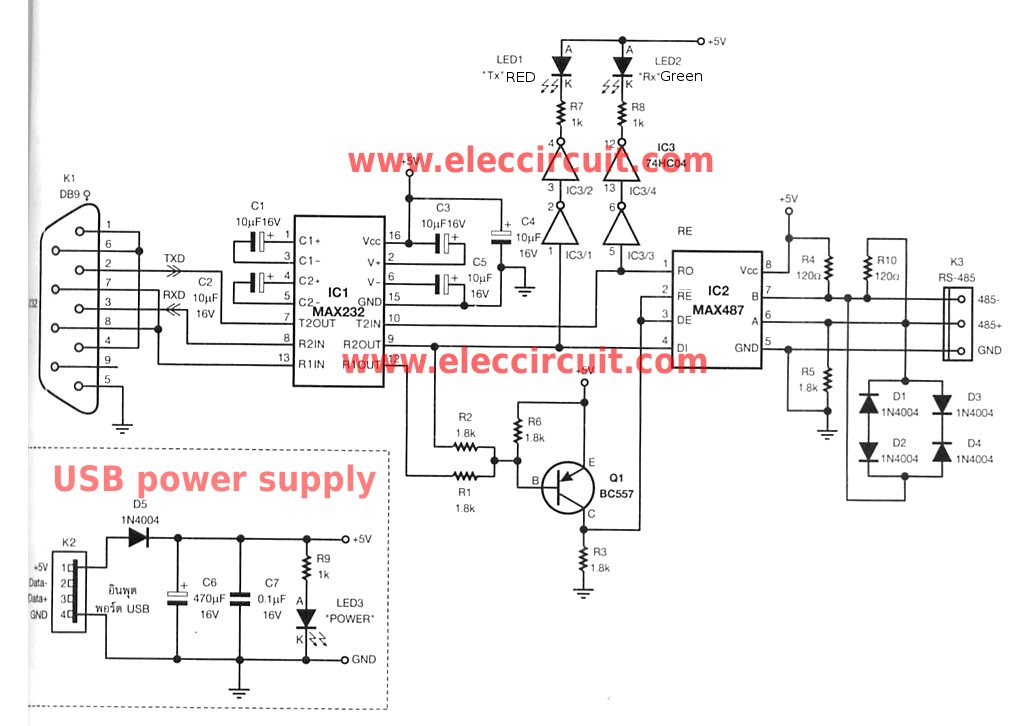
The RS-232 system connection is faster and easier, but the distance is limited. Therefore, this project involves using an RS-485 system with an RS-232 to RS-485 converter.
The RS-232 to RS-485 converter project aims to extend the communication range and improve the reliability of data transmission in serial communication systems. The RS-232 standard is typically limited to short distances, usually up to 15 meters, and is not suitable for multi-drop configurations. In contrast, RS-485 supports longer distances, up to 1200 meters, and allows for multiple devices to communicate on the same bus, making it ideal for industrial applications.
The converter works by translating the voltage levels of the RS-232 signals into the differential signals used by RS-485. This is accomplished using a dedicated RS-232 to RS-485 converter chip, which handles the necessary level shifting and signal conditioning. The circuit typically includes the following components:
1. **RS-232 Connector**: A DB9 or DB25 connector is used to interface with the RS-232 device. The connector facilitates the connection of the RS-232 signals, including TX (transmit), RX (receive), GND (ground), and optionally control signals like RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send).
2. **Level Shifting Circuit**: The converter chip implements a level shifting mechanism that converts the single-ended RS-232 signals to differential signals suitable for RS-485 communication. This often involves using operational amplifiers or dedicated level shifter ICs.
3. **RS-485 Connector**: A terminal block or DB9 connector is used for RS-485 communication. The RS-485 signals (A and B) are transmitted differentially, which helps to reduce noise and allows for longer transmission distances.
4. **Power Supply**: The converter may require a power supply, typically +5V or +12V, depending on the specifications of the converter chip used. This supply powers the logic circuitry and the level shifting components.
5. **Termination Resistors**: In longer RS-485 networks, termination resistors may be added at the ends of the communication line to prevent signal reflections, ensuring better signal integrity.
6. **Isolation (optional)**: For improved protection against electrical noise and ground loops, isolation circuitry can be incorporated, which separates the RS-232 side from the RS-485 side.
This converter allows seamless communication between RS-232 devices and RS-485 networks, enabling the integration of legacy systems with modern multi-drop serial communication systems. The design must ensure proper grounding and shielding to minimize interference, especially in industrial environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) can be prevalent.RS-232 system connection faster and easier, But distance is not far. so to change to use the system RS-485 with this RS-232 to RS-485 converter projects. It.. 🔗 External reference
The RS-232 to RS-485 converter project aims to extend the communication range and improve the reliability of data transmission in serial communication systems. The RS-232 standard is typically limited to short distances, usually up to 15 meters, and is not suitable for multi-drop configurations. In contrast, RS-485 supports longer distances, up to 1200 meters, and allows for multiple devices to communicate on the same bus, making it ideal for industrial applications.
The converter works by translating the voltage levels of the RS-232 signals into the differential signals used by RS-485. This is accomplished using a dedicated RS-232 to RS-485 converter chip, which handles the necessary level shifting and signal conditioning. The circuit typically includes the following components:
1. **RS-232 Connector**: A DB9 or DB25 connector is used to interface with the RS-232 device. The connector facilitates the connection of the RS-232 signals, including TX (transmit), RX (receive), GND (ground), and optionally control signals like RTS (Request to Send) and CTS (Clear to Send).
2. **Level Shifting Circuit**: The converter chip implements a level shifting mechanism that converts the single-ended RS-232 signals to differential signals suitable for RS-485 communication. This often involves using operational amplifiers or dedicated level shifter ICs.
3. **RS-485 Connector**: A terminal block or DB9 connector is used for RS-485 communication. The RS-485 signals (A and B) are transmitted differentially, which helps to reduce noise and allows for longer transmission distances.
4. **Power Supply**: The converter may require a power supply, typically +5V or +12V, depending on the specifications of the converter chip used. This supply powers the logic circuitry and the level shifting components.
5. **Termination Resistors**: In longer RS-485 networks, termination resistors may be added at the ends of the communication line to prevent signal reflections, ensuring better signal integrity.
6. **Isolation (optional)**: For improved protection against electrical noise and ground loops, isolation circuitry can be incorporated, which separates the RS-232 side from the RS-485 side.
This converter allows seamless communication between RS-232 devices and RS-485 networks, enabling the integration of legacy systems with modern multi-drop serial communication systems. The design must ensure proper grounding and shielding to minimize interference, especially in industrial environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) can be prevalent.RS-232 system connection faster and easier, But distance is not far. so to change to use the system RS-485 with this RS-232 to RS-485 converter projects. It.. 🔗 External reference