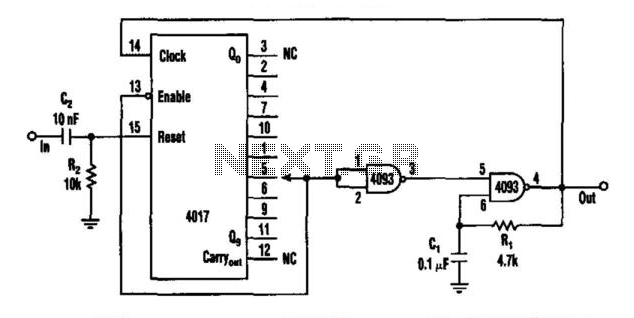
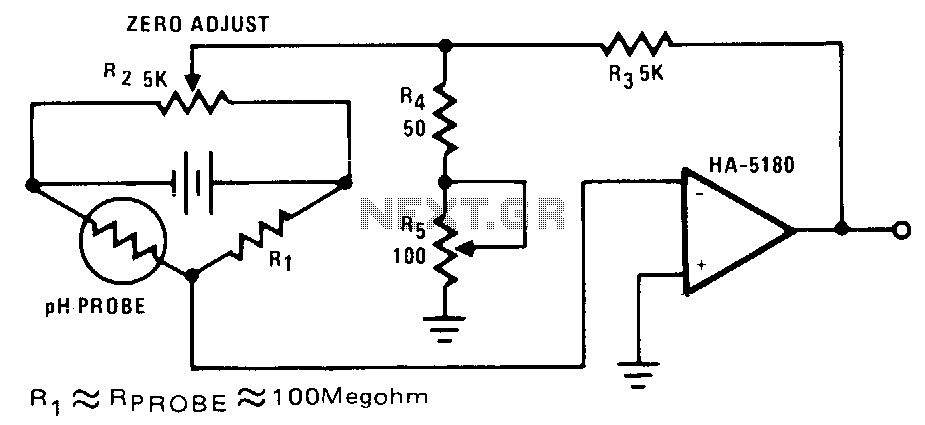
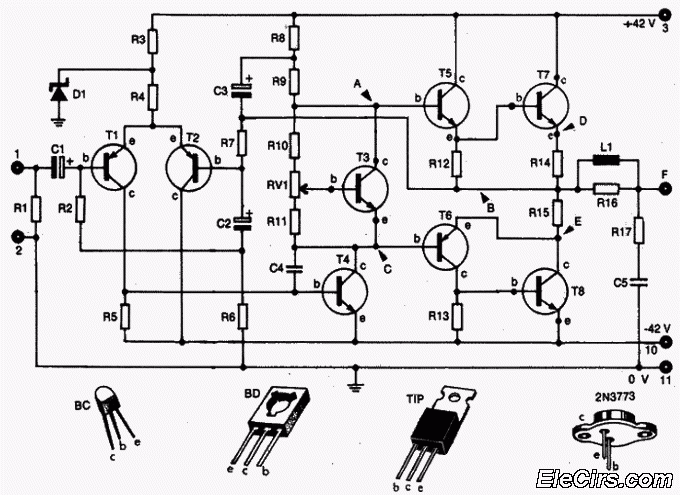
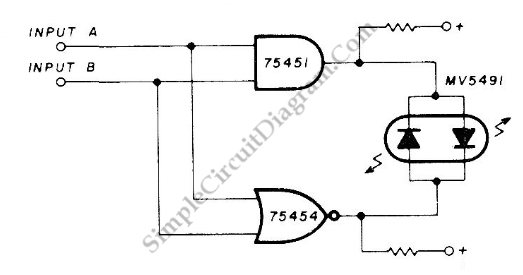
model train detector using photocell
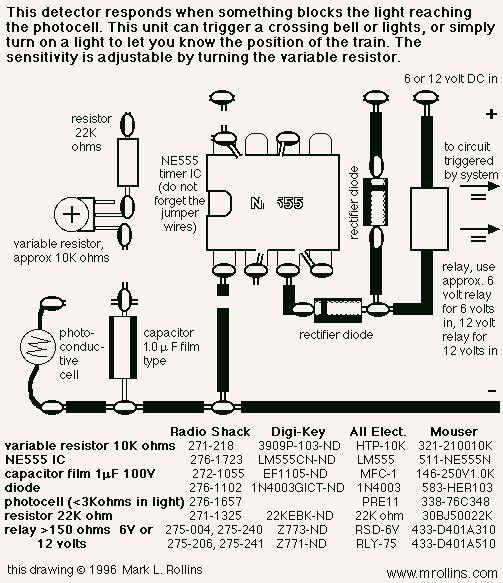
This photocell is best mounted at tie level between the rails. The variable resistor adjusts the sensitivity of the circuit. This circuit can be powered by either 6 or 12 volts - BE SURE to use the proper relay; More: note that some relays are rated for 5 volts, these should be okay with 6 volts.
The described photocell circuit is designed for applications where light detection is necessary, such as in model railroading or outdoor lighting systems. It is essential to mount the photocell at tie level between the rails to ensure optimal light exposure for accurate readings.
The circuit utilizes a variable resistor, commonly known as a potentiometer, which allows for the adjustment of sensitivity. This feature is crucial as it enables the user to calibrate the photocell to respond to varying levels of ambient light, accommodating different environmental conditions or specific user requirements.
Powering the circuit can be achieved with either 6 volts or 12 volts, providing flexibility based on the relay specifications used in conjunction with the photocell. When selecting a relay, it is critical to ensure compatibility with the operating voltage. Some relays are rated for 5 volts; however, they can typically handle 6 volts without issues. It is advisable to verify the relay's specifications to prevent any potential damage or malfunction.
The circuit layout should include a photocell sensor, the variable resistor, and a relay connected to an appropriate load. If the circuit is to be used in an outdoor environment, it should be housed in a weatherproof enclosure to protect the components from moisture and dust. Proper wiring practices should be followed to ensure reliable operation, including secure connections and insulation of exposed wires.
In summary, this photocell circuit with adjustable sensitivity and dual voltage options is suitable for various applications, provided that the proper relay is selected and installed correctly.This photocell is best mounted at tie level between the rails. The variable resistor adjusts the sensitivity of the circuit. This circuit can be powered by either 6 or 12 volts - BE SURE to use the proper relay; note that some relays are rated for 5 volts, these should be okay with 6 volts. 🔗 External reference
The described photocell circuit is designed for applications where light detection is necessary, such as in model railroading or outdoor lighting systems. It is essential to mount the photocell at tie level between the rails to ensure optimal light exposure for accurate readings.
The circuit utilizes a variable resistor, commonly known as a potentiometer, which allows for the adjustment of sensitivity. This feature is crucial as it enables the user to calibrate the photocell to respond to varying levels of ambient light, accommodating different environmental conditions or specific user requirements.
Powering the circuit can be achieved with either 6 volts or 12 volts, providing flexibility based on the relay specifications used in conjunction with the photocell. When selecting a relay, it is critical to ensure compatibility with the operating voltage. Some relays are rated for 5 volts; however, they can typically handle 6 volts without issues. It is advisable to verify the relay's specifications to prevent any potential damage or malfunction.
The circuit layout should include a photocell sensor, the variable resistor, and a relay connected to an appropriate load. If the circuit is to be used in an outdoor environment, it should be housed in a weatherproof enclosure to protect the components from moisture and dust. Proper wiring practices should be followed to ensure reliable operation, including secure connections and insulation of exposed wires.
In summary, this photocell circuit with adjustable sensitivity and dual voltage options is suitable for various applications, provided that the proper relay is selected and installed correctly.This photocell is best mounted at tie level between the rails. The variable resistor adjusts the sensitivity of the circuit. This circuit can be powered by either 6 or 12 volts - BE SURE to use the proper relay; note that some relays are rated for 5 volts, these should be okay with 6 volts. 🔗 External reference