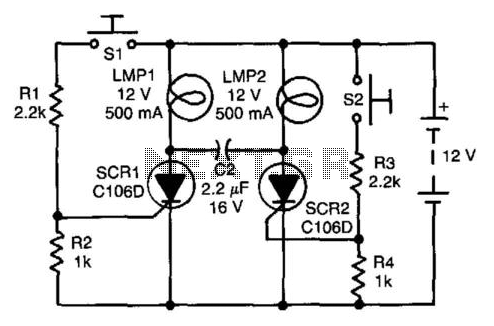
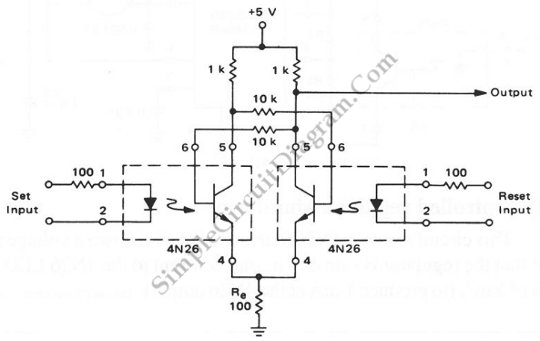
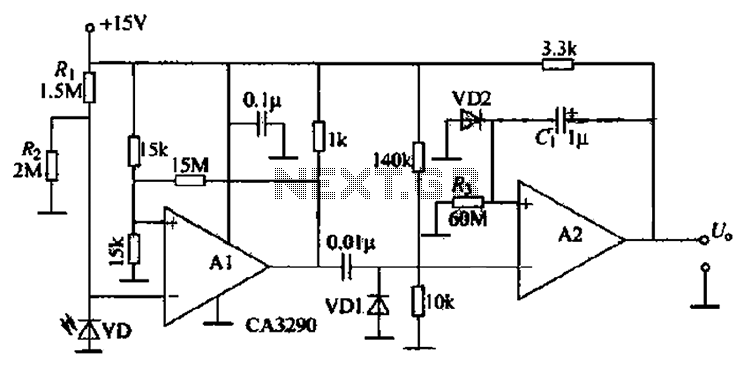
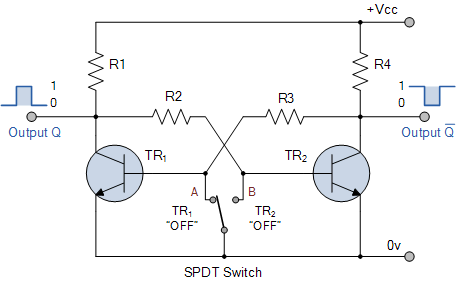
S/R Flip-Flop
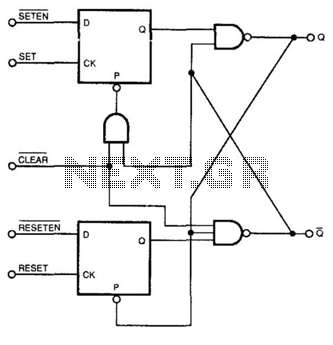
This circuit combines the characteristics of an asynchronous S/R flip-flop and an edge-triggered JK flip-flop. It changes state on the leading edges of its inputs and ignores the levels at all other times. In operation, the outputs of both D flip-flops are normally high, going low for brief periods after detecting an edge at their respective clock inputs.
The described circuit functions as a hybrid flip-flop, leveraging the operational principles of both asynchronous S/R and edge-triggered JK flip-flops. The asynchronous S/R flip-flop is characterized by its ability to set and reset its output based on the levels of its inputs, while the edge-triggered JK flip-flop responds to the transitions of its clock input, providing a more controlled state change.
In this configuration, the circuit is designed to respond exclusively to the leading edge of the clock signals applied to its inputs. This means that the state of the outputs will only change when there is a rising edge detected, allowing for precise timing control. At all other times, the circuit maintains its previous state, effectively ignoring any changes in input levels until the next clock edge occurs.
The outputs of the D flip-flops, which are the primary components of this circuit, are typically in a high state. Upon receiving a clock pulse, the output will briefly transition to a low state, indicating that the flip-flop has registered an input change. This behavior is particularly useful in digital circuits where synchronization and timing are critical, as it allows for the reliable propagation of signals without the risk of false triggering from noise or spurious signals.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various digital systems, such as counters, shift registers, and memory storage devices, where the combination of asynchronous and synchronous characteristics provides enhanced functionality. The design considerations should include proper timing analysis to ensure that the flip-flops operate within their specified limits, especially regarding setup and hold times relative to the clock edges. Additionally, debouncing mechanisms may be necessary if the inputs are subject to mechanical switching or other forms of noise. This circuit combines the characteristics of an asynchronous S/R flip-flop and an edge-triggered JK flip-flop. It changes sta te on the leading edges of its inputs, and ignores the levels at all other times. In operation, outputs of both D flip-flops are normally high, going low for brief periods after seeing an edge at their respective clock inputs. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions as a hybrid flip-flop, leveraging the operational principles of both asynchronous S/R and edge-triggered JK flip-flops. The asynchronous S/R flip-flop is characterized by its ability to set and reset its output based on the levels of its inputs, while the edge-triggered JK flip-flop responds to the transitions of its clock input, providing a more controlled state change.
In this configuration, the circuit is designed to respond exclusively to the leading edge of the clock signals applied to its inputs. This means that the state of the outputs will only change when there is a rising edge detected, allowing for precise timing control. At all other times, the circuit maintains its previous state, effectively ignoring any changes in input levels until the next clock edge occurs.
The outputs of the D flip-flops, which are the primary components of this circuit, are typically in a high state. Upon receiving a clock pulse, the output will briefly transition to a low state, indicating that the flip-flop has registered an input change. This behavior is particularly useful in digital circuits where synchronization and timing are critical, as it allows for the reliable propagation of signals without the risk of false triggering from noise or spurious signals.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various digital systems, such as counters, shift registers, and memory storage devices, where the combination of asynchronous and synchronous characteristics provides enhanced functionality. The design considerations should include proper timing analysis to ensure that the flip-flops operate within their specified limits, especially regarding setup and hold times relative to the clock edges. Additionally, debouncing mechanisms may be necessary if the inputs are subject to mechanical switching or other forms of noise. This circuit combines the characteristics of an asynchronous S/R flip-flop and an edge-triggered JK flip-flop. It changes sta te on the leading edges of its inputs, and ignores the levels at all other times. In operation, outputs of both D flip-flops are normally high, going low for brief periods after seeing an edge at their respective clock inputs. 🔗 External reference