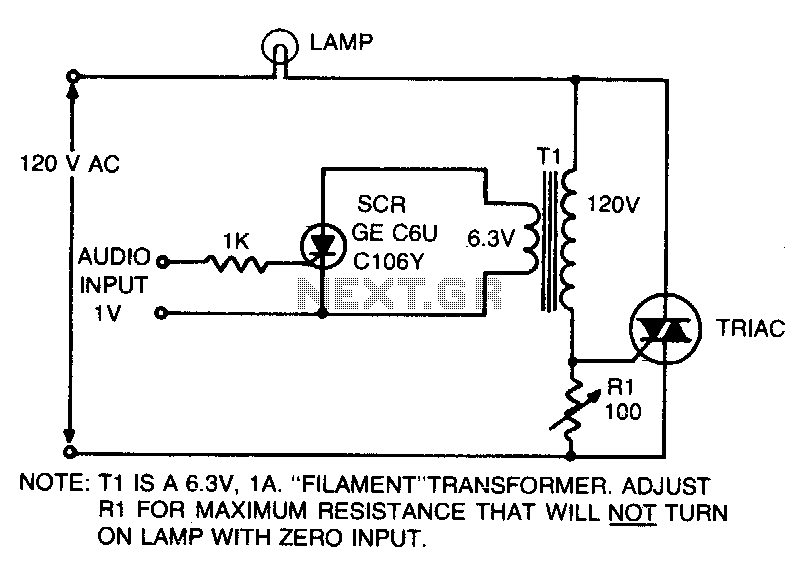
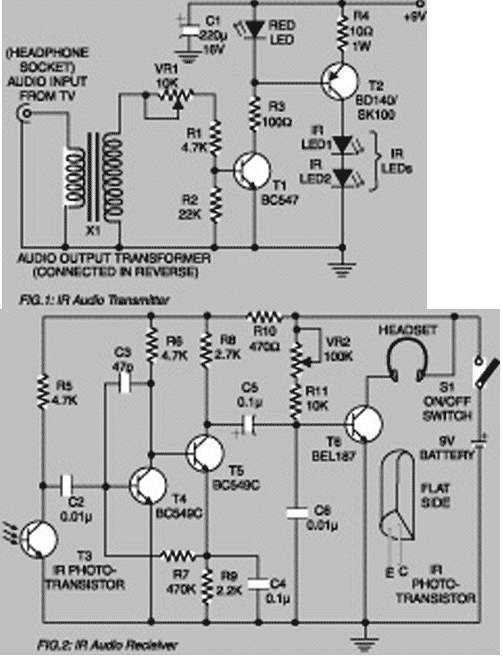
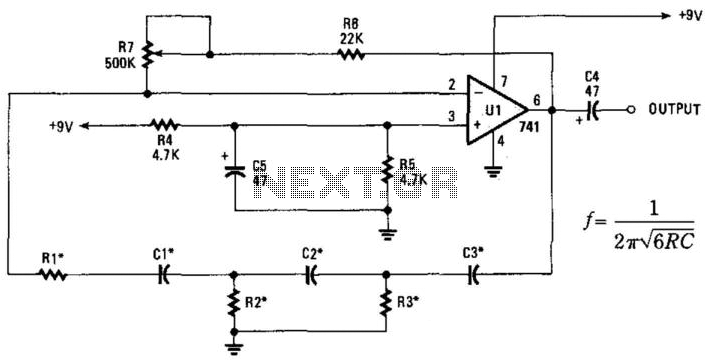
Satellite Tv Audio Switcher

Some channels provide a separate audio mode (SAP) in an alternate language, typically transmitted at 6.8 MHz, which is the frequency designated for unscrambled channels. In scrambled channels, audio is transmitted alongside the video signal, allowing the descrambler to decode both simultaneously, resulting in stereo audio output. When a channel offers SAP, it can be accessed at 6.8 MHz. The audio selection is facilitated by a pair of DPDT switches with their toggle handles interconnected. In one switch position, stereo audio is heard, while the alternate position provides the SAP. Users can lower the TV volume and connect it to a stereo amplifier and speakers for enhanced audio experience.
The described circuit involves a dual-pole double-throw (DPDT) switch configuration, which is essential for selecting between standard stereo audio and the secondary audio program (SAP). The DPDT switches are mechanically linked, ensuring that both switches toggle simultaneously, providing a seamless user experience when switching audio modes.
The circuit operates by receiving the audio signal from the television, which transmits audio at 6.8 MHz for unscrambled channels. The audio output from the television is routed through the DPDT switches. When the switches are set to the stereo position, the audio signal is directed to the output, allowing the user to hear the standard audio. Conversely, when switched to the SAP position, the circuit reroutes the audio signal to access the alternate language audio track.
To enhance the audio experience, the circuit design allows for the connection of a stereo amplifier. This is achieved by lowering the volume on the television to prevent audio feedback or distortion. The output from the DPDT switches can be connected to the input of the stereo amplifier, which then drives a set of external speakers. This setup provides an improved sound quality and allows for a more immersive listening experience, especially when viewing content in a different language.
In summary, this circuit design effectively facilitates the selection between standard audio and SAP, utilizing a straightforward DPDT switch mechanism, while also providing the flexibility to integrate with external audio amplification systems. Some channels offer a separate audio mode (SAP) in a second language. It is usually transmitted on 6.8 MHz, whi ch is the frequency used for unscrambled channels. The audio in the scrambled channels is transmitted along with the picture, so when the descrambler descrambles the signal, it also descrambles the audio in stereo. When the channel offers SAP, you"ll find it on 6.8 MHz. The switches are a pair of DPDT switches that have the toggle handles tied together. In one position, you hear the audio in stereo and in the other position, you hear the SAP. Just turn down the volume level on the TV and you can connect it to a stereo amplifier and a pair of speakers.
The described circuit involves a dual-pole double-throw (DPDT) switch configuration, which is essential for selecting between standard stereo audio and the secondary audio program (SAP). The DPDT switches are mechanically linked, ensuring that both switches toggle simultaneously, providing a seamless user experience when switching audio modes.
The circuit operates by receiving the audio signal from the television, which transmits audio at 6.8 MHz for unscrambled channels. The audio output from the television is routed through the DPDT switches. When the switches are set to the stereo position, the audio signal is directed to the output, allowing the user to hear the standard audio. Conversely, when switched to the SAP position, the circuit reroutes the audio signal to access the alternate language audio track.
To enhance the audio experience, the circuit design allows for the connection of a stereo amplifier. This is achieved by lowering the volume on the television to prevent audio feedback or distortion. The output from the DPDT switches can be connected to the input of the stereo amplifier, which then drives a set of external speakers. This setup provides an improved sound quality and allows for a more immersive listening experience, especially when viewing content in a different language.
In summary, this circuit design effectively facilitates the selection between standard audio and SAP, utilizing a straightforward DPDT switch mechanism, while also providing the flexibility to integrate with external audio amplification systems. Some channels offer a separate audio mode (SAP) in a second language. It is usually transmitted on 6.8 MHz, whi ch is the frequency used for unscrambled channels. The audio in the scrambled channels is transmitted along with the picture, so when the descrambler descrambles the signal, it also descrambles the audio in stereo. When the channel offers SAP, you"ll find it on 6.8 MHz. The switches are a pair of DPDT switches that have the toggle handles tied together. In one position, you hear the audio in stereo and in the other position, you hear the SAP. Just turn down the volume level on the TV and you can connect it to a stereo amplifier and a pair of speakers.