Infrared Audio TX/RX
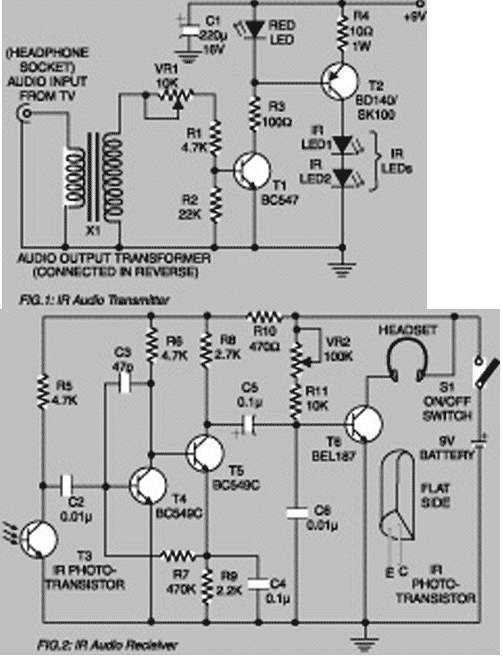
Using this low-cost project one can reproduce audio from TV without disturbing others. It does not use any wire connection between TV and headphones. In place of a pair of wires, it uses invisible infrared light to transmit audio signals from TV to headphones. Without using any lens, a range of up to 6 metres is possible. Range can be extended by using lenses and reflectors with IR sensors comprising transmitters and receivers. IR transmitter uses two-stage transistor amplifier to drive two series-connected IR LEDs. An audio output transformer is used (in reverse) to couple audio output from TV to the IR transmitter. Transistors T1 and T2 amplify the audio signals received from TV through the audio transformer. More: Low-impedance output windings (lower gauge or thicker wires) are used for connection to TV side while high-impedance windings are connected to IR transmitter. This IR transmitter can be powered from a 9-volt mains adapter or battery. Red LED1 in transmitter circuit functions as a zener diode (0.65V) as well as supply-on indicator. IR receiver uses 3-stage transistor amplifier. The first two transistors (T4 and T5) form audio signal amplifier while the third transistor T6 is used to drive a headphone. Adjust potmeter VR2 for max. clarity. Direct photo-transistor towards IR LEDs of transmitter for max. range. A 9-volt battery can be used with receiver for portable operation.
The described circuit is an infrared (IR) audio transmission system designed to wirelessly transmit audio signals from a television to headphones, facilitating private listening without disturbing others. The system consists of two primary components: an IR transmitter and an IR receiver.
The IR transmitter is equipped with a two-stage transistor amplifier, which enhances the audio signal derived from the television's output. The audio output transformer operates in reverse to couple the audio signals from the TV into the IR transmitter circuit. The use of transistors T1 and T2 amplifies the audio signals effectively. The transmitter includes two infrared LEDs arranged in series, which emit infrared light corresponding to the audio signals. The circuit is designed to operate on a 9-volt power supply, which can be sourced from either a mains adapter or a battery. A red LED (LED1) serves dual purposes: it acts as a zener diode, providing a reference voltage of 0.65V, and it functions as a power-on indicator, allowing users to confirm that the transmitter is operational.
On the receiving end, the IR receiver employs a three-stage transistor amplifier. The first two transistors (T4 and T5) amplify the audio signal received from the infrared light emitted by the transmitter. The third transistor (T6) is responsible for driving the headphones, allowing users to listen to the transmitted audio. A potentiometer (VR2) is included in the circuit to allow users to adjust the volume for optimal clarity. For effective operation, the phototransistor in the receiver should be oriented directly towards the IR LEDs of the transmitter to maximize the range of audio transmission.
The system is capable of achieving a transmission range of up to 6 meters without any lenses, although this range can be extended by incorporating lenses and reflectors into the design. The receiver can also be powered by a 9-volt battery, making it suitable for portable applications. This wireless audio transmission system is an innovative solution for private listening, leveraging infrared technology to eliminate the need for physical connections between the television and headphones.Using this low-cost project one can reproduce audio from TV without disturbing others. It does not use any wire connection between TV and headphones. In place of a pair of wires, it uses invisible infrared light to transmit audio signals from TV to headphones. Without using any lens, a range of up to 6 metres is possible. Range can be extended by using lenses and reflectors with IR sensors comprising transmitters and receivers.
IR transmitter uses two-stage transistor amplifier to drive two series-connected IR LEDs. An audio output transformer is used (in reverse) to couple audio output from TV to the IR transmitter. Transistors T1 and T2 amplify the audio signals received from TV through the audio transformer. Low-impedance output windings (lower gauge or thicker wires) are used for connection to TV side while high-impedance windings are connected to IR transmitter. This IR transmitter can be powered from a 9-volt mains adapter or battery. Red LED1 in transmitter circuit functions as a zener diode (0.65V) as well as supply-on indicator. IR receiver uses 3-stage transistor amplifier. The first two transistors (T4 and T5) form audio signal amplifier while the third transistor T6 is used to drive a headphone.
Adjust potmeter VR2 for max. clarity. Direct photo-transistor towards IR LEDs of transmitter for max. range. A 9-volt battery can be used with receiver for portable operation. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is an infrared (IR) audio transmission system designed to wirelessly transmit audio signals from a television to headphones, facilitating private listening without disturbing others. The system consists of two primary components: an IR transmitter and an IR receiver.
The IR transmitter is equipped with a two-stage transistor amplifier, which enhances the audio signal derived from the television's output. The audio output transformer operates in reverse to couple the audio signals from the TV into the IR transmitter circuit. The use of transistors T1 and T2 amplifies the audio signals effectively. The transmitter includes two infrared LEDs arranged in series, which emit infrared light corresponding to the audio signals. The circuit is designed to operate on a 9-volt power supply, which can be sourced from either a mains adapter or a battery. A red LED (LED1) serves dual purposes: it acts as a zener diode, providing a reference voltage of 0.65V, and it functions as a power-on indicator, allowing users to confirm that the transmitter is operational.
On the receiving end, the IR receiver employs a three-stage transistor amplifier. The first two transistors (T4 and T5) amplify the audio signal received from the infrared light emitted by the transmitter. The third transistor (T6) is responsible for driving the headphones, allowing users to listen to the transmitted audio. A potentiometer (VR2) is included in the circuit to allow users to adjust the volume for optimal clarity. For effective operation, the phototransistor in the receiver should be oriented directly towards the IR LEDs of the transmitter to maximize the range of audio transmission.
The system is capable of achieving a transmission range of up to 6 meters without any lenses, although this range can be extended by incorporating lenses and reflectors into the design. The receiver can also be powered by a 9-volt battery, making it suitable for portable applications. This wireless audio transmission system is an innovative solution for private listening, leveraging infrared technology to eliminate the need for physical connections between the television and headphones.Using this low-cost project one can reproduce audio from TV without disturbing others. It does not use any wire connection between TV and headphones. In place of a pair of wires, it uses invisible infrared light to transmit audio signals from TV to headphones. Without using any lens, a range of up to 6 metres is possible. Range can be extended by using lenses and reflectors with IR sensors comprising transmitters and receivers.
IR transmitter uses two-stage transistor amplifier to drive two series-connected IR LEDs. An audio output transformer is used (in reverse) to couple audio output from TV to the IR transmitter. Transistors T1 and T2 amplify the audio signals received from TV through the audio transformer. Low-impedance output windings (lower gauge or thicker wires) are used for connection to TV side while high-impedance windings are connected to IR transmitter. This IR transmitter can be powered from a 9-volt mains adapter or battery. Red LED1 in transmitter circuit functions as a zener diode (0.65V) as well as supply-on indicator. IR receiver uses 3-stage transistor amplifier. The first two transistors (T4 and T5) form audio signal amplifier while the third transistor T6 is used to drive a headphone.
Adjust potmeter VR2 for max. clarity. Direct photo-transistor towards IR LEDs of transmitter for max. range. A 9-volt battery can be used with receiver for portable operation. 🔗 External reference