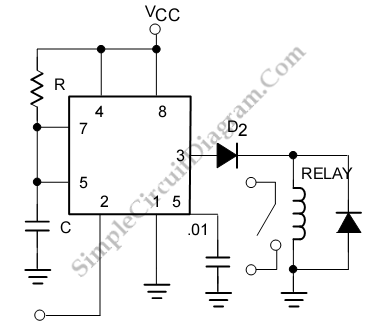
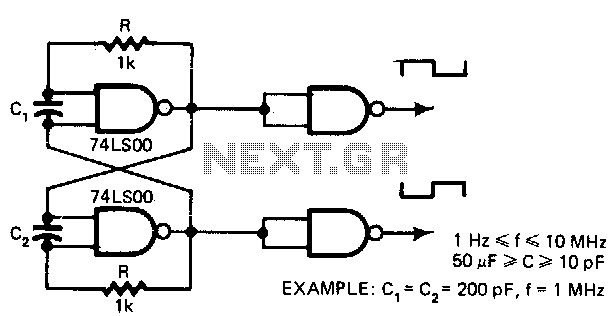
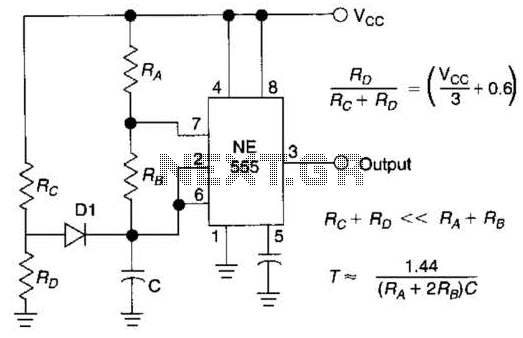
Sawtooth Wave Oscillator Using 555 IC
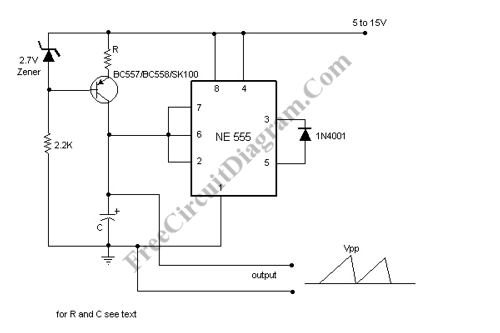
A sawtooth wave oscillator circuit can be implemented using several methods. Here, one design that employs the 555 integrated circuit is presented, along with its schematic diagram.
The sawtooth wave oscillator utilizing the 555 timer IC operates in astable mode, generating a continuous sawtooth waveform. The circuit consists of the 555 timer, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply. The frequency and amplitude of the output waveform can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values.
In the astable configuration, the 555 timer alternates between its high and low states, charging and discharging the timing capacitor. The output waveform rises linearly during the charging phase and falls rapidly during the discharging phase, creating the characteristic sawtooth shape.
The timing capacitor (C1) is charged through two resistors (R1 and R2), and the discharge occurs through R2. The frequency of oscillation (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C1} \]
Where R1 is the resistor connected to the positive supply voltage, R2 is connected to the discharge pin, and C1 is the timing capacitor. The duty cycle can be adjusted by changing the ratio of R1 to R2, which in turn affects the slope of the rising edge of the sawtooth waveform.
The output of the 555 timer can be connected to other circuitry for signal processing, modulation, or as a clock signal for digital devices. The sawtooth wave is particularly useful in applications such as waveform generation, audio synthesis, and as a timing reference in various electronic circuits.
Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power supply pins of the 555 timer to ensure stable operation, and the circuit should be designed to handle the required load based on the intended application.Sawtooth wave oscillator? circuit can be implemented using several methods, here we present one design that employs 555 IC.? Here is the schematic diagram of. 🔗 External reference
The sawtooth wave oscillator utilizing the 555 timer IC operates in astable mode, generating a continuous sawtooth waveform. The circuit consists of the 555 timer, resistors, capacitors, and a power supply. The frequency and amplitude of the output waveform can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values.
In the astable configuration, the 555 timer alternates between its high and low states, charging and discharging the timing capacitor. The output waveform rises linearly during the charging phase and falls rapidly during the discharging phase, creating the characteristic sawtooth shape.
The timing capacitor (C1) is charged through two resistors (R1 and R2), and the discharge occurs through R2. The frequency of oscillation (f) can be calculated using the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \cdot C1} \]
Where R1 is the resistor connected to the positive supply voltage, R2 is connected to the discharge pin, and C1 is the timing capacitor. The duty cycle can be adjusted by changing the ratio of R1 to R2, which in turn affects the slope of the rising edge of the sawtooth waveform.
The output of the 555 timer can be connected to other circuitry for signal processing, modulation, or as a clock signal for digital devices. The sawtooth wave is particularly useful in applications such as waveform generation, audio synthesis, and as a timing reference in various electronic circuits.
Proper decoupling capacitors should be placed near the power supply pins of the 555 timer to ensure stable operation, and the circuit should be designed to handle the required load based on the intended application.Sawtooth wave oscillator? circuit can be implemented using several methods, here we present one design that employs 555 IC.? Here is the schematic diagram of. 🔗 External reference