Self Parking Robot Car
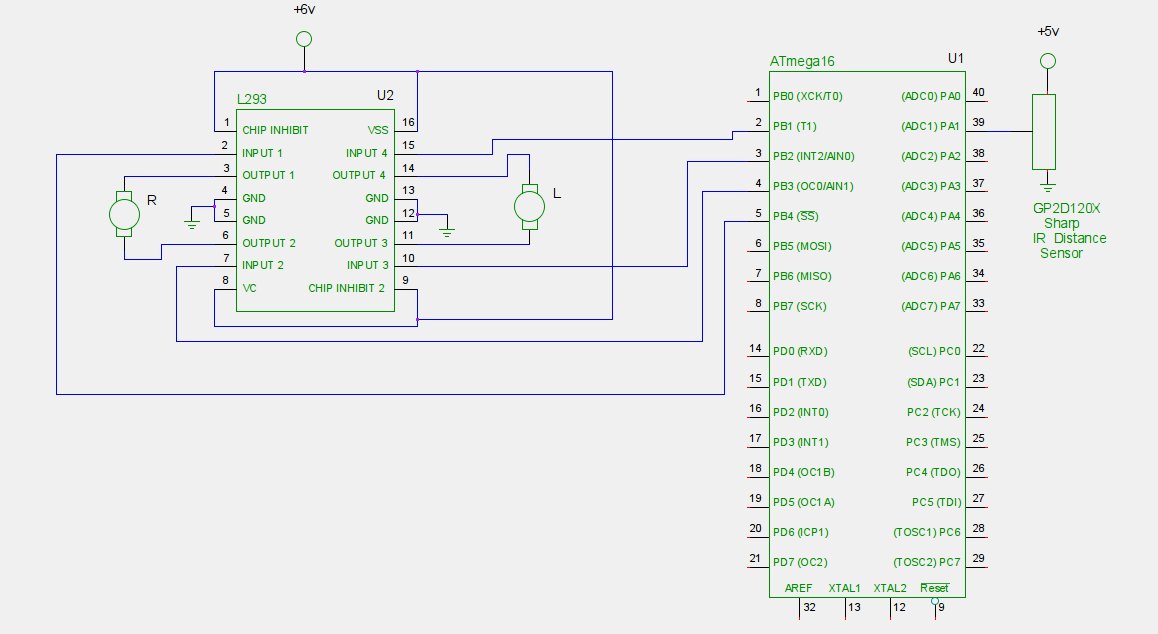
Self-parking is an automatic parking system found in modern vehicles. It utilizes various sensors such as cameras, sonars, and infrared rangefinders to collect information about the vehicle's surroundings. Complex processing algorithms are then employed to park the vehicle without driver intervention. This system differs from parking assistant systems.
The self-parking system integrates multiple sensor technologies to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's environment. Cameras provide visual input, enabling the system to detect obstacles, lane markings, and parking space dimensions. Sonar sensors emit sound waves to measure distances to nearby objects, while infrared rangefinders can detect proximity in low-light conditions.
The data gathered from these sensors is processed using sophisticated algorithms that analyze the vehicle's position and orientation in relation to potential parking spaces. The system calculates optimal maneuvers, including steering angles and throttle control, to execute parking maneuvers autonomously.
Control units within the vehicle process the sensor data in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to the vehicle's trajectory. The system typically includes fail-safe mechanisms to ensure safety during operation, such as automatic braking if an obstacle is detected during parking.
Self-parking technology enhances convenience for drivers, particularly in tight urban environments where parking can be challenging. It represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, contributing to the development of fully autonomous vehicles in the future.Self Parking is a automatic parking system found in modern cars. It makes use of various sensors like cameras, sonars, infrared rangefinders etc. to gather information about the surroundings of a car and then use complex processing algorithms to park the car without the help of the driver. It is different from parking assistant systems. 🔗 External reference
The self-parking system integrates multiple sensor technologies to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's environment. Cameras provide visual input, enabling the system to detect obstacles, lane markings, and parking space dimensions. Sonar sensors emit sound waves to measure distances to nearby objects, while infrared rangefinders can detect proximity in low-light conditions.
The data gathered from these sensors is processed using sophisticated algorithms that analyze the vehicle's position and orientation in relation to potential parking spaces. The system calculates optimal maneuvers, including steering angles and throttle control, to execute parking maneuvers autonomously.
Control units within the vehicle process the sensor data in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments to the vehicle's trajectory. The system typically includes fail-safe mechanisms to ensure safety during operation, such as automatic braking if an obstacle is detected during parking.
Self-parking technology enhances convenience for drivers, particularly in tight urban environments where parking can be challenging. It represents a significant advancement in automotive technology, contributing to the development of fully autonomous vehicles in the future.Self Parking is a automatic parking system found in modern cars. It makes use of various sensors like cameras, sonars, infrared rangefinders etc. to gather information about the surroundings of a car and then use complex processing algorithms to park the car without the help of the driver. It is different from parking assistant systems. 🔗 External reference