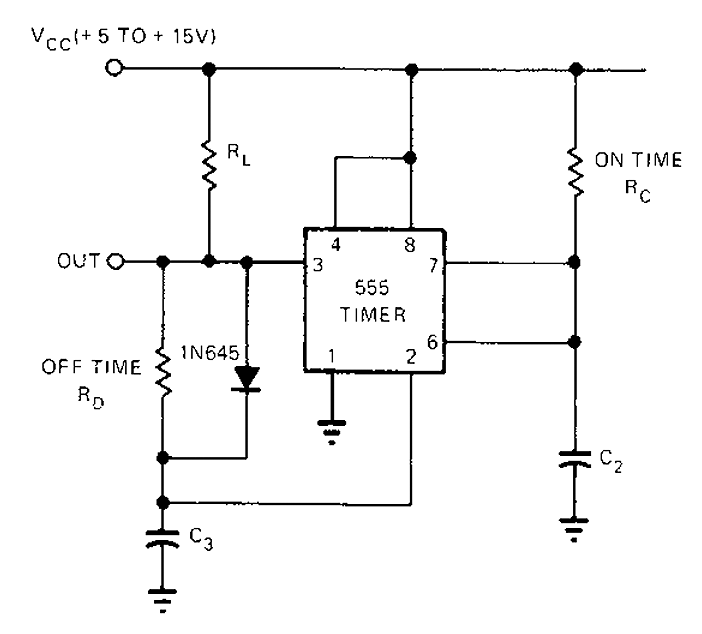
Sequential timer
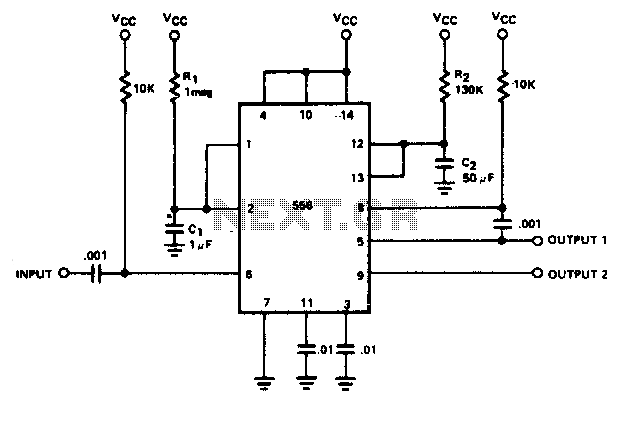
By utilizing both halves of a dual timer, sequential timing can be achieved. The output of the first half is connected to the input of the second half through a 0.1 µF coupling capacitor. The delay time ti is determined by the first half, while the delay ta is determined by the second half. The first half of the timer is initiated by momentarily connecting pin 6 to ground. The duration of the second half is determined by the resistor R2 and capacitor C2.
The described circuit employs a dual timer, typically a 555 timer IC, to create a sequential timing mechanism. The first half of the timer operates in monostable mode, generating a time delay ti based on the values of resistor R1 and capacitor C1. When the circuit is powered, a momentary connection of pin 6 to ground triggers the timer, causing it to output a high signal for a duration defined by the time constant τ1 = R1 × C1.
The output from the first half is then fed into the second half of the timer through a 0.1 µF coupling capacitor. This capacitor serves to block any DC offset while allowing the timing pulse to pass through, effectively triggering the second half of the timer. The second half operates similarly in monostable mode, with its timing determined by resistor R2 and capacitor C2, resulting in a delay ta.
This configuration allows for a precise control of timing sequences in various applications, such as in flashing LEDs, pulse generation, or timed events in control systems. The selection of R1, C1, R2, and C2 values will define the specific timing intervals, enabling customization for different operational requirements. The circuit can be further enhanced by adding additional components such as diodes for protection, or transistors for driving higher loads, depending on the intended application.By utilizing both halves of a dual timer it is possible to obtain sequential timing. By connecting the output of the first half to the input of the second half via a 01 µF coupling capacitor sequential timing may be obtained. Delay ti is determined by the first half and ta by the second half delay. The first half of the timer is started by momentarily connecting pin 6 to ground When it is turned out (determined by 1R1C1), the second half begins. Its duration is determined by 1R2C2. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a dual timer, typically a 555 timer IC, to create a sequential timing mechanism. The first half of the timer operates in monostable mode, generating a time delay ti based on the values of resistor R1 and capacitor C1. When the circuit is powered, a momentary connection of pin 6 to ground triggers the timer, causing it to output a high signal for a duration defined by the time constant τ1 = R1 × C1.
The output from the first half is then fed into the second half of the timer through a 0.1 µF coupling capacitor. This capacitor serves to block any DC offset while allowing the timing pulse to pass through, effectively triggering the second half of the timer. The second half operates similarly in monostable mode, with its timing determined by resistor R2 and capacitor C2, resulting in a delay ta.
This configuration allows for a precise control of timing sequences in various applications, such as in flashing LEDs, pulse generation, or timed events in control systems. The selection of R1, C1, R2, and C2 values will define the specific timing intervals, enabling customization for different operational requirements. The circuit can be further enhanced by adding additional components such as diodes for protection, or transistors for driving higher loads, depending on the intended application.By utilizing both halves of a dual timer it is possible to obtain sequential timing. By connecting the output of the first half to the input of the second half via a 01 µF coupling capacitor sequential timing may be obtained. Delay ti is determined by the first half and ta by the second half delay. The first half of the timer is started by momentarily connecting pin 6 to ground When it is turned out (determined by 1R1C1), the second half begins. Its duration is determined by 1R2C2. 🔗 External reference