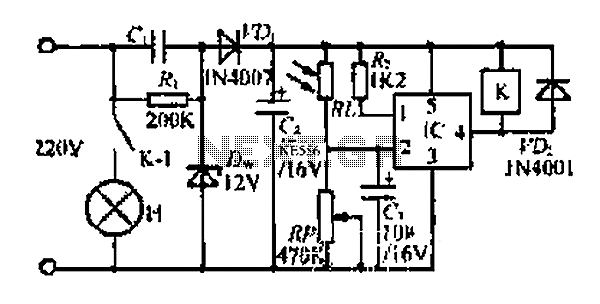
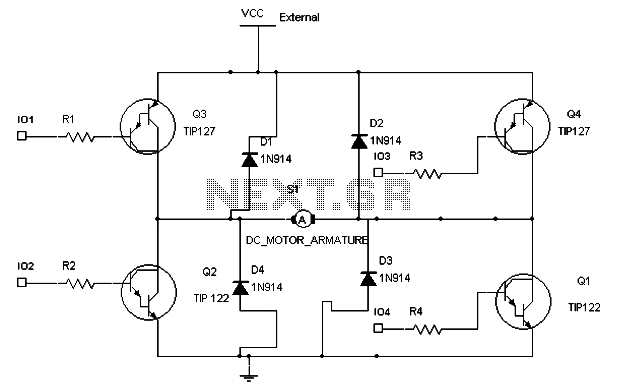
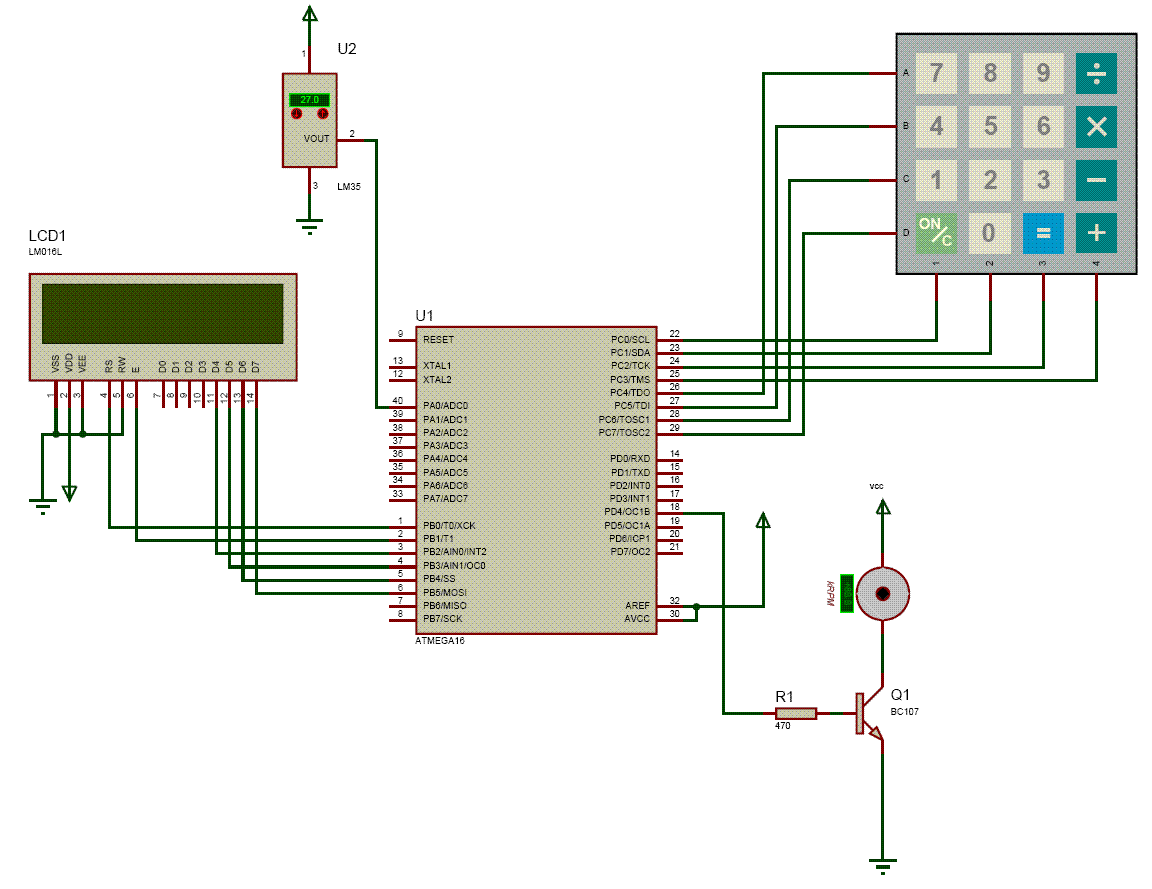
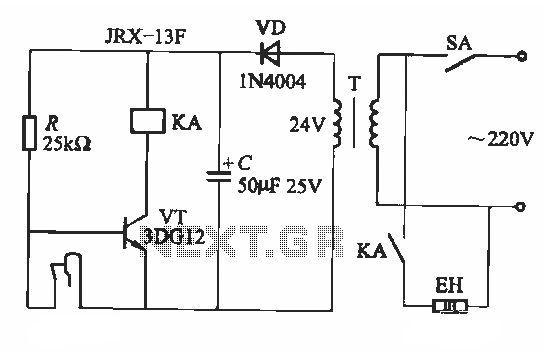
servo motor pot control
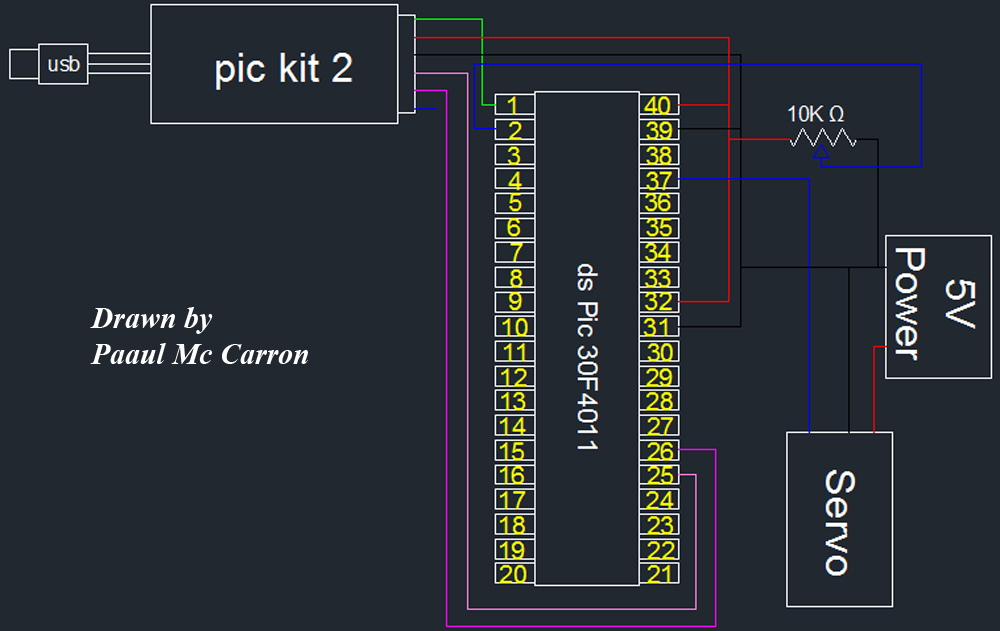
One of the motors utilized in the module is a servo motor. A servo motor is a compact motor that allows for precise positioning at various angles. It is equipped with internal circuitry that automatically maintains the specified angle. However, it is important to note that a servo motor does not permit full revolutions and is limited to a specific range of motion.
A servo motor operates based on a feedback control system, which typically includes a potentiometer to monitor the angle of the motor shaft. The control signal, usually a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, determines the position of the motor. The width of the pulse corresponds to the desired angle, and the servo adjusts its position accordingly to match this input.
Servo motors are commonly used in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, radio-controlled vehicles, and automation systems. They are available in various sizes and torque ratings, allowing for flexibility in design based on the specific requirements of the project. The typical range of motion for most standard servo motors is between 0 to 180 degrees, but there are continuous rotation servos available that can rotate indefinitely in either direction, though they do not provide positional feedback.
When integrating a servo motor into a circuit, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements, as servo motors can draw significant current during operation. Additionally, the control circuitry must be designed to handle the PWM signal accurately to ensure smooth and responsive movement. Overall, the use of a servo motor adds a high level of precision and control to various electronic projects.As part of the module one of the motors we will be using is a servo motor.A servo motor is a small motor that you can position at any angle very accurately. It contains internal circuits that will automatically maintain that particular angle. However, you cannot do full revolutions with a servo. You are restricted to.. 🔗 External reference
A servo motor operates based on a feedback control system, which typically includes a potentiometer to monitor the angle of the motor shaft. The control signal, usually a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal, determines the position of the motor. The width of the pulse corresponds to the desired angle, and the servo adjusts its position accordingly to match this input.
Servo motors are commonly used in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, radio-controlled vehicles, and automation systems. They are available in various sizes and torque ratings, allowing for flexibility in design based on the specific requirements of the project. The typical range of motion for most standard servo motors is between 0 to 180 degrees, but there are continuous rotation servos available that can rotate indefinitely in either direction, though they do not provide positional feedback.
When integrating a servo motor into a circuit, it is essential to consider the power supply requirements, as servo motors can draw significant current during operation. Additionally, the control circuitry must be designed to handle the PWM signal accurately to ensure smooth and responsive movement. Overall, the use of a servo motor adds a high level of precision and control to various electronic projects.As part of the module one of the motors we will be using is a servo motor.A servo motor is a small motor that you can position at any angle very accurately. It contains internal circuits that will automatically maintain that particular angle. However, you cannot do full revolutions with a servo. You are restricted to.. 🔗 External reference