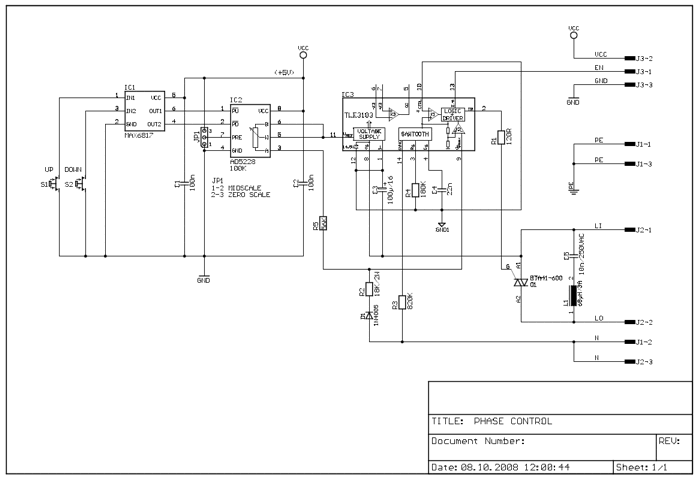
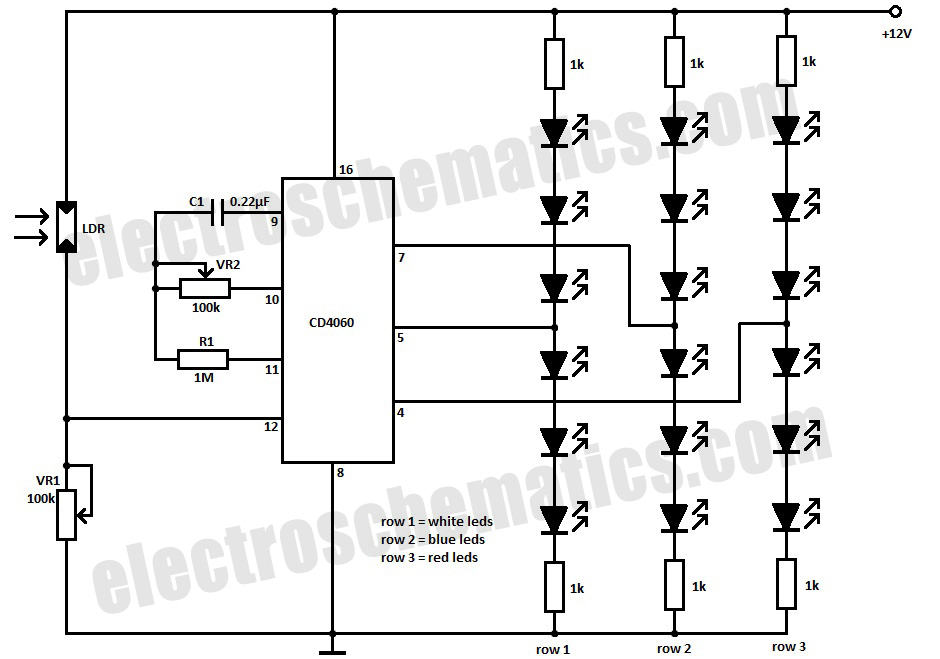
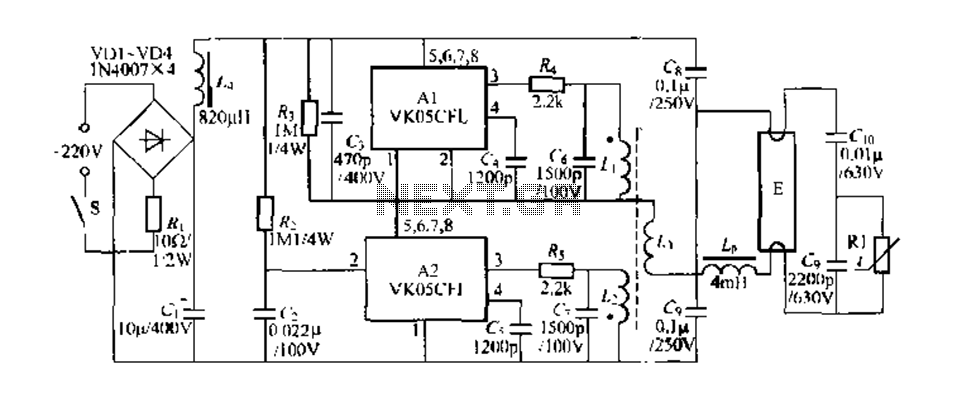
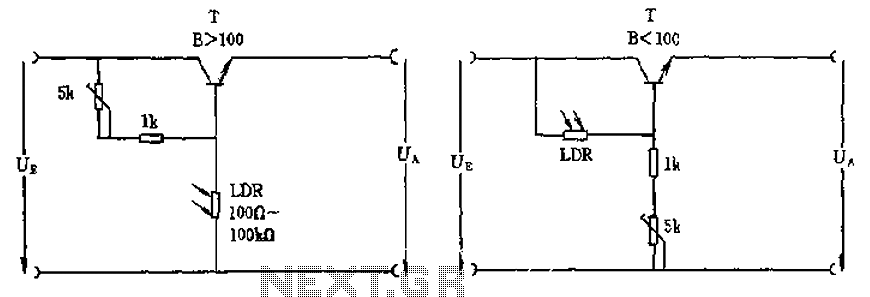
Simple Circuit Communicates Over Low-Voltage Power Lines
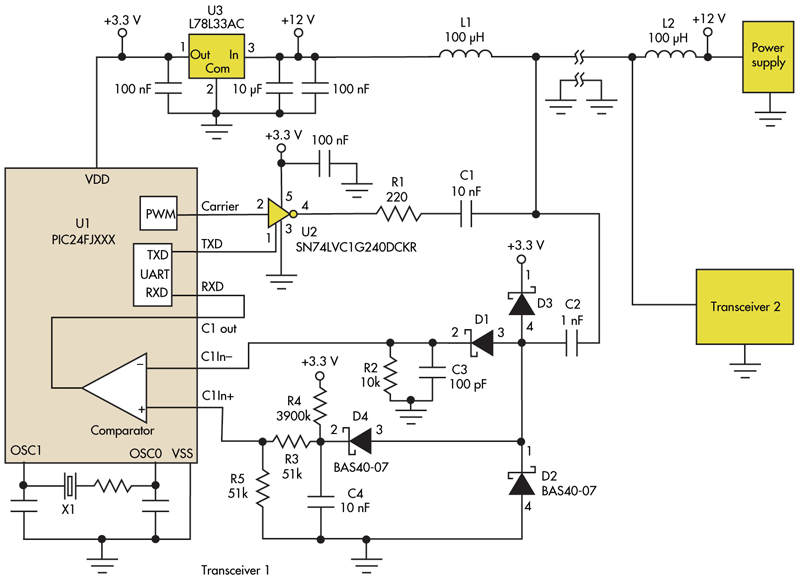
This circuit addresses the challenge of transmitting data over a cable that lacks available conductors. The data is modulated using On-Off Keying (OOK) and superimposed on a high-frequency carrier, allowing it to be transmitted over a low-voltage power supply line.
The circuit utilizes OOK modulation to encode digital data, where the presence of a carrier signal represents a binary '1' and the absence indicates a binary '0'. This method is particularly effective for low-bandwidth applications, as it simplifies the modulation process and allows for efficient use of existing power lines without requiring additional wiring.
The high-frequency carrier is generated by an oscillator circuit, which ensures that the signal remains above the noise floor of the power supply line. Typically, the carrier frequency is chosen to be significantly higher than the fundamental frequency of the power line to minimize interference and ensure reliable data transmission.
At the transmitter side, the data to be sent is fed into the modulator, which combines the data signal with the carrier frequency. This modulated signal is then coupled onto the power line using a coupling capacitor or transformer, depending on the design requirements. The coupling element allows the high-frequency signal to pass while blocking the low-frequency AC power, ensuring that the data does not interfere with the power delivery.
On the receiver side, a demodulation circuit is employed to extract the data from the received modulated signal. This typically involves a band-pass filter that isolates the carrier frequency, followed by a demodulator that converts the OOK signal back into its original digital format. The demodulated data can then be processed or utilized as needed.
Overall, this circuit design provides a practical solution for data transmission over existing infrastructure, reducing the need for additional cabling and simplifying installation in various applications, such as home automation systems, remote monitoring, and industrial control systems.This circuit solves the problem of sending data over a cable with no free conductors. The data is OOK (on-off keying) modulated and superimposed on a high-frequency carrier so it can be sent over a low-voltage power supply line 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes OOK modulation to encode digital data, where the presence of a carrier signal represents a binary '1' and the absence indicates a binary '0'. This method is particularly effective for low-bandwidth applications, as it simplifies the modulation process and allows for efficient use of existing power lines without requiring additional wiring.
The high-frequency carrier is generated by an oscillator circuit, which ensures that the signal remains above the noise floor of the power supply line. Typically, the carrier frequency is chosen to be significantly higher than the fundamental frequency of the power line to minimize interference and ensure reliable data transmission.
At the transmitter side, the data to be sent is fed into the modulator, which combines the data signal with the carrier frequency. This modulated signal is then coupled onto the power line using a coupling capacitor or transformer, depending on the design requirements. The coupling element allows the high-frequency signal to pass while blocking the low-frequency AC power, ensuring that the data does not interfere with the power delivery.
On the receiver side, a demodulation circuit is employed to extract the data from the received modulated signal. This typically involves a band-pass filter that isolates the carrier frequency, followed by a demodulator that converts the OOK signal back into its original digital format. The demodulated data can then be processed or utilized as needed.
Overall, this circuit design provides a practical solution for data transmission over existing infrastructure, reducing the need for additional cabling and simplifying installation in various applications, such as home automation systems, remote monitoring, and industrial control systems.This circuit solves the problem of sending data over a cable with no free conductors. The data is OOK (on-off keying) modulated and superimposed on a high-frequency carrier so it can be sent over a low-voltage power supply line 🔗 External reference