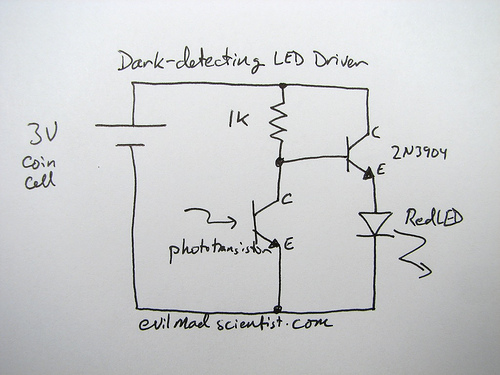
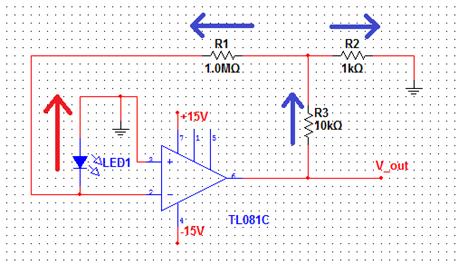
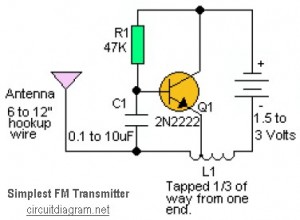
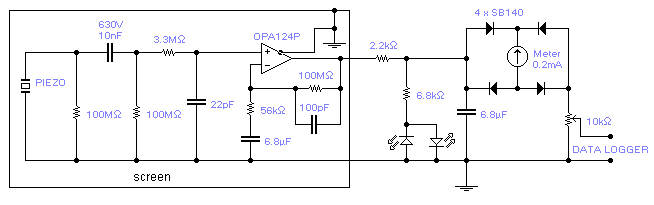
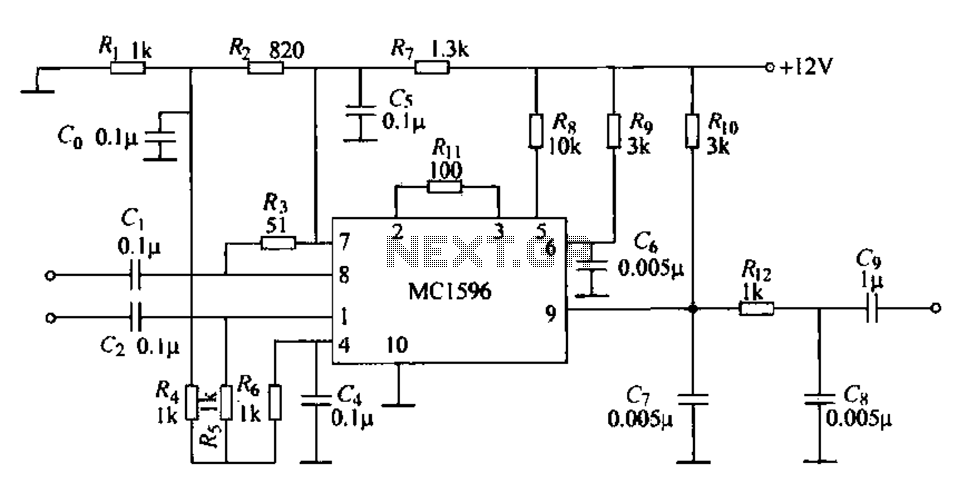
simple metal detector
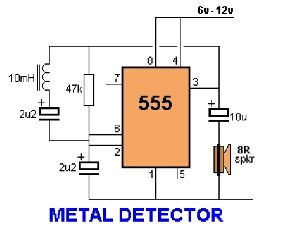
Assemble the circuit on a perfboard or PCB, excluding the inductor. Attach two long wires in place of the inductor. Use a long rod and position the inductor.
The circuit assembly begins with the preparation of a perfboard or printed circuit board (PCB) as the base for mounting the components. The inductor, which is a critical component in many electronic circuits, is intentionally excluded from the initial assembly. Instead, two long wires are attached at the designated location where the inductor would typically be connected. This approach allows for flexibility in testing and tuning the circuit without the inductor's influence during the initial setup.
Next, a long rod is used to position the inductor. This rod serves as a means to create a variable inductance effect, enabling adjustments to be made based on the circuit's performance during testing. The use of a rod allows for easy manipulation of the inductor's placement, which can significantly affect the circuit's overall behavior, particularly in applications involving RF (radio frequency) or tuned circuits.
It is essential to ensure that all connections are secure and that the wires are appropriately insulated to prevent any unintended short circuits. The circuit should be powered on only after verifying that all components are correctly placed and connected. Testing can then commence to evaluate the circuit's performance, with adjustments made as necessary based on the results observed. This method provides a practical approach to circuit assembly, allowing for modifications and enhancements in real-time.Assemble the circuit on a perfboard or pcb except the inductor. Attach two long wires at the place of the inductor. Use a long rod and place the induc.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit assembly begins with the preparation of a perfboard or printed circuit board (PCB) as the base for mounting the components. The inductor, which is a critical component in many electronic circuits, is intentionally excluded from the initial assembly. Instead, two long wires are attached at the designated location where the inductor would typically be connected. This approach allows for flexibility in testing and tuning the circuit without the inductor's influence during the initial setup.
Next, a long rod is used to position the inductor. This rod serves as a means to create a variable inductance effect, enabling adjustments to be made based on the circuit's performance during testing. The use of a rod allows for easy manipulation of the inductor's placement, which can significantly affect the circuit's overall behavior, particularly in applications involving RF (radio frequency) or tuned circuits.
It is essential to ensure that all connections are secure and that the wires are appropriately insulated to prevent any unintended short circuits. The circuit should be powered on only after verifying that all components are correctly placed and connected. Testing can then commence to evaluate the circuit's performance, with adjustments made as necessary based on the results observed. This method provides a practical approach to circuit assembly, allowing for modifications and enhancements in real-time.Assemble the circuit on a perfboard or pcb except the inductor. Attach two long wires at the place of the inductor. Use a long rod and place the induc.. 🔗 External reference