Simple Touch Alarm circuit
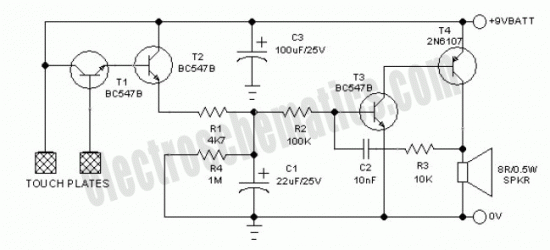
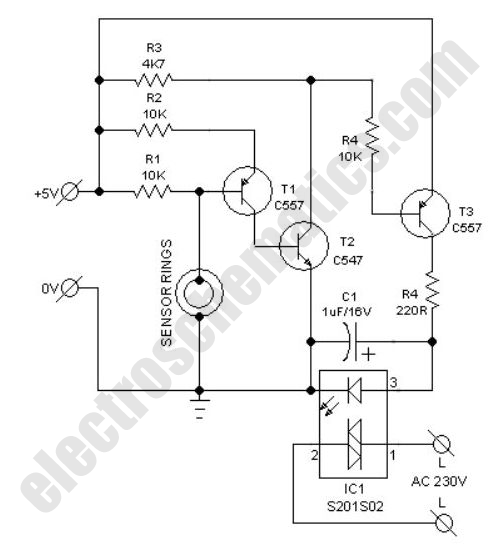
Touch the sensor of the alarm with your finger, and it starts beeping. It continues for a period and then stops. Touching it again will activate the beeping once more.
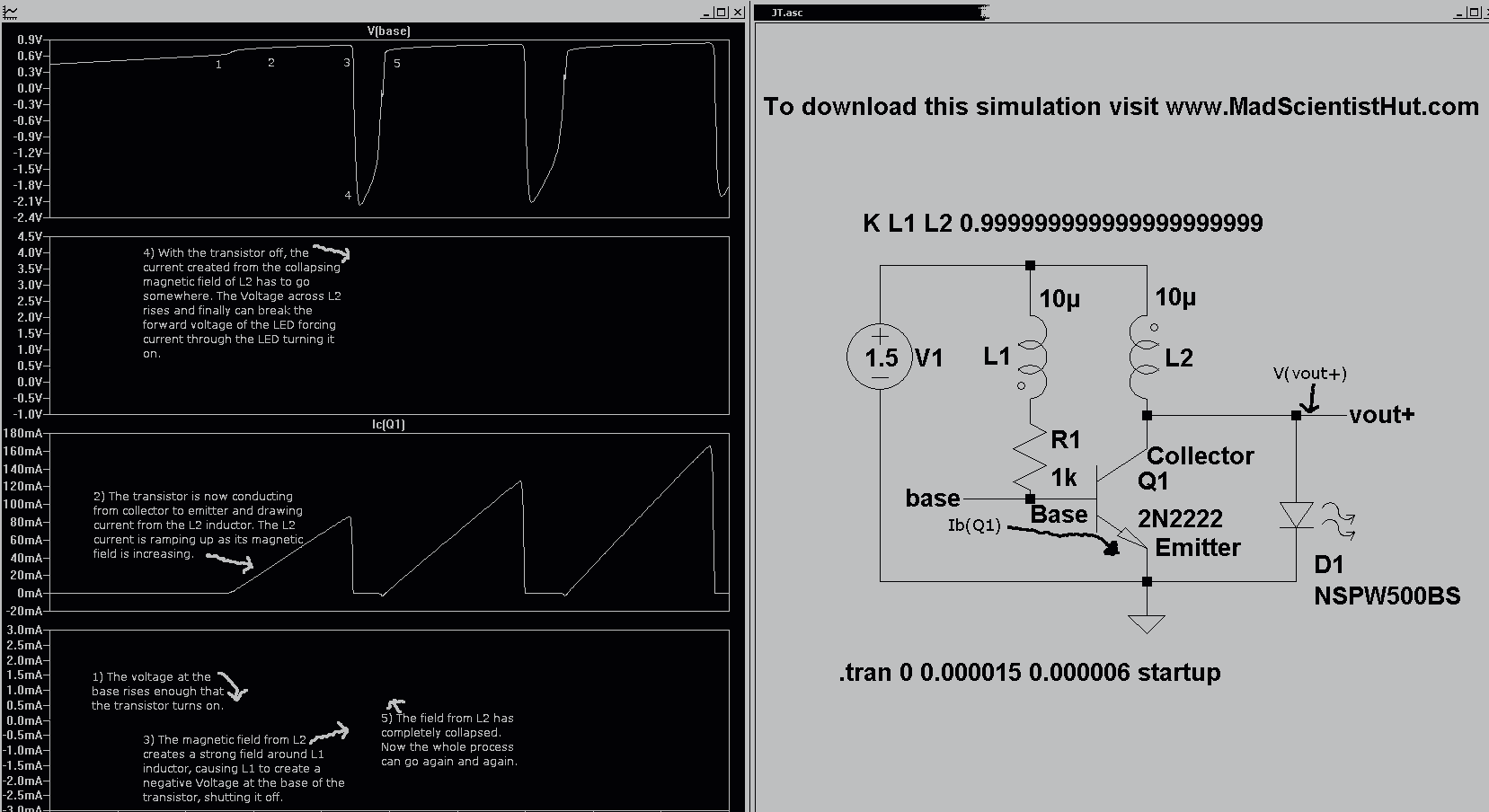
This description outlines a basic touch-activated alarm system. The circuit typically consists of a touch-sensitive sensor, a microcontroller, a sound output device (such as a buzzer or speaker), and a power supply.
The touch-sensitive sensor can be implemented using capacitive or resistive technology, which detects the presence of a finger through changes in capacitance or resistance. Upon detection, the sensor sends a signal to the microcontroller, which processes the input.
The microcontroller is programmed to activate the sound output device for a predetermined duration once the sensor is triggered. This duration can be adjusted in the firmware to suit the application. After the set time elapses, the microcontroller deactivates the sound output, effectively silencing the alarm.
When the sensor is touched again, the process repeats, allowing for multiple activations. The circuit may also include additional features such as LED indicators to provide visual feedback during activation or a reset mechanism to stop the alarm after a certain number of activations.
Power management is crucial in such designs, especially if the device is battery-operated. The circuit can include a low-power mode to conserve energy when not in use. Overall, the schematic for this touch-activated alarm would include the sensor, microcontroller, sound output, power supply, and any additional components for functionality and user interface.Touch the sensor of the alarm with your finger and it starts beeping, goes on for some time and then stops. Touching it again, and it goes again! This litt. 🔗 External reference
This description outlines a basic touch-activated alarm system. The circuit typically consists of a touch-sensitive sensor, a microcontroller, a sound output device (such as a buzzer or speaker), and a power supply.
The touch-sensitive sensor can be implemented using capacitive or resistive technology, which detects the presence of a finger through changes in capacitance or resistance. Upon detection, the sensor sends a signal to the microcontroller, which processes the input.
The microcontroller is programmed to activate the sound output device for a predetermined duration once the sensor is triggered. This duration can be adjusted in the firmware to suit the application. After the set time elapses, the microcontroller deactivates the sound output, effectively silencing the alarm.
When the sensor is touched again, the process repeats, allowing for multiple activations. The circuit may also include additional features such as LED indicators to provide visual feedback during activation or a reset mechanism to stop the alarm after a certain number of activations.
Power management is crucial in such designs, especially if the device is battery-operated. The circuit can include a low-power mode to conserve energy when not in use. Overall, the schematic for this touch-activated alarm would include the sensor, microcontroller, sound output, power supply, and any additional components for functionality and user interface.Touch the sensor of the alarm with your finger and it starts beeping, goes on for some time and then stops. Touching it again, and it goes again! This litt. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713