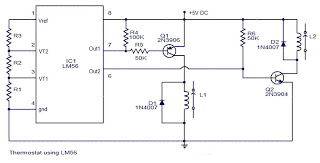
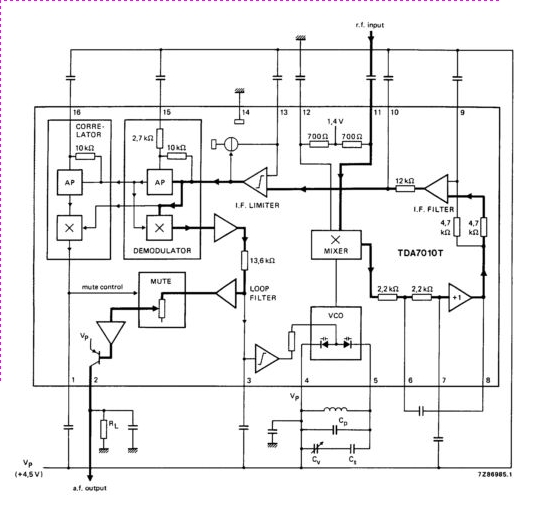
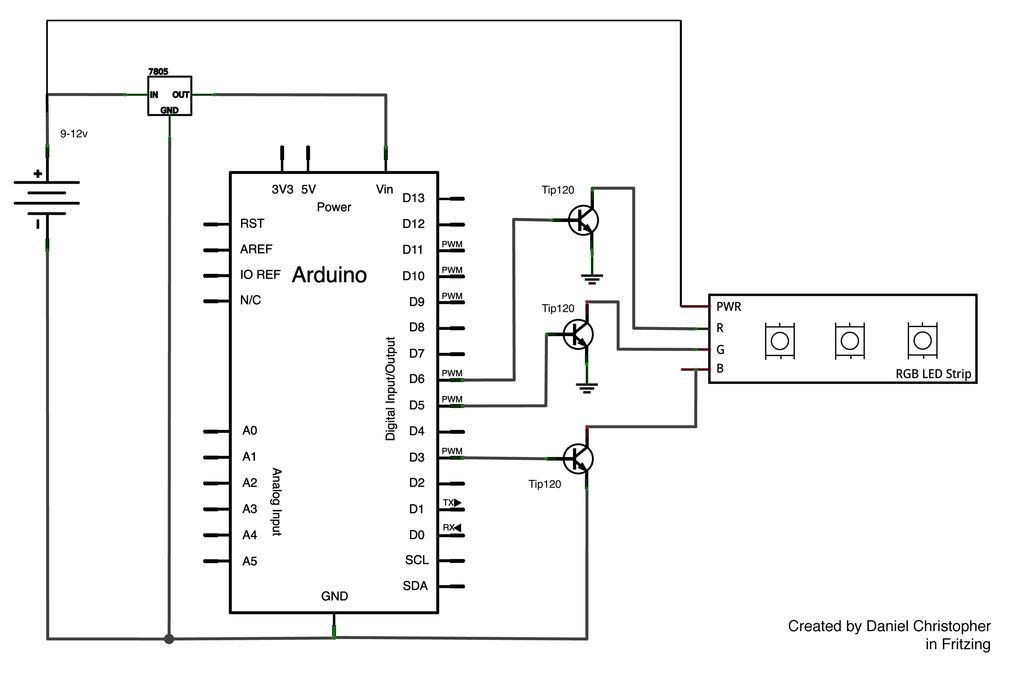
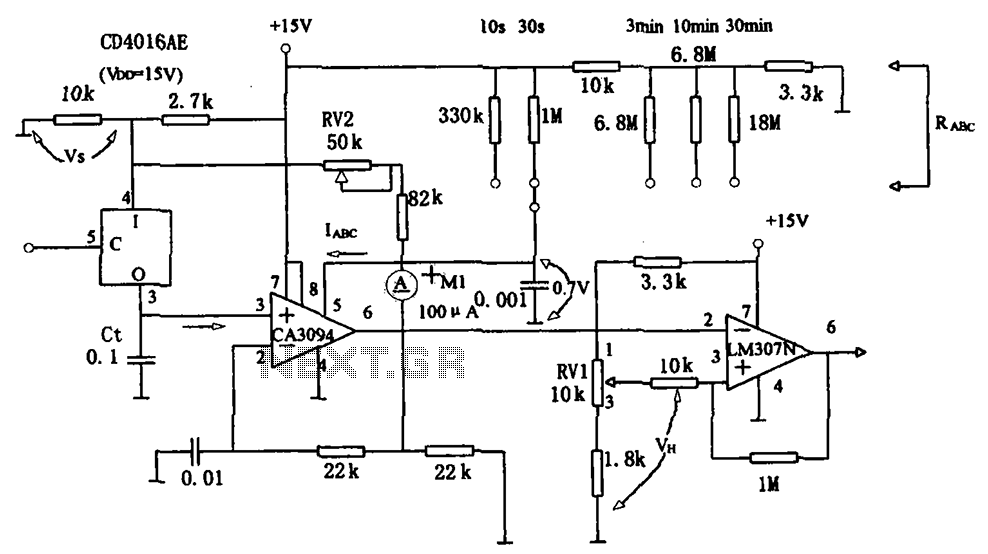
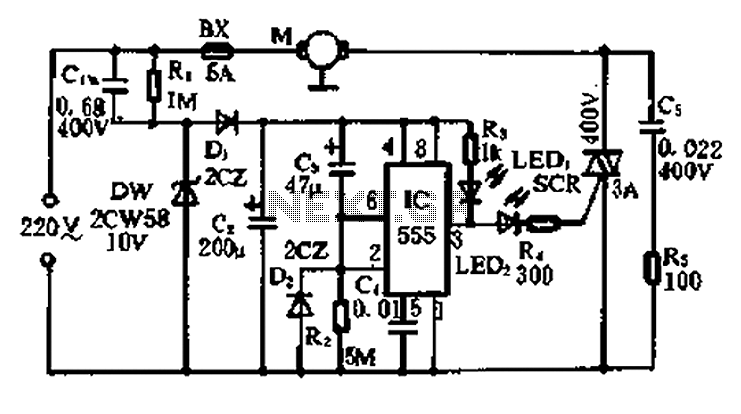
SMPS circuit
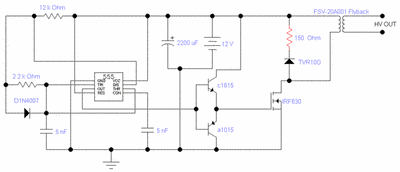
This is a simple flyback tester circuit designed to test high-frequency transformers, such as those used in switch-mode power supplies (SMPS) or flyback transformers. The circuit operates as an astable multivibrator with a frequency of approximately 90 kHz, powered by a 12 V DC supply. To test an SMPS transformer or flyback transformer, the input and output connections need to be reversed, using the secondary winding (12 V or 24 V) as the input. The circuit provides 12 V DC at one output pin, while another pin serves as the output for the circuit. When the circuit is activated, an AC voltmeter should be used to measure the voltage at the primary winding, which should range from 80 to 480 VAC, depending on the specifications of the transformer being tested. If no voltage is detected at the primary winding, it indicates that the transformer may be damaged. The same measurement procedure can be applied to other pins as well.
The flyback tester circuit employs an astable multivibrator configuration, which allows it to oscillate continuously without requiring any external triggering. The core components typically include two transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a transformer. The transistors are configured to alternately switch on and off, creating a square wave output that drives the primary winding of the transformer. The frequency of oscillation, around 90 kHz, is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
In practice, the circuit is powered by a 12 V DC supply, which is connected to the collector of the first transistor. The output from the secondary winding of the transformer is connected to the input of the circuit, allowing for testing of various transformer configurations. The voltage measurement at the primary winding can be performed using an AC voltmeter, which will indicate the output voltage generated by the oscillation in the transformer. A successful measurement will show a voltage within the specified range, confirming the operational integrity of the transformer.
In cases where the primary winding does not produce any voltage, further investigation is required, as this may suggest a fault in the transformer. The circuit can be modified to accommodate different transformer specifications by adjusting component values or transformer connections, making it a versatile tool for testing a wide range of transformers in electronic applications.Its a simple fly back tester, I believe you can built it, i use this circuit to test all of high freq transformer like SMPS transformer or fly back, this circuit is an astable multivibrator with about 90Khz freq, 12 vdc as vcc. To check SMPS transformer or fly back you should reverse the input and output, i mean you use secondary 12v or 24v out pu
t as input, give 12 or 24 output pin 12 vdc and another pin to output this circuit, when you turn on this circuit, use ac volt meter to measure primary, it should be come out 80 - 480 vac, depend to transformer spec, if there is no voltage come out from the primary transformer, so the transformer is damage, you can also measure another pin with the same step. 🔗 External reference
The flyback tester circuit employs an astable multivibrator configuration, which allows it to oscillate continuously without requiring any external triggering. The core components typically include two transistors, resistors, capacitors, and a transformer. The transistors are configured to alternately switch on and off, creating a square wave output that drives the primary winding of the transformer. The frequency of oscillation, around 90 kHz, is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the circuit.
In practice, the circuit is powered by a 12 V DC supply, which is connected to the collector of the first transistor. The output from the secondary winding of the transformer is connected to the input of the circuit, allowing for testing of various transformer configurations. The voltage measurement at the primary winding can be performed using an AC voltmeter, which will indicate the output voltage generated by the oscillation in the transformer. A successful measurement will show a voltage within the specified range, confirming the operational integrity of the transformer.
In cases where the primary winding does not produce any voltage, further investigation is required, as this may suggest a fault in the transformer. The circuit can be modified to accommodate different transformer specifications by adjusting component values or transformer connections, making it a versatile tool for testing a wide range of transformers in electronic applications.Its a simple fly back tester, I believe you can built it, i use this circuit to test all of high freq transformer like SMPS transformer or fly back, this circuit is an astable multivibrator with about 90Khz freq, 12 vdc as vcc. To check SMPS transformer or fly back you should reverse the input and output, i mean you use secondary 12v or 24v out pu
t as input, give 12 or 24 output pin 12 vdc and another pin to output this circuit, when you turn on this circuit, use ac volt meter to measure primary, it should be come out 80 - 480 vac, depend to transformer spec, if there is no voltage come out from the primary transformer, so the transformer is damage, you can also measure another pin with the same step. 🔗 External reference