Sound operated flip flop
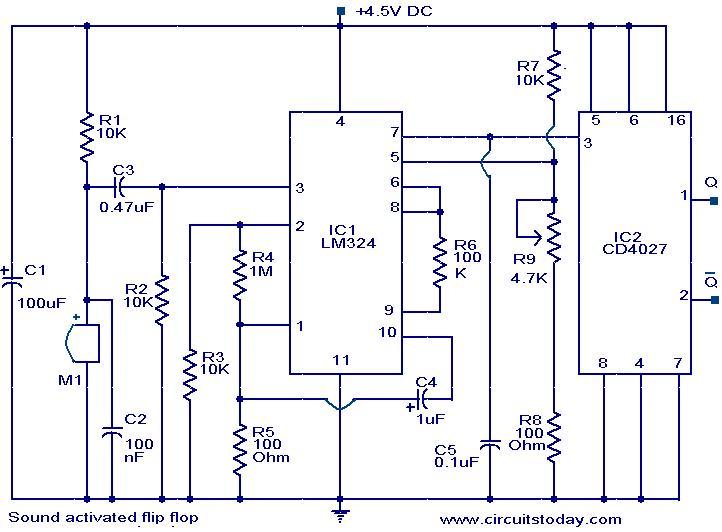
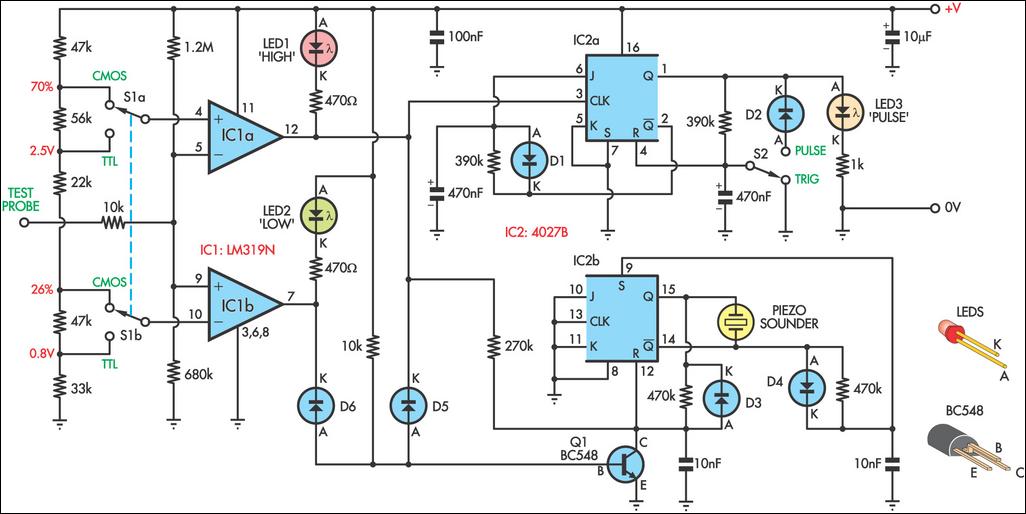
This circuit allows the output pins of a Flip Flop IC to be toggled using sound. A condenser microphone captures the sound, and the first two operational amplifiers in the LM324 IC amplify the signal. The third operational amplifier is configured as a level detector. Whenever the voltage generated by the sound exceeds the reference voltage at pin 5 of the third op-amp, its output at pin 7 goes high, triggering the CD4027 Flip Flop IC. Consequently, the output pins of the CD4027 (pins 1 and 2) toggle with each sound burst.
The described circuit utilizes a condenser microphone to detect sound waves, converting them into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed by the first two operational amplifiers within the LM324 IC, which serve to amplify the weak audio signal captured by the microphone. The amplification is crucial as it ensures that the signal is strong enough for further processing.
The third operational amplifier in the LM324 is configured as a level detector. This configuration allows it to compare the amplified audio signal against a predetermined reference voltage applied to pin 5. When the sound level surpasses this reference, the output of the third op-amp at pin 7 transitions to a high state. This transition serves as a trigger for the CD4027 Flip Flop IC.
The CD4027 is a dual J-K flip-flop, which means that it can toggle its output state based on the triggering signal received. Each time the output from the level detector goes high, the flip-flop changes its state, effectively toggling the output pins (pins 1 and 2). This functionality can be used in various applications, such as sound-activated switches, where the presence of sound can control electronic devices or systems.
To ensure proper operation, the circuit may require additional components such as resistors and capacitors for biasing and stability. The design should also consider the power supply requirements for both the LM324 and CD4027 ICs, ensuring that they operate within their specified voltage ranges. Overall, this circuit exemplifies the integration of audio detection and digital logic control in electronic design.Here given is a circuit in which the status of the output pins of a Flip Flop IC can be toggled by using sound. A condenser microphone is used for picking up the sound. The first two op-amps in the IC1 LM 324 is used to amplify the sound picked by the condenser microphone.
The third op-amp inside LM 324 is wired as a level detector. When ever the voltage produced due to sound have a level more than that of the reference voltage at pin 5 of the third op-amp, its output (pin 7) goes high, triggering the flip flop IC1 CD 4027. As a result the state of the output pins of CD 4027 ( pin 1 & pin 2) toggles for each burst of sound.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a condenser microphone to detect sound waves, converting them into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed by the first two operational amplifiers within the LM324 IC, which serve to amplify the weak audio signal captured by the microphone. The amplification is crucial as it ensures that the signal is strong enough for further processing.
The third operational amplifier in the LM324 is configured as a level detector. This configuration allows it to compare the amplified audio signal against a predetermined reference voltage applied to pin 5. When the sound level surpasses this reference, the output of the third op-amp at pin 7 transitions to a high state. This transition serves as a trigger for the CD4027 Flip Flop IC.
The CD4027 is a dual J-K flip-flop, which means that it can toggle its output state based on the triggering signal received. Each time the output from the level detector goes high, the flip-flop changes its state, effectively toggling the output pins (pins 1 and 2). This functionality can be used in various applications, such as sound-activated switches, where the presence of sound can control electronic devices or systems.
To ensure proper operation, the circuit may require additional components such as resistors and capacitors for biasing and stability. The design should also consider the power supply requirements for both the LM324 and CD4027 ICs, ensuring that they operate within their specified voltage ranges. Overall, this circuit exemplifies the integration of audio detection and digital logic control in electronic design.Here given is a circuit in which the status of the output pins of a Flip Flop IC can be toggled by using sound. A condenser microphone is used for picking up the sound. The first two op-amps in the IC1 LM 324 is used to amplify the sound picked by the condenser microphone.
The third op-amp inside LM 324 is wired as a level detector. When ever the voltage produced due to sound have a level more than that of the reference voltage at pin 5 of the third op-amp, its output (pin 7) goes high, triggering the flip flop IC1 CD 4027. As a result the state of the output pins of CD 4027 ( pin 1 & pin 2) toggles for each burst of sound.
🔗 External reference