Static Detector
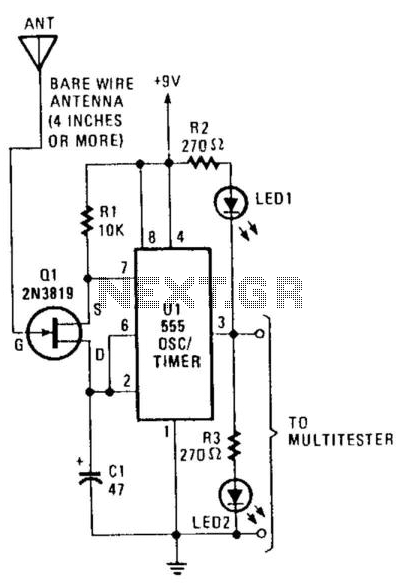
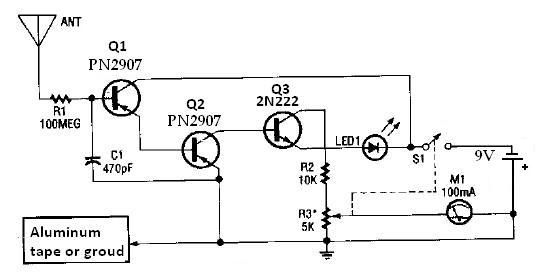
This circuit detects the presence of electrostatic fields by using a Field Effect Transistor (FET) to alter the flash rate of two Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). The FET is installed in the timing circuit and causes a change in the flash rate of the two LEDs.
The circuit operates by sensing variations in electrostatic fields through the FET, which is sensitive to electric fields due to its high input impedance. When an electrostatic field is detected, the FET's gate receives a voltage change, influencing its conduction state. This change in the FET's behavior is used to modulate the timing characteristics of a connected oscillator circuit.
The timing circuit typically consists of a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that defines the charge and discharge time, thereby determining the frequency at which the LEDs flash. The FET acts as a variable resistor within this RC network, adjusting the charge time based on the intensity of the detected electrostatic field. As the electrostatic field strength increases, the FET allows more current to flow, which results in a faster charge time and, consequently, a quicker flash rate of the LEDs.
The two LEDs are connected in parallel, each capable of emitting light at different frequencies, thereby providing a visual indication of the electrostatic field's presence and strength. The differing flash rates can be used to indicate varying levels of electrostatic energy, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the field's characteristics.
Overall, this circuit serves as a simple yet effective method for visualizing electrostatic fields, making it useful in various applications such as educational demonstrations, research, and industrial monitoring where electrostatic fields may pose risks or require measurement. This circuit detects the presence of electrostatic fields by using an FET to alter the flash rate of two LEDs. The FET is i nstalled in the timing circuit and causes a change in the flash rate of the two LEDs. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by sensing variations in electrostatic fields through the FET, which is sensitive to electric fields due to its high input impedance. When an electrostatic field is detected, the FET's gate receives a voltage change, influencing its conduction state. This change in the FET's behavior is used to modulate the timing characteristics of a connected oscillator circuit.
The timing circuit typically consists of a resistor-capacitor (RC) network that defines the charge and discharge time, thereby determining the frequency at which the LEDs flash. The FET acts as a variable resistor within this RC network, adjusting the charge time based on the intensity of the detected electrostatic field. As the electrostatic field strength increases, the FET allows more current to flow, which results in a faster charge time and, consequently, a quicker flash rate of the LEDs.
The two LEDs are connected in parallel, each capable of emitting light at different frequencies, thereby providing a visual indication of the electrostatic field's presence and strength. The differing flash rates can be used to indicate varying levels of electrostatic energy, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the field's characteristics.
Overall, this circuit serves as a simple yet effective method for visualizing electrostatic fields, making it useful in various applications such as educational demonstrations, research, and industrial monitoring where electrostatic fields may pose risks or require measurement. This circuit detects the presence of electrostatic fields by using an FET to alter the flash rate of two LEDs. The FET is i nstalled in the timing circuit and causes a change in the flash rate of the two LEDs. 🔗 External reference