Ion detector circuit diagram electronic project
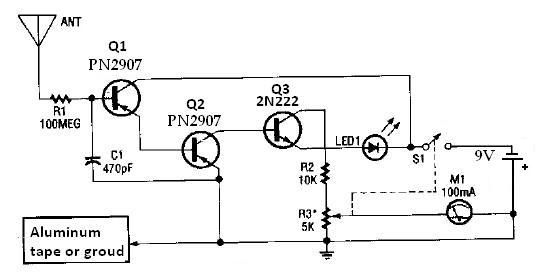
This ion detector circuit is designed to sense static charges and free ions present in the air. It is capable of detecting the presence of free ions, static electricity, or high voltage leakage. The project utilizes a short whip antenna, and a resistor (R3) is incorporated to adjust the circuit's sensitivity. The circuit includes a micro-ammeter (M1) rated at 100 mA, which is configured to detect negative ions. To enable the detection of positive ions, one can simply reverse the polarity of the transistors within the circuit; this involves replacing PNP transistors with NPN transistors and vice versa.
This ion detector circuit operates on the principle of measuring ion concentration in the air, which can indicate the presence of static electricity or high voltage leakage. The short whip antenna serves as the primary sensing element, capturing free ions in the vicinity. The sensitivity of the circuit is adjustable via the resistor R3, allowing for fine-tuning based on the environmental conditions or specific detection requirements.
The micro-ammeter (M1), with a full-scale deflection of 100 mA, provides a visual representation of the ion concentration detected by the circuit. It is important to ensure that the meter is calibrated correctly to reflect accurate ion measurements. The configuration of the circuit is primarily focused on detecting negative ions; however, for applications requiring the detection of positive ions, the transistor configuration must be altered. This involves swapping the roles of PNP and NPN transistors, which changes the biasing conditions and allows the circuit to respond to positive ion charges.
The overall design is relatively straightforward, making it suitable for educational purposes or hobbyist projects. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy troubleshooting and modifications, making it an excellent platform for understanding the principles of ion detection and static charge measurement. Care should be taken to ensure proper component ratings and connections to maintain circuit integrity and safety during operation.This ion detector circuit detects static charges and free ions in the air. This ion detector circuit can be used for detecting presence of free ions, static electricity or high voltage leakage. Antenna used in this project is a short whip antenna and the R3 resistor is used to adjust the sensitivity of the circuit.
The M1 from this circuit is a n 100mA micro-Ampere-meter. The detector is set up to detect negative ions. It can be made to detect positive ions by simply reversing the polarity of the transistors that comprise the circuit, i. e. , PNP units become NPN units, and NPN transistor is replaced by a PNP unit. 🔗 External reference
This ion detector circuit operates on the principle of measuring ion concentration in the air, which can indicate the presence of static electricity or high voltage leakage. The short whip antenna serves as the primary sensing element, capturing free ions in the vicinity. The sensitivity of the circuit is adjustable via the resistor R3, allowing for fine-tuning based on the environmental conditions or specific detection requirements.
The micro-ammeter (M1), with a full-scale deflection of 100 mA, provides a visual representation of the ion concentration detected by the circuit. It is important to ensure that the meter is calibrated correctly to reflect accurate ion measurements. The configuration of the circuit is primarily focused on detecting negative ions; however, for applications requiring the detection of positive ions, the transistor configuration must be altered. This involves swapping the roles of PNP and NPN transistors, which changes the biasing conditions and allows the circuit to respond to positive ion charges.
The overall design is relatively straightforward, making it suitable for educational purposes or hobbyist projects. The simplicity of the circuit allows for easy troubleshooting and modifications, making it an excellent platform for understanding the principles of ion detection and static charge measurement. Care should be taken to ensure proper component ratings and connections to maintain circuit integrity and safety during operation.This ion detector circuit detects static charges and free ions in the air. This ion detector circuit can be used for detecting presence of free ions, static electricity or high voltage leakage. Antenna used in this project is a short whip antenna and the R3 resistor is used to adjust the sensitivity of the circuit.
The M1 from this circuit is a n 100mA micro-Ampere-meter. The detector is set up to detect negative ions. It can be made to detect positive ions by simply reversing the polarity of the transistors that comprise the circuit, i. e. , PNP units become NPN units, and NPN transistor is replaced by a PNP unit. 🔗 External reference