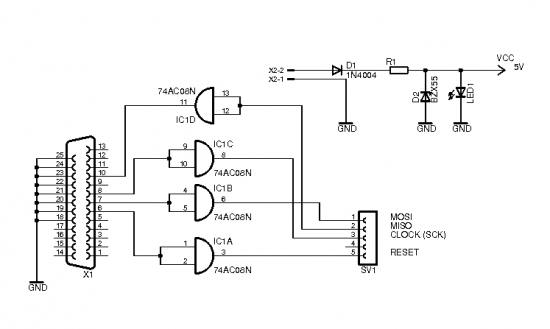
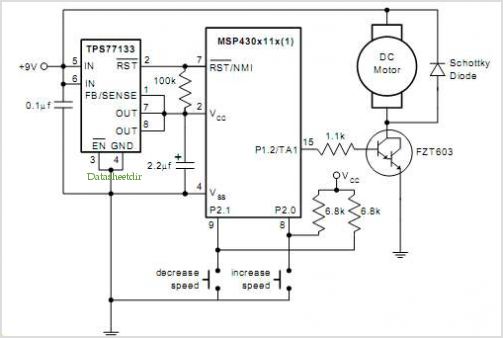
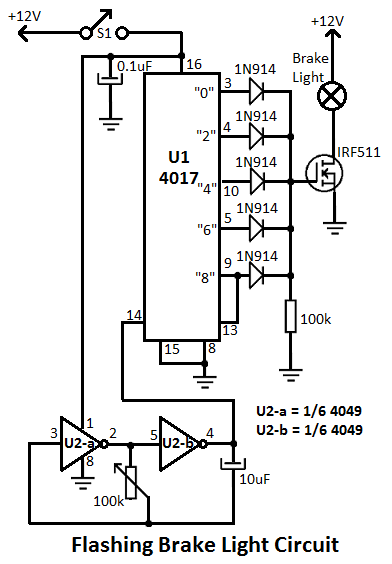
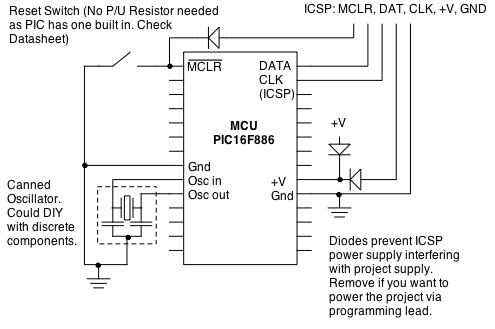
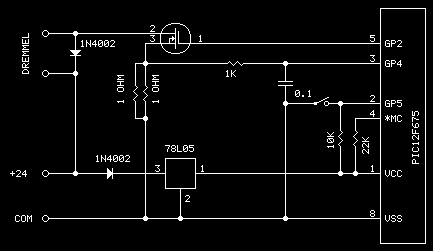
Stepper Motor Controller
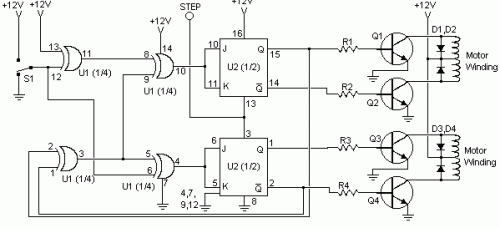
This circuit is constructed using standard components and can be easily adapted for computer control. By utilizing inexpensive surplus transistors and a stepper motor, the overall cost of the circuit can be maintained at under $10.
The described circuit is a versatile and cost-effective solution for applications requiring precise motor control. It employs standard electronic components, which are widely available and easy to source. The adaptability for computer control allows for integration with various digital systems, enabling automated operation and enhanced functionality.
The use of surplus transistors is a key factor in minimizing costs. These transistors can handle the current and voltage requirements of the circuit while providing reliable switching capabilities. Additionally, the incorporation of a stepper motor allows for precise control of position and speed, making this circuit suitable for applications such as robotics, CNC machines, or automated systems.
The circuit design typically includes a microcontroller or a computer interface to send control signals to the transistors. The transistors act as switches, driving the stepper motor based on the input signals received. Properly selecting the transistor type and ensuring they can handle the motor's power requirements is crucial for the circuit's performance.
To further enhance the circuit's functionality, additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes may be included to manage signal integrity, protect against back EMF from the motor, and stabilize the power supply. This modular approach allows for easy modifications and scalability, making it an ideal choice for hobbyists and engineers alike.
In summary, this circuit represents an economical and efficient solution for motor control applications, leveraging standard components and computer interfacing to achieve desired operational outcomes.his circuit is built from standard components and can easily be adapted to be controlled by a computer. If you use cheap surplus transistors and stepper motor, the price of the circuit can be kept to under $10
🔗 External reference
The described circuit is a versatile and cost-effective solution for applications requiring precise motor control. It employs standard electronic components, which are widely available and easy to source. The adaptability for computer control allows for integration with various digital systems, enabling automated operation and enhanced functionality.
The use of surplus transistors is a key factor in minimizing costs. These transistors can handle the current and voltage requirements of the circuit while providing reliable switching capabilities. Additionally, the incorporation of a stepper motor allows for precise control of position and speed, making this circuit suitable for applications such as robotics, CNC machines, or automated systems.
The circuit design typically includes a microcontroller or a computer interface to send control signals to the transistors. The transistors act as switches, driving the stepper motor based on the input signals received. Properly selecting the transistor type and ensuring they can handle the motor's power requirements is crucial for the circuit's performance.
To further enhance the circuit's functionality, additional components such as resistors, capacitors, and diodes may be included to manage signal integrity, protect against back EMF from the motor, and stabilize the power supply. This modular approach allows for easy modifications and scalability, making it an ideal choice for hobbyists and engineers alike.
In summary, this circuit represents an economical and efficient solution for motor control applications, leveraging standard components and computer interfacing to achieve desired operational outcomes.his circuit is built from standard components and can easily be adapted to be controlled by a computer. If you use cheap surplus transistors and stepper motor, the price of the circuit can be kept to under $10
🔗 External reference