Stitching Machine Motor Speed Control
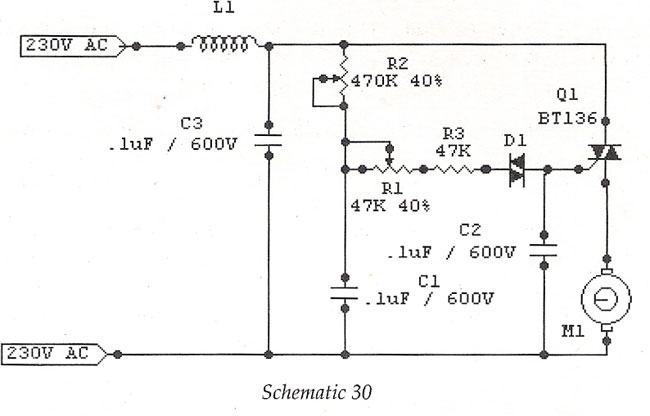
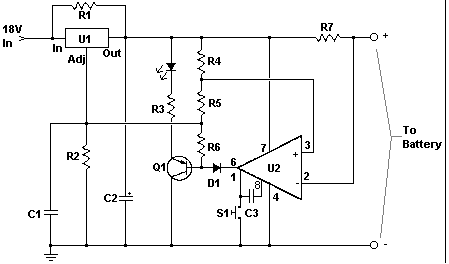
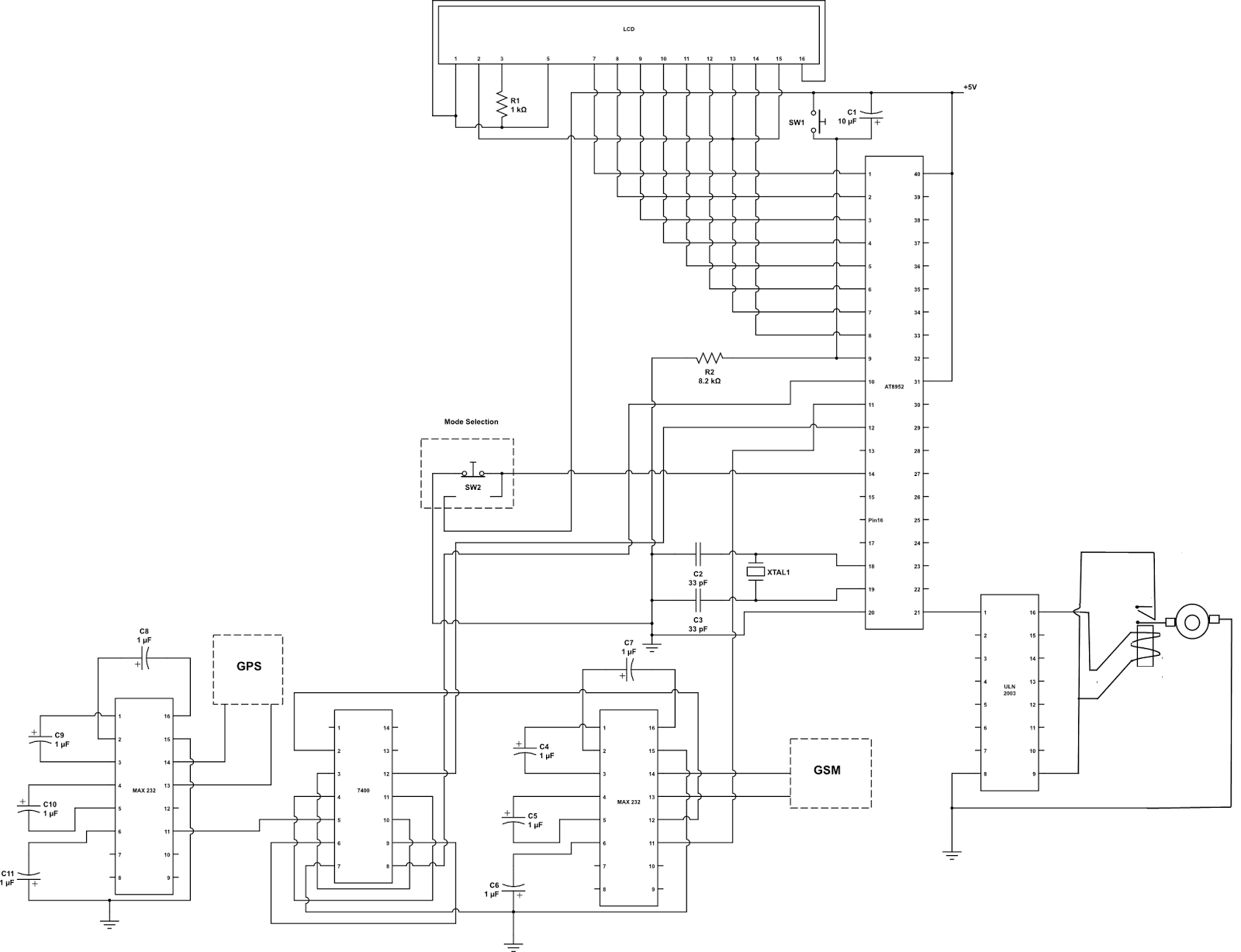
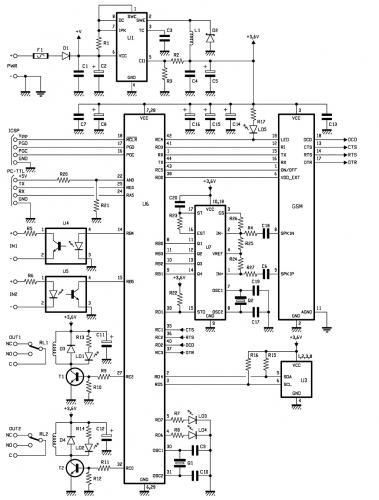
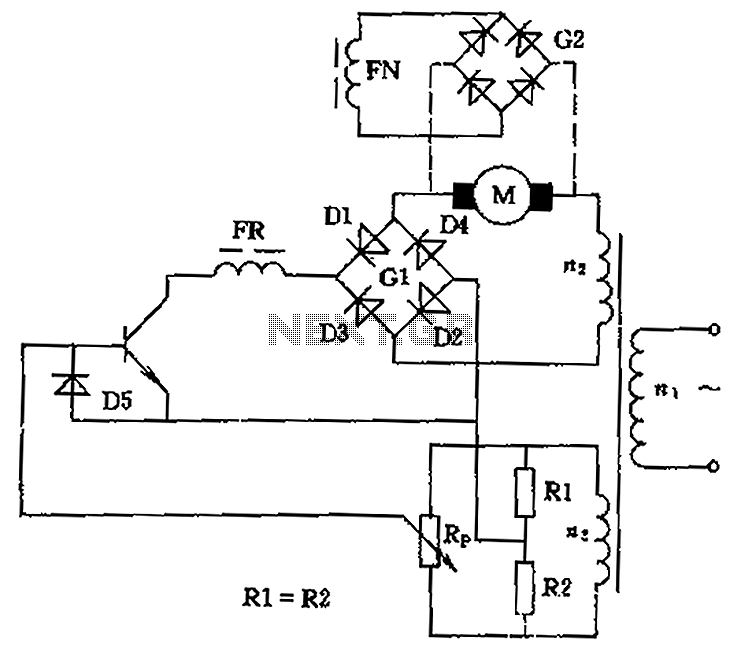
The motor speed control for stitching machines utilizes a series of carbon buttons housed within an enclosure, which are activated by a foot pedal. As the pressure on the foot pedal increases, the motor speed is adjusted accordingly.
The motor speed control circuit for stitching machines is designed to provide precise control over the operation of the motor, allowing for varying stitching speeds based on user input. The system typically includes a foot pedal interface, which incorporates a variable resistor or potentiometer to detect the pressure applied by the operator.
When the foot pedal is pressed, the resistance changes, sending a corresponding voltage signal to the motor controller. This controller interprets the voltage level and adjusts the power supplied to the motor, thereby controlling its speed. The enclosure containing the carbon buttons serves as a protective housing, ensuring durability and reliability in a workshop environment.
Additional components may include a microcontroller for enhanced functionality, enabling features such as programmable speed settings and feedback mechanisms. Safety features such as overcurrent protection and thermal shutdown may also be integrated into the circuit to prevent damage to the motor and associated components.
The overall design emphasizes efficiency and user-friendliness, allowing operators to achieve optimal stitching results with minimal effort. Proper attention to the selection of materials and components is essential to ensure longevity and consistent performance in industrial applications.Stitching Machine Motor Speed Control, Motor operated stitching machines have a series of carbon buttons in an enclosure operated by foot pedal. As the pressure on the foot pedal is increase.. 🔗 External reference
The motor speed control circuit for stitching machines is designed to provide precise control over the operation of the motor, allowing for varying stitching speeds based on user input. The system typically includes a foot pedal interface, which incorporates a variable resistor or potentiometer to detect the pressure applied by the operator.
When the foot pedal is pressed, the resistance changes, sending a corresponding voltage signal to the motor controller. This controller interprets the voltage level and adjusts the power supplied to the motor, thereby controlling its speed. The enclosure containing the carbon buttons serves as a protective housing, ensuring durability and reliability in a workshop environment.
Additional components may include a microcontroller for enhanced functionality, enabling features such as programmable speed settings and feedback mechanisms. Safety features such as overcurrent protection and thermal shutdown may also be integrated into the circuit to prevent damage to the motor and associated components.
The overall design emphasizes efficiency and user-friendliness, allowing operators to achieve optimal stitching results with minimal effort. Proper attention to the selection of materials and components is essential to ensure longevity and consistent performance in industrial applications.Stitching Machine Motor Speed Control, Motor operated stitching machines have a series of carbon buttons in an enclosure operated by foot pedal. As the pressure on the foot pedal is increase.. 🔗 External reference