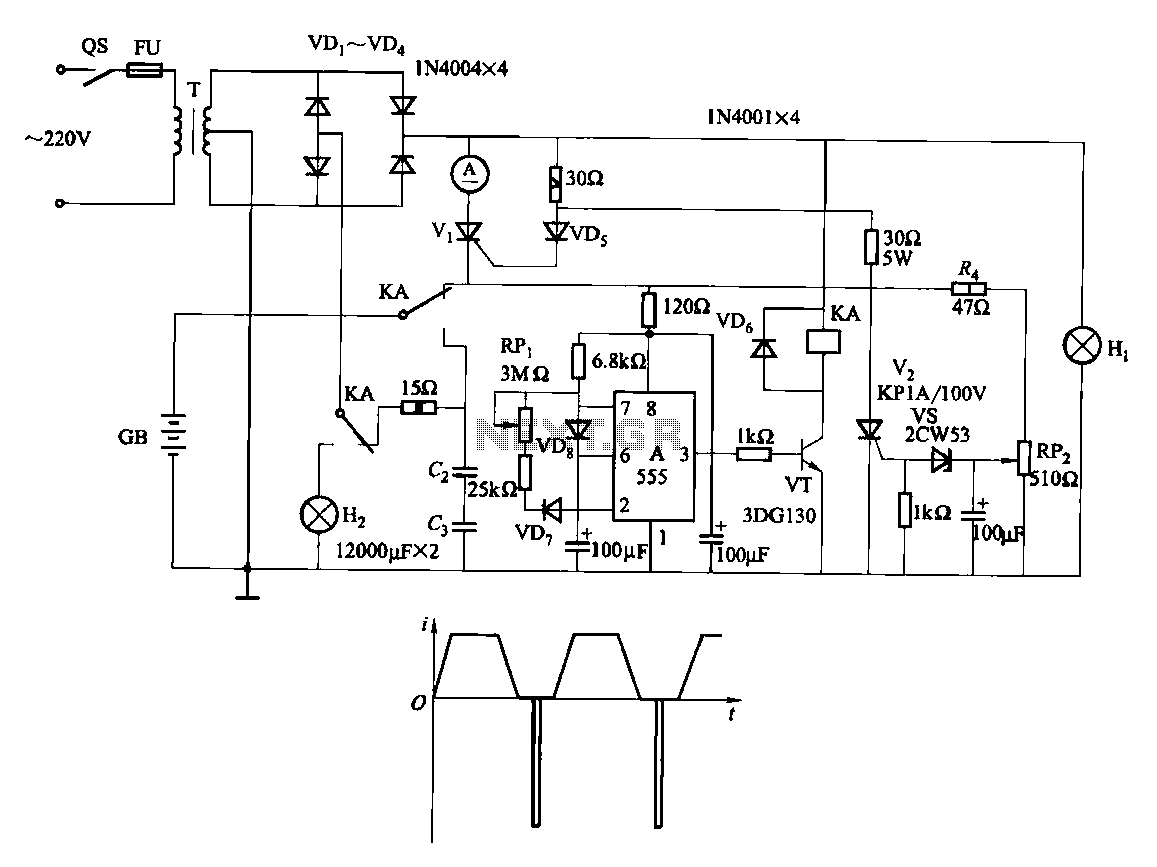
Car battery charger Automative car and motorcycle schematics
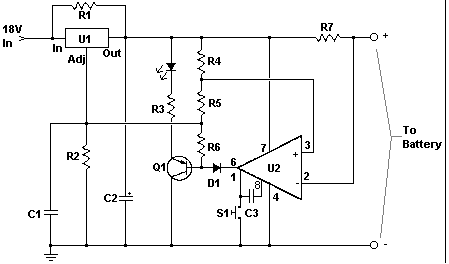
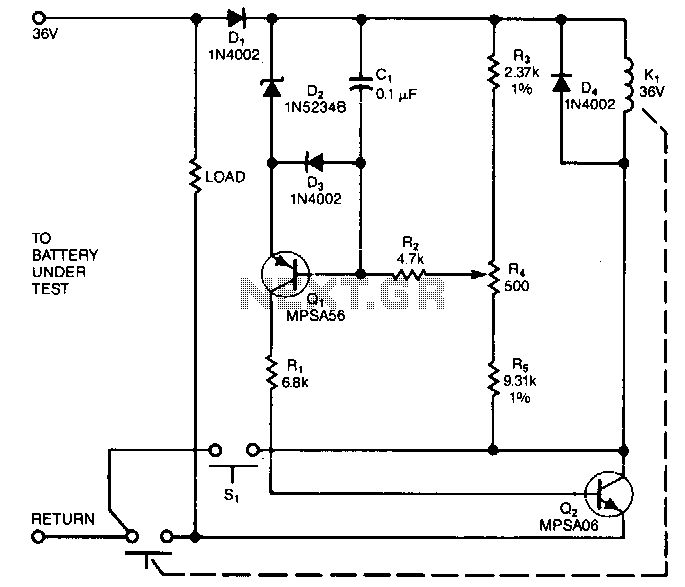
The circuit is designed to operate with an external power supply, which is why it does not include a transformer, rectifier, or filter capacitors in the schematic. However, these components can be added if desired. To utilize the circuit, connect it to a power supply and attach the battery that requires charging to the output terminals. After making these connections, activate the circuit by pressing the "Start" switch (S1) and monitor the charging process. It is advisable to check on the circuit periodically during its initial operation to ensure it functions correctly and that the battery is not being overcharged.
The circuit operates by directly connecting to a power supply, which provides the necessary voltage and current for charging a battery. The absence of a transformer indicates that the circuit is designed for a specific voltage level, typically from a DC power supply. Users may consider incorporating a transformer and rectifier if AC power is used, which would allow for voltage adjustment and conversion to DC.
The charging mechanism is initiated by pressing the "Start" switch (S1), which completes the circuit and allows current to flow from the power supply to the battery. It is essential to ensure that the output terminals are correctly connected to the battery to prevent damage or inefficient charging.
Monitoring the circuit during its initial use is crucial, as it allows for the detection of any potential issues, such as overheating or excessive voltage, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan. Implementing a simple voltage or current monitoring system can provide real-time feedback on the charging status, enhancing safety and efficiency.
For added protection, users may consider integrating a charge controller or a battery management system (BMS) that can automatically regulate the charging process, prevent overcharging, and optimize battery health. These systems often include features such as temperature sensors and automatic shut-off mechanisms, which further enhance the reliability of the charging circuit.The circuit was meant to be powered by a power supply, which is why there is no transformer, rectifier, or filter capacitors on the schematic. There is no reason why you cannot add these. To use the circuit, hook it up to a power supply/plug it in. Then, connect the battery to be charged to the output terminals. All you have to do now is push S1 ( the "Start" switch), and wait for the circuit to finish. The first time you use the circuit, you should check up on it every once and a while to make sure that it is working properly and the battery is not being over charged. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by directly connecting to a power supply, which provides the necessary voltage and current for charging a battery. The absence of a transformer indicates that the circuit is designed for a specific voltage level, typically from a DC power supply. Users may consider incorporating a transformer and rectifier if AC power is used, which would allow for voltage adjustment and conversion to DC.
The charging mechanism is initiated by pressing the "Start" switch (S1), which completes the circuit and allows current to flow from the power supply to the battery. It is essential to ensure that the output terminals are correctly connected to the battery to prevent damage or inefficient charging.
Monitoring the circuit during its initial use is crucial, as it allows for the detection of any potential issues, such as overheating or excessive voltage, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan. Implementing a simple voltage or current monitoring system can provide real-time feedback on the charging status, enhancing safety and efficiency.
For added protection, users may consider integrating a charge controller or a battery management system (BMS) that can automatically regulate the charging process, prevent overcharging, and optimize battery health. These systems often include features such as temperature sensors and automatic shut-off mechanisms, which further enhance the reliability of the charging circuit.The circuit was meant to be powered by a power supply, which is why there is no transformer, rectifier, or filter capacitors on the schematic. There is no reason why you cannot add these. To use the circuit, hook it up to a power supply/plug it in. Then, connect the battery to be charged to the output terminals. All you have to do now is push S1 ( the "Start" switch), and wait for the circuit to finish. The first time you use the circuit, you should check up on it every once and a while to make sure that it is working properly and the battery is not being over charged. 🔗 External reference