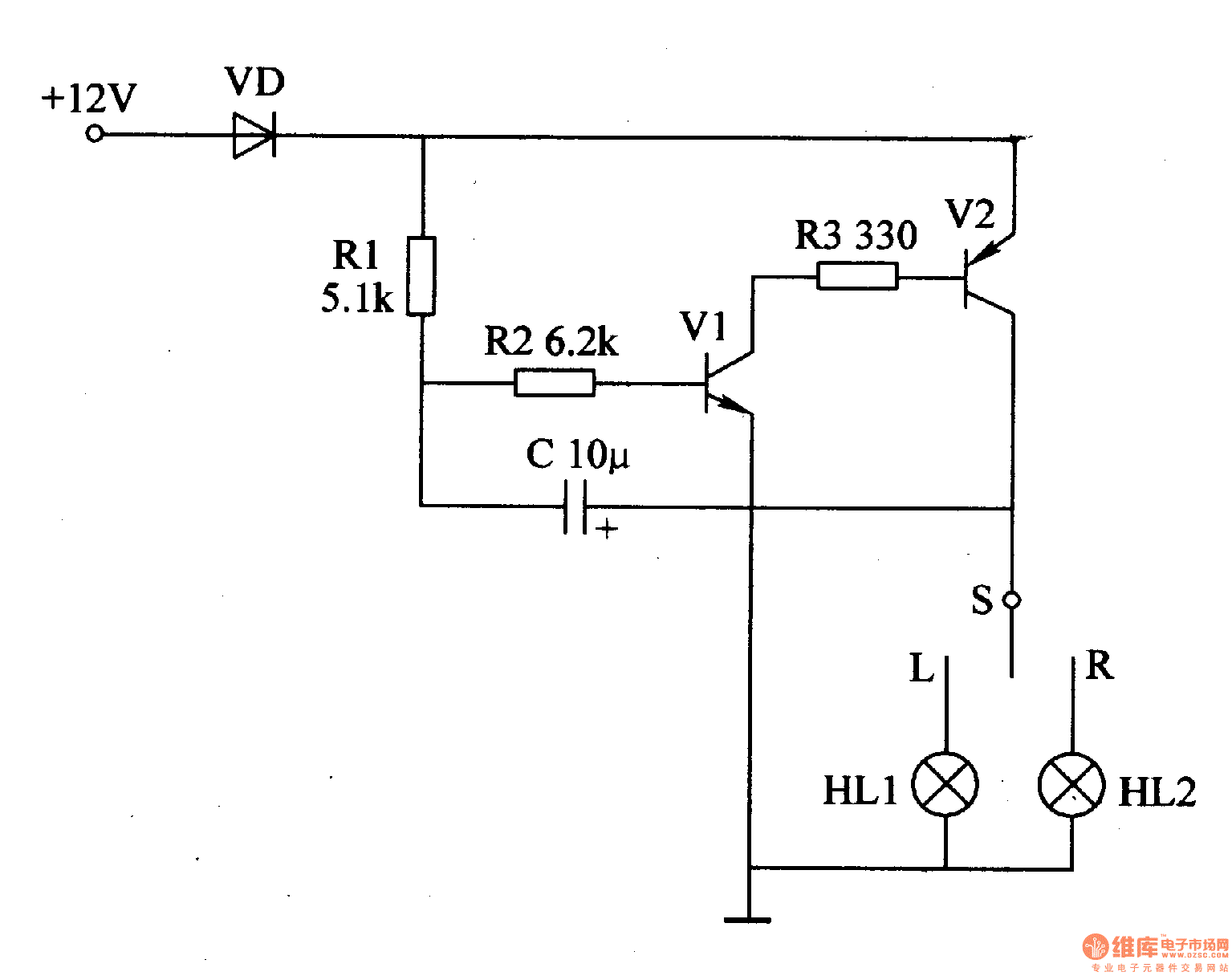
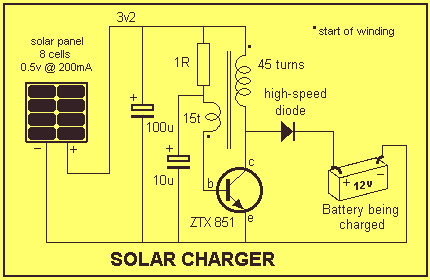
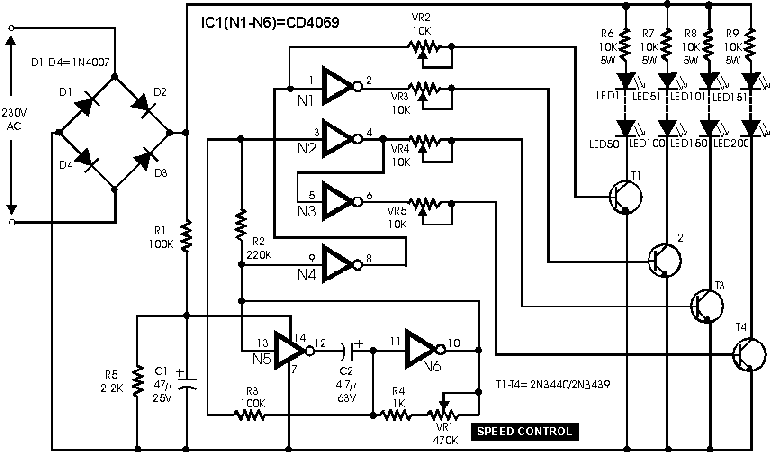
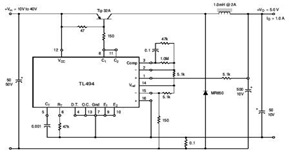
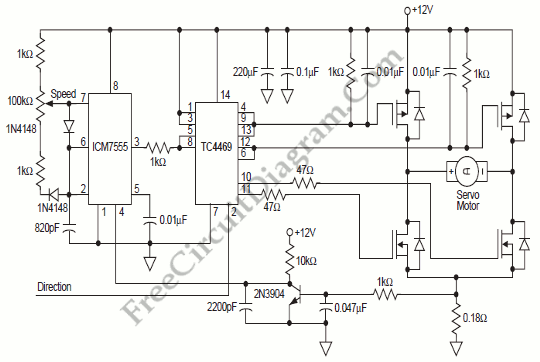
DC motor speed control circuit diagram of a song
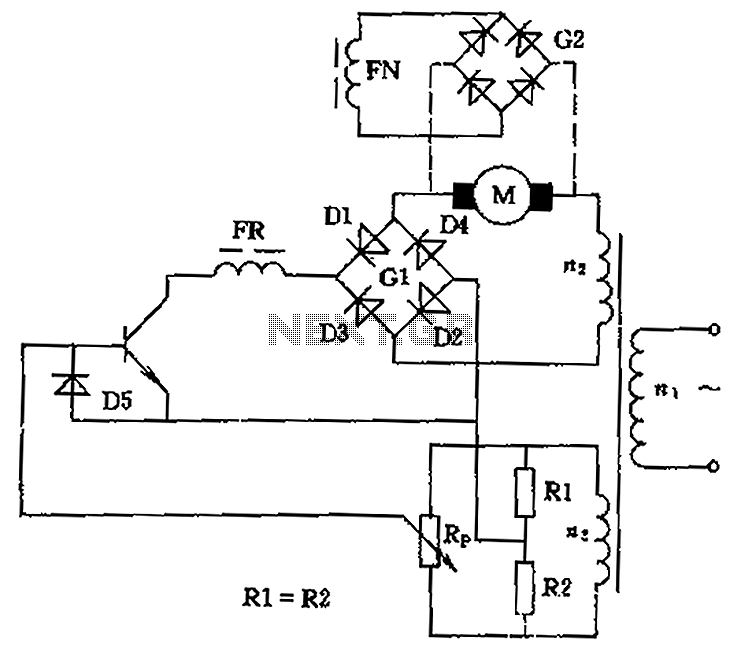
The circuit is designed to control the speed and direction of low-power DC motors, including series and shunt motors. It utilizes a rectifier bridge (G1) connected in series with the motor and linked to the secondary winding (n2) of a transformer. In the event of a failure in the rectifier bridge output, the motor halts, analogous to the sliding contact potentiometer (Rp) being in the neutral position. By adjusting the sliding contact upward or downward, the motor can be made to operate in forward or reverse directions, allowing for precise control of its operation.
The circuit employs a rectifier bridge configuration (G1) to convert AC voltage from the transformer’s secondary winding into a usable DC voltage for the motor. This rectification process is crucial for providing a steady and reliable power supply to the motor, which is essential for consistent speed control. The control mechanism is further enhanced by the use of a sliding contact potentiometer (Rp), which functions as a variable resistor. Adjusting the position of the sliding contact alters the resistance in the circuit, thereby modifying the voltage supplied to the motor.
When the sliding contact is positioned at the midpoint, the circuit effectively disconnects the motor, stopping its operation. This feature serves as a safety mechanism, preventing unintended motor activation. Conversely, moving the sliding contact in either direction allows for the adjustment of motor speed and direction. The upward movement increases the voltage, causing the motor to rotate in the forward direction, while downward movement decreases the voltage, reversing the motor's rotation.
In practical applications, this circuit can be implemented in various settings, including robotics, conveyor systems, and other automated machinery where precise motor control is necessary. The design ensures that operators can easily manage the motor's performance, providing flexibility and adaptability to different operational requirements. Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for controlling low-power DC motors with both speed and directional capabilities, making it a valuable component in electronic control systems. Circuit can be used to control low power DC motor, series motor or shunt motor speed and direction. Motor and rectifier bridge G1 series, and then connected to the grid transfo rmer secondary winding n2. If the output of the rectifier bridge fails, the motor stops, which is equivalent to the sliding contact potentiometer Rp in the middle position, if the upward or downward movement of the sliding contact, the motor will forward or reverse, it can control the motor operation.
The circuit employs a rectifier bridge configuration (G1) to convert AC voltage from the transformer’s secondary winding into a usable DC voltage for the motor. This rectification process is crucial for providing a steady and reliable power supply to the motor, which is essential for consistent speed control. The control mechanism is further enhanced by the use of a sliding contact potentiometer (Rp), which functions as a variable resistor. Adjusting the position of the sliding contact alters the resistance in the circuit, thereby modifying the voltage supplied to the motor.
When the sliding contact is positioned at the midpoint, the circuit effectively disconnects the motor, stopping its operation. This feature serves as a safety mechanism, preventing unintended motor activation. Conversely, moving the sliding contact in either direction allows for the adjustment of motor speed and direction. The upward movement increases the voltage, causing the motor to rotate in the forward direction, while downward movement decreases the voltage, reversing the motor's rotation.
In practical applications, this circuit can be implemented in various settings, including robotics, conveyor systems, and other automated machinery where precise motor control is necessary. The design ensures that operators can easily manage the motor's performance, providing flexibility and adaptability to different operational requirements. Overall, this circuit represents a robust solution for controlling low-power DC motors with both speed and directional capabilities, making it a valuable component in electronic control systems. Circuit can be used to control low power DC motor, series motor or shunt motor speed and direction. Motor and rectifier bridge G1 series, and then connected to the grid transfo rmer secondary winding n2. If the output of the rectifier bridge fails, the motor stops, which is equivalent to the sliding contact potentiometer Rp in the middle position, if the upward or downward movement of the sliding contact, the motor will forward or reverse, it can control the motor operation.