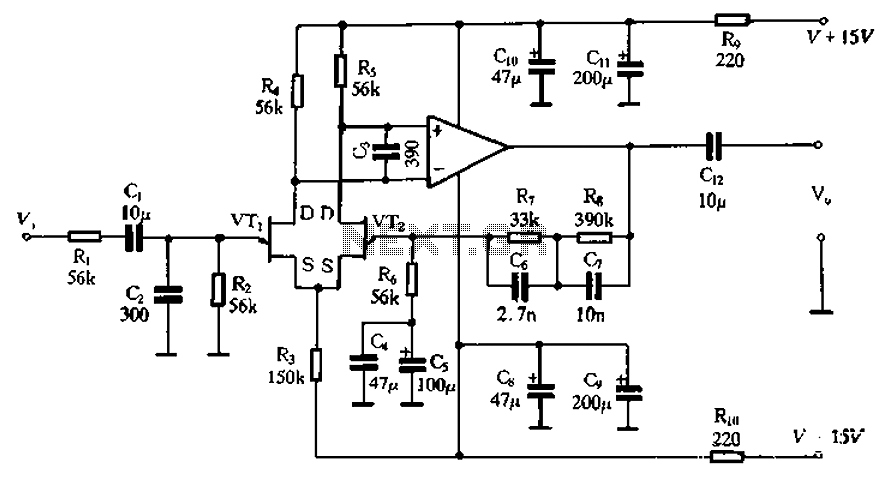
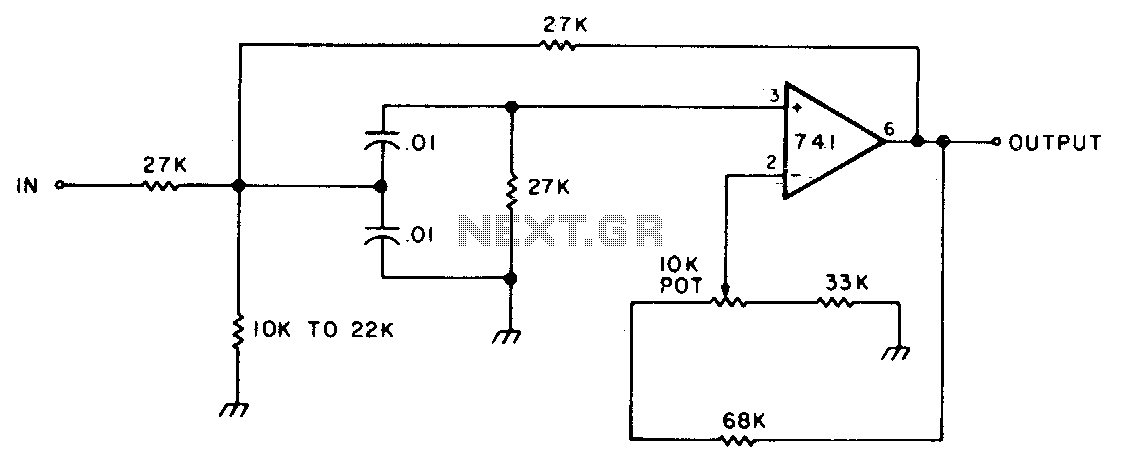
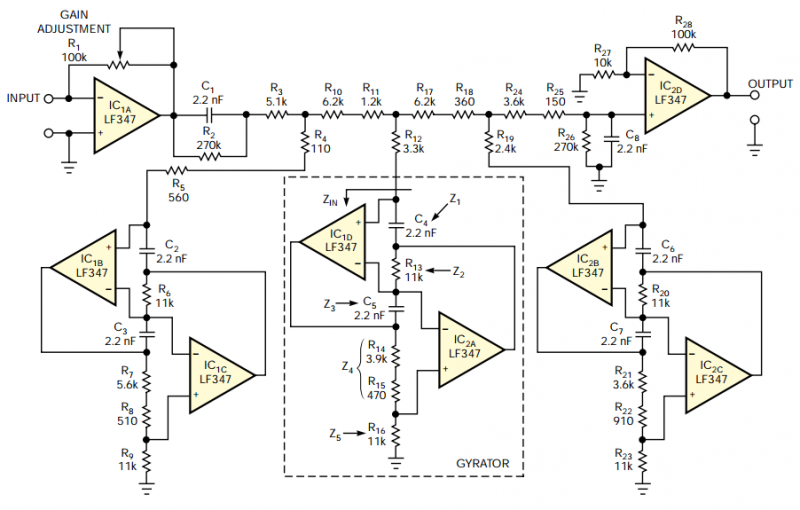
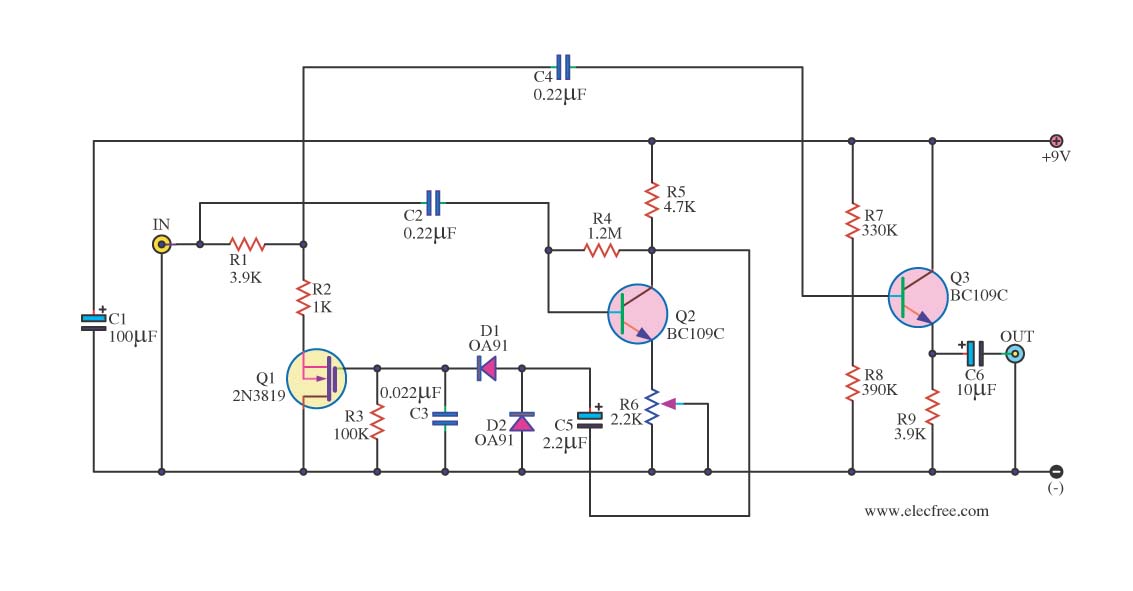
Subwoofer Low pass filter
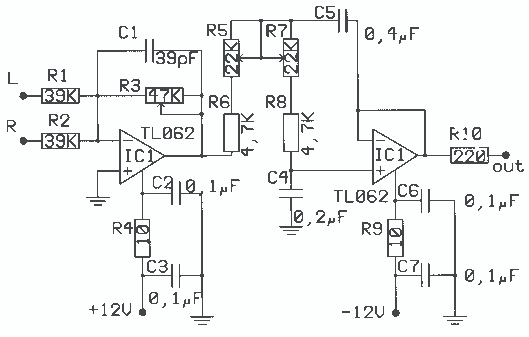
The application that we propose is a simple filter of region that limits the acoustic region (20-20000Hz) in the region 20-100Hz. With the manufacture that we propose, you can make an active filter in order to drive a loudspeaker of very low frequencies. With this, you will place a bigger speaker between the HIFI speakers. In order to have a complete picture of sound, you will need also the corresponding amplifier. In the entry of the circuit, you will connect the two outputs of the preamplifier or the output of line of some preamplifier. More: The acoustic spectrum is extended by very low frequencies 20Hz and reaches up to 20000Hz in high frequencies. In the low frequencies, the sense of direction is degraded. This reason leads us to the utilization of a speaker for the attribution of very low frequencies.
The proposed circuit design involves an active low-pass filter that operates within the frequency range of 20 Hz to 100 Hz, effectively allowing the passage of low-frequency audio signals while attenuating higher frequencies. This filter can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps), capacitors, and resistors configured in a standard second-order low-pass filter topology.
The circuit will begin with a preamplifier stage, which accepts the audio input signal from a source such as a line output from a preamplifier or directly from a music player. The output of this preamplifier will be connected to the input of the active filter circuit. The filter itself will consist of an op-amp configured in a non-inverting configuration, with feedback and input capacitors that set the cutoff frequency at 100 Hz.
To achieve the desired frequency response, the values of the resistors (R1, R2) and capacitors (C1, C2) must be carefully selected according to the formula for the cutoff frequency, which is given by:
\[ f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where \( f_c \) is the cutoff frequency, \( R \) is the resistance, and \( C \) is the capacitance. For the proposed design, the components should be chosen to ensure that frequencies below 100 Hz are allowed to pass while attenuating those above this threshold.
The output of the filter will be connected to a larger subwoofer speaker, which is capable of reproducing low frequencies effectively. An additional amplifier stage may be necessary to drive the subwoofer adequately, depending on the power requirements and impedance characteristics of the loudspeaker used.
In conclusion, this circuit design will enhance the overall acoustic experience by providing a dedicated channel for low-frequency sounds, thereby improving the sound quality and depth of the audio playback system. This configuration allows for a more comprehensive auditory experience, particularly in music genres that emphasize bass frequencies.The application that to you we propose is a simple filter of region that limits the acoustic region (20-20000Hz) in the region 20-100Hz. With the manufacture that to you we propose you can make a active filter in order to you lead a loudspeaker of very low frequencies.
With this you will place one bigger speaker between the HIFI speakers of you. In order to you have a complete picture of sound you will need also the corresponding amplifier. In the entry of circuit you will connect the two exits of preamplifier or the exit of line of some preamplifier. The acoustic spectrum is extended by very low frequencies 20Iz and reaches as the 20000Iz in high frequencies. In the low frequencies is degraded the sense of direction. This reason us leads to the utilization speaker for the attribution of very low freq 🔗 External reference
The proposed circuit design involves an active low-pass filter that operates within the frequency range of 20 Hz to 100 Hz, effectively allowing the passage of low-frequency audio signals while attenuating higher frequencies. This filter can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps), capacitors, and resistors configured in a standard second-order low-pass filter topology.
The circuit will begin with a preamplifier stage, which accepts the audio input signal from a source such as a line output from a preamplifier or directly from a music player. The output of this preamplifier will be connected to the input of the active filter circuit. The filter itself will consist of an op-amp configured in a non-inverting configuration, with feedback and input capacitors that set the cutoff frequency at 100 Hz.
To achieve the desired frequency response, the values of the resistors (R1, R2) and capacitors (C1, C2) must be carefully selected according to the formula for the cutoff frequency, which is given by:
\[ f_c = \frac{1}{2\pi R C} \]
where \( f_c \) is the cutoff frequency, \( R \) is the resistance, and \( C \) is the capacitance. For the proposed design, the components should be chosen to ensure that frequencies below 100 Hz are allowed to pass while attenuating those above this threshold.
The output of the filter will be connected to a larger subwoofer speaker, which is capable of reproducing low frequencies effectively. An additional amplifier stage may be necessary to drive the subwoofer adequately, depending on the power requirements and impedance characteristics of the loudspeaker used.
In conclusion, this circuit design will enhance the overall acoustic experience by providing a dedicated channel for low-frequency sounds, thereby improving the sound quality and depth of the audio playback system. This configuration allows for a more comprehensive auditory experience, particularly in music genres that emphasize bass frequencies.The application that to you we propose is a simple filter of region that limits the acoustic region (20-20000Hz) in the region 20-100Hz. With the manufacture that to you we propose you can make a active filter in order to you lead a loudspeaker of very low frequencies.
With this you will place one bigger speaker between the HIFI speakers of you. In order to you have a complete picture of sound you will need also the corresponding amplifier. In the entry of circuit you will connect the two exits of preamplifier or the exit of line of some preamplifier. The acoustic spectrum is extended by very low frequencies 20Iz and reaches as the 20000Iz in high frequencies. In the low frequencies is degraded the sense of direction. This reason us leads to the utilization speaker for the attribution of very low freq 🔗 External reference