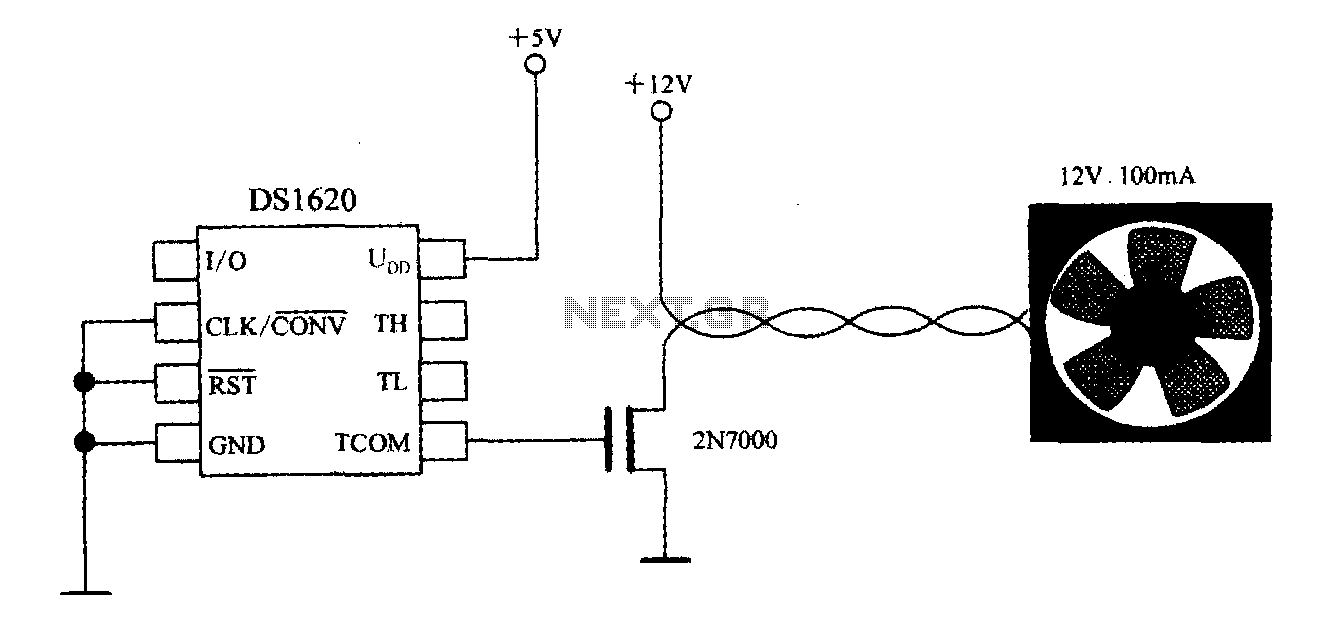
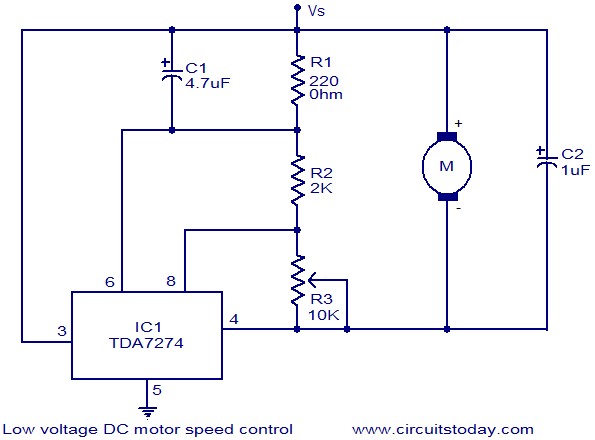
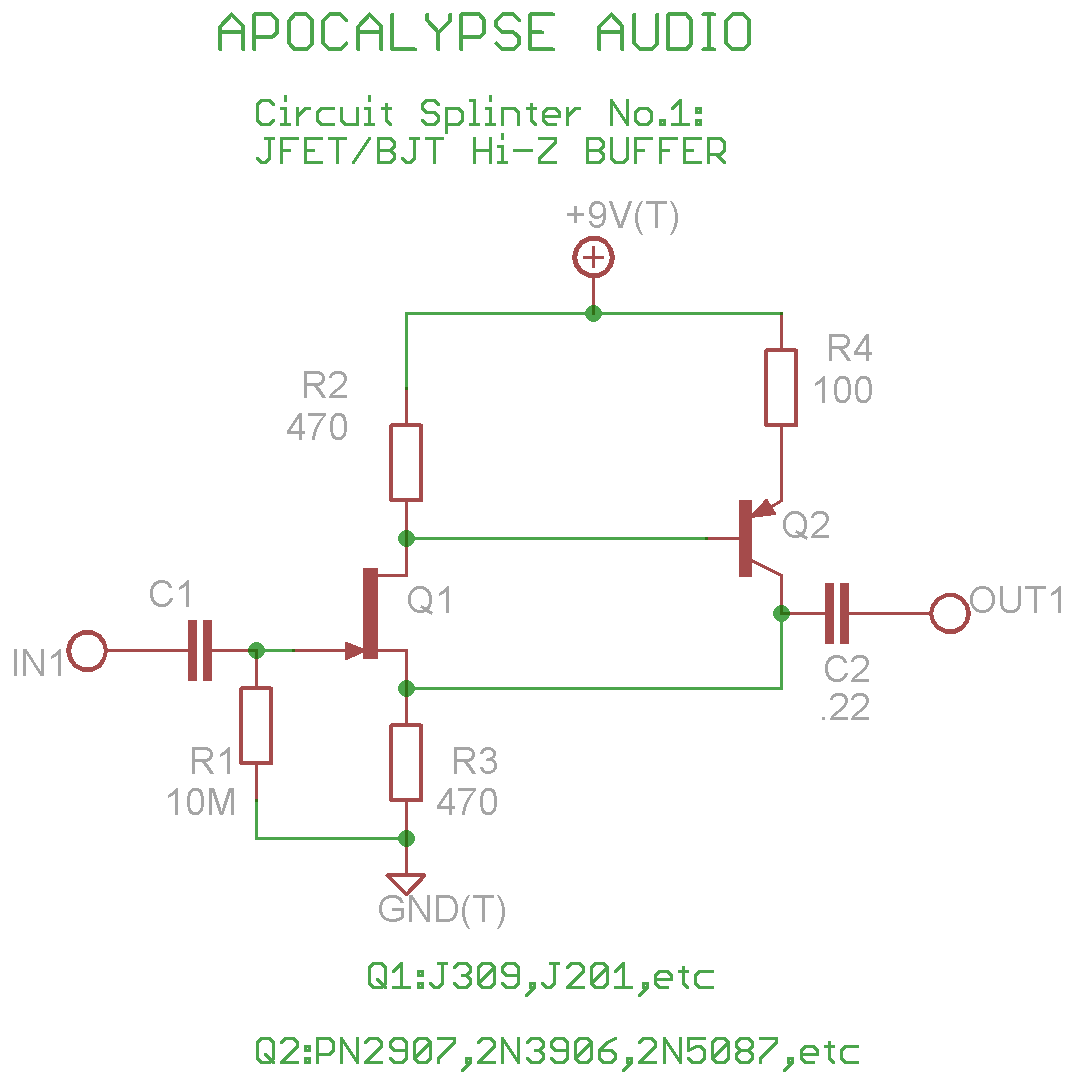
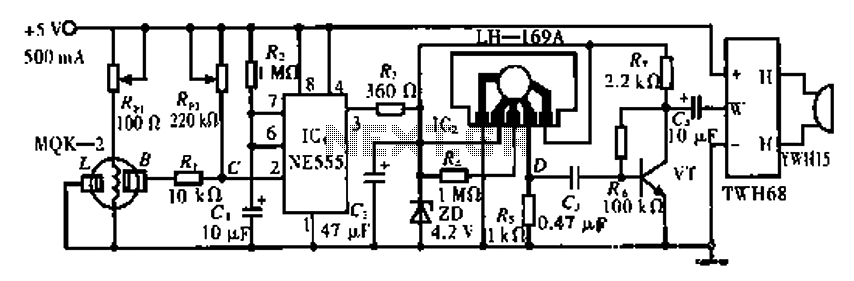
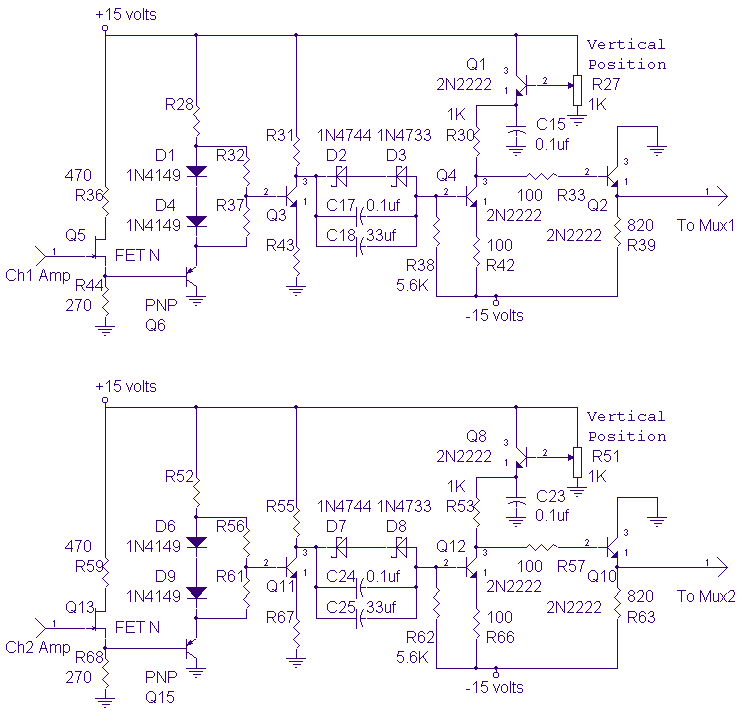
tda7384 class ab audio power amplifier circuit design electronic project
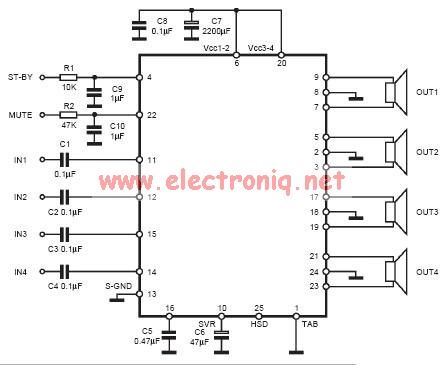
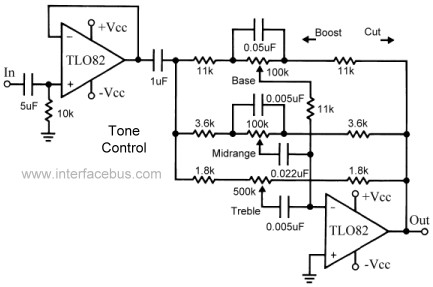
The input capacitor is used for low-frequency cut-off, with a standard value of 0.1 µF, resulting in a cut-off frequency of approximately 16 Hz.
The input capacitor plays a crucial role in filtering unwanted low-frequency signals in electronic circuits. By selecting a capacitance of 0.1 µF, the circuit is designed to attenuate frequencies below 16 Hz, effectively blocking DC components and allowing only AC signals above this threshold to pass through. This is particularly important in audio applications, where low-frequency noise can interfere with signal integrity.
The cut-off frequency (fc) can be calculated using the formula:
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads. In scenarios where the resistance value (R) is known, the selection of a 0.1 µF capacitor will ensure that the circuit operates effectively above the specified cut-off frequency.
In practical applications, the input capacitor is typically connected in series with the signal path. This configuration allows the capacitor to block any DC offset present in the input signal while permitting the desired AC signal to reach subsequent stages of the circuit, such as amplifiers or filters.
It is also essential to consider the voltage rating of the capacitor to ensure it can withstand the applied voltage without failure. Additionally, the choice of capacitor type, whether ceramic, electrolytic, or film, can influence the performance characteristics, including frequency response and equivalent series resistance (ESR).
Overall, the input capacitor is a critical component in achieving desired frequency response and signal integrity in various electronic applications.The input capacitor is for the low frequency cut-off and the standard value for the input capacitors is 0. 1uF ( the cut-off for this value is amount to 16Hz). 🔗 External reference
The input capacitor plays a crucial role in filtering unwanted low-frequency signals in electronic circuits. By selecting a capacitance of 0.1 µF, the circuit is designed to attenuate frequencies below 16 Hz, effectively blocking DC components and allowing only AC signals above this threshold to pass through. This is particularly important in audio applications, where low-frequency noise can interfere with signal integrity.
The cut-off frequency (fc) can be calculated using the formula:
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
where R is the resistance in ohms and C is the capacitance in farads. In scenarios where the resistance value (R) is known, the selection of a 0.1 µF capacitor will ensure that the circuit operates effectively above the specified cut-off frequency.
In practical applications, the input capacitor is typically connected in series with the signal path. This configuration allows the capacitor to block any DC offset present in the input signal while permitting the desired AC signal to reach subsequent stages of the circuit, such as amplifiers or filters.
It is also essential to consider the voltage rating of the capacitor to ensure it can withstand the applied voltage without failure. Additionally, the choice of capacitor type, whether ceramic, electrolytic, or film, can influence the performance characteristics, including frequency response and equivalent series resistance (ESR).
Overall, the input capacitor is a critical component in achieving desired frequency response and signal integrity in various electronic applications.The input capacitor is for the low frequency cut-off and the standard value for the input capacitors is 0. 1uF ( the cut-off for this value is amount to 16Hz). 🔗 External reference