TDA8932B/33(B) Class D Audio Amplifier in Symmetric Supply Single Ended Configuration
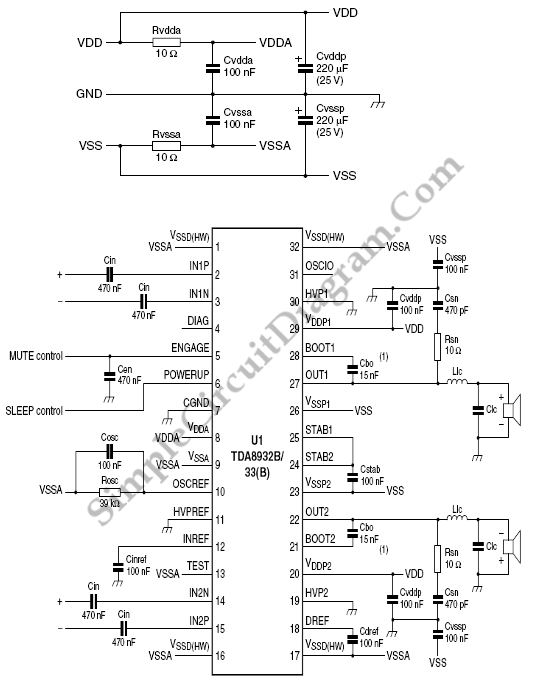
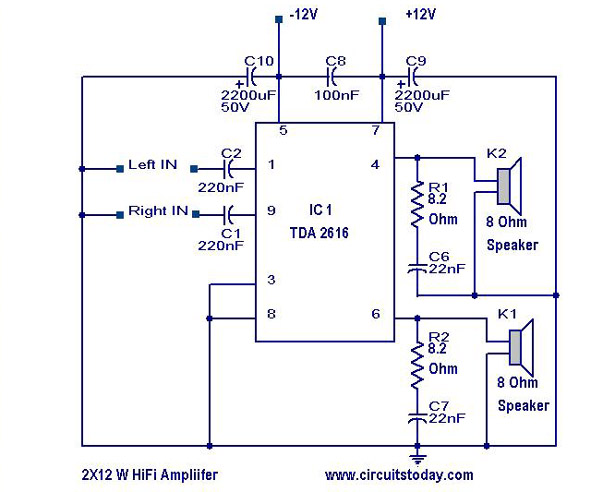
The TDA8932B/33(B) can operate with a symmetrical power supply. In this configuration, three half supply voltage buffers are disabled when powered from a symmetrical source.
The TDA8932B/33(B) is a high-efficiency Class D audio amplifier designed for various audio applications. Operating the amplifier from a symmetrical power supply allows for improved performance by minimizing the distortion and enhancing the audio quality. In this configuration, the amplifier can effectively utilize the positive and negative supply voltages, which can lead to a more balanced output signal.
The diagram referenced indicates that three half supply voltage buffers are disabled. This design choice may be relevant in scenarios where the application does not require the additional buffering, thus allowing for a more straightforward circuit layout and potentially reducing power consumption. The disabling of these buffers can also help in simplifying the design, minimizing component count, and enhancing reliability.
In a typical symmetrical power supply setup, the positive voltage rail and negative voltage rail are equal in magnitude but opposite in polarity. This arrangement allows the amplifier to drive the output signal both above and below ground level, which is essential for producing a full-range audio output without clipping.
Furthermore, when designing the accompanying circuitry, it is crucial to ensure that the power supply is adequately decoupled to avoid noise and maintain signal integrity. Capacitors should be placed near the power pins of the amplifier to filter out high-frequency noise and provide a stable voltage supply during dynamic audio signals.
In summary, utilizing the TDA8932B/33(B) with a symmetrical power supply configuration enhances its operational efficiency while allowing for flexible design choices that can be tailored to specific audio applications.We can also operate TDA8932B/33(B) from a symmetrical supply. On this diagram, three half supply voltage buffers are disabled. When supplied from a symmetrical.. 🔗 External reference
The TDA8932B/33(B) is a high-efficiency Class D audio amplifier designed for various audio applications. Operating the amplifier from a symmetrical power supply allows for improved performance by minimizing the distortion and enhancing the audio quality. In this configuration, the amplifier can effectively utilize the positive and negative supply voltages, which can lead to a more balanced output signal.
The diagram referenced indicates that three half supply voltage buffers are disabled. This design choice may be relevant in scenarios where the application does not require the additional buffering, thus allowing for a more straightforward circuit layout and potentially reducing power consumption. The disabling of these buffers can also help in simplifying the design, minimizing component count, and enhancing reliability.
In a typical symmetrical power supply setup, the positive voltage rail and negative voltage rail are equal in magnitude but opposite in polarity. This arrangement allows the amplifier to drive the output signal both above and below ground level, which is essential for producing a full-range audio output without clipping.
Furthermore, when designing the accompanying circuitry, it is crucial to ensure that the power supply is adequately decoupled to avoid noise and maintain signal integrity. Capacitors should be placed near the power pins of the amplifier to filter out high-frequency noise and provide a stable voltage supply during dynamic audio signals.
In summary, utilizing the TDA8932B/33(B) with a symmetrical power supply configuration enhances its operational efficiency while allowing for flexible design choices that can be tailored to specific audio applications.We can also operate TDA8932B/33(B) from a symmetrical supply. On this diagram, three half supply voltage buffers are disabled. When supplied from a symmetrical.. 🔗 External reference