Testatika Free energy
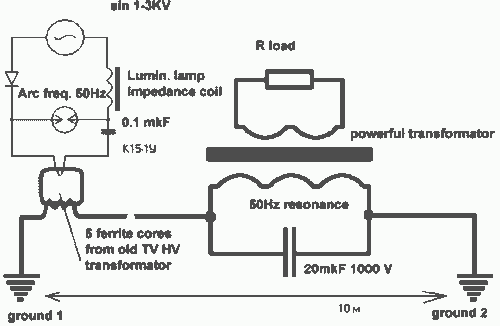
The Testatika design, based on the Pidgeon/Wimshurst machine, represents one type of electrostatic generator that can be used to construct this system. Since the early 1900s, such power generators have significantly evolved in terms of sophistication and power output. Recently developed machines can produce up to 300,000 volts, which can then be transformed and utilized.
The Testatika machine is an electrostatic generator that operates on the principles of electrostatic induction and charge separation. It employs a combination of rotating disks and brushes to create high-voltage electricity. The Pidgeon/Wimshurst machine, a predecessor to the Testatika, utilizes two counter-rotating disks to generate static electricity through friction and induction. As the disks rotate, they accumulate electric charge, which is collected by metal brushes that transfer the charge to Leyden jars or capacitors for storage.
The recent advancements in electrostatic generators have led to the development of machines capable of producing voltage levels reaching 300,000 volts. This high voltage can be transformed using transformers and rectifiers to produce usable electrical power. The output from these generators can be utilized for various applications, including powering electronic devices, charging batteries, or even providing energy for small-scale electrical systems.
The design of electrostatic generators like the Testatika emphasizes efficiency and reliability. Key components include the rotating disks, which must be made from materials with high dielectric properties to maximize charge accumulation, and the brushes, which should be designed to minimize arcing and energy loss. Additionally, the use of capacitors allows for the stabilization of the output voltage, making it suitable for practical applications.
Overall, the evolution of electrostatic generators reflects advancements in materials science and engineering, enabling the creation of sophisticated machines that harness static electricity for practical use.The Testatika design based on the Pidgeon/Wimshurst machine is of course only one type of electrostatic generator to build this system around. Since the early 1900s such power generators have come a long way in sophistication - and in power output - recently developed machines output 300,000 volts which can then be transformed and utilized..
🔗 External reference
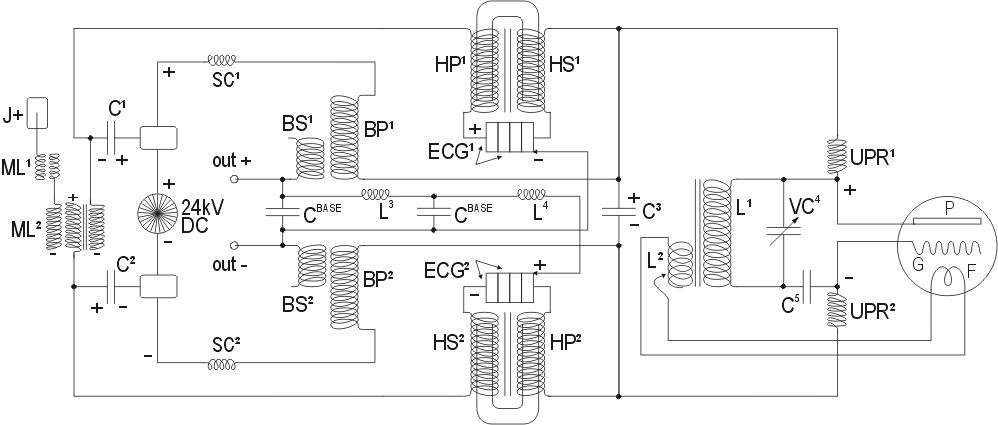
The Testatika machine is an electrostatic generator that operates on the principles of electrostatic induction and charge separation. It employs a combination of rotating disks and brushes to create high-voltage electricity. The Pidgeon/Wimshurst machine, a predecessor to the Testatika, utilizes two counter-rotating disks to generate static electricity through friction and induction. As the disks rotate, they accumulate electric charge, which is collected by metal brushes that transfer the charge to Leyden jars or capacitors for storage.
The recent advancements in electrostatic generators have led to the development of machines capable of producing voltage levels reaching 300,000 volts. This high voltage can be transformed using transformers and rectifiers to produce usable electrical power. The output from these generators can be utilized for various applications, including powering electronic devices, charging batteries, or even providing energy for small-scale electrical systems.
The design of electrostatic generators like the Testatika emphasizes efficiency and reliability. Key components include the rotating disks, which must be made from materials with high dielectric properties to maximize charge accumulation, and the brushes, which should be designed to minimize arcing and energy loss. Additionally, the use of capacitors allows for the stabilization of the output voltage, making it suitable for practical applications.
Overall, the evolution of electrostatic generators reflects advancements in materials science and engineering, enabling the creation of sophisticated machines that harness static electricity for practical use.The Testatika design based on the Pidgeon/Wimshurst machine is of course only one type of electrostatic generator to build this system around. Since the early 1900s such power generators have come a long way in sophistication - and in power output - recently developed machines output 300,000 volts which can then be transformed and utilized..
🔗 External reference