The Active Low Pass Filter
Electronics tutorial about active low pass filters, including low pass filter frequency response, op-amp voltage gain, and active filter construction.
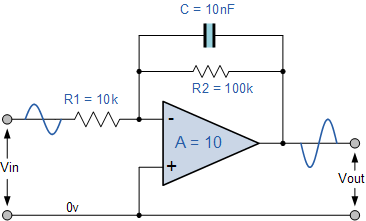
An active low pass filter (ALPF) is an essential component in electronics, designed to allow low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating high-frequency signals. The primary elements of an ALPF typically include operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and capacitors. The frequency response of a low pass filter is characterized by its cutoff frequency, which defines the point at which the output signal begins to decline in amplitude.
The cutoff frequency (fc) can be calculated using the formula:
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance in the circuit. The op-amp in the filter configuration provides gain, allowing the filter to not only pass the desired frequency range but also amplify the signal. The voltage gain (Av) of the op-amp can be determined by the feedback network, typically comprising resistors that set the gain level.
Construction of an active low pass filter involves connecting these components in a specific configuration. A common design includes a non-inverting op-amp configuration, where the input signal is fed into the non-inverting terminal, and the feedback loop includes a resistor and capacitor to establish the desired frequency response.
The output of the filter will exhibit a gradual decrease in amplitude beyond the cutoff frequency, typically following a slope of -20 dB/decade. This behavior is critical in applications such as audio processing, where unwanted high-frequency noise must be minimized to preserve the integrity of the audio signal.
Overall, the active low pass filter is a versatile tool in signal processing, offering both frequency selection and amplification capabilities, making it a fundamental element in various electronic circuit designs.Electronics Tutorial about Active Low Pass Filter including Low Pass Filter Frequency Response, Op-amp Voltage Gain and Active Filter Construction.. 🔗 External reference
An active low pass filter (ALPF) is an essential component in electronics, designed to allow low-frequency signals to pass while attenuating high-frequency signals. The primary elements of an ALPF typically include operational amplifiers (op-amps), resistors, and capacitors. The frequency response of a low pass filter is characterized by its cutoff frequency, which defines the point at which the output signal begins to decline in amplitude.
The cutoff frequency (fc) can be calculated using the formula:
fc = 1 / (2πRC)
where R is the resistance and C is the capacitance in the circuit. The op-amp in the filter configuration provides gain, allowing the filter to not only pass the desired frequency range but also amplify the signal. The voltage gain (Av) of the op-amp can be determined by the feedback network, typically comprising resistors that set the gain level.
Construction of an active low pass filter involves connecting these components in a specific configuration. A common design includes a non-inverting op-amp configuration, where the input signal is fed into the non-inverting terminal, and the feedback loop includes a resistor and capacitor to establish the desired frequency response.
The output of the filter will exhibit a gradual decrease in amplitude beyond the cutoff frequency, typically following a slope of -20 dB/decade. This behavior is critical in applications such as audio processing, where unwanted high-frequency noise must be minimized to preserve the integrity of the audio signal.
Overall, the active low pass filter is a versatile tool in signal processing, offering both frequency selection and amplification capabilities, making it a fundamental element in various electronic circuit designs.Electronics Tutorial about Active Low Pass Filter including Low Pass Filter Frequency Response, Op-amp Voltage Gain and Active Filter Construction.. 🔗 External reference