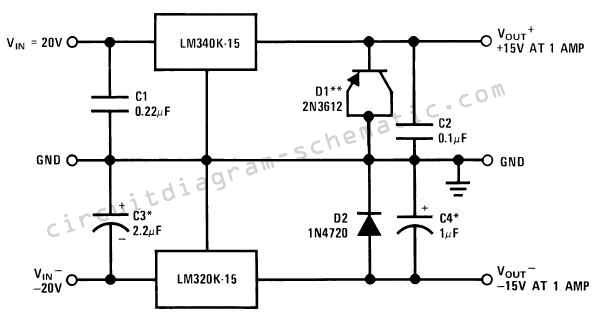
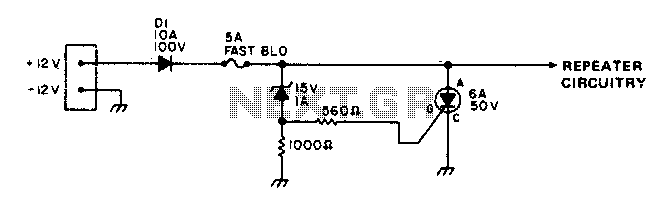
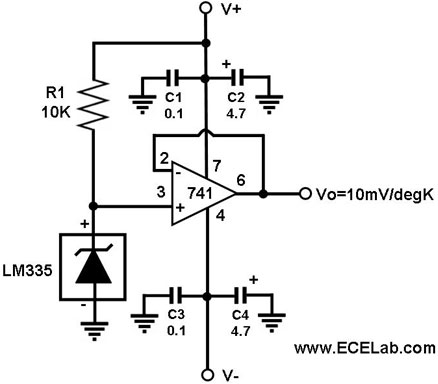
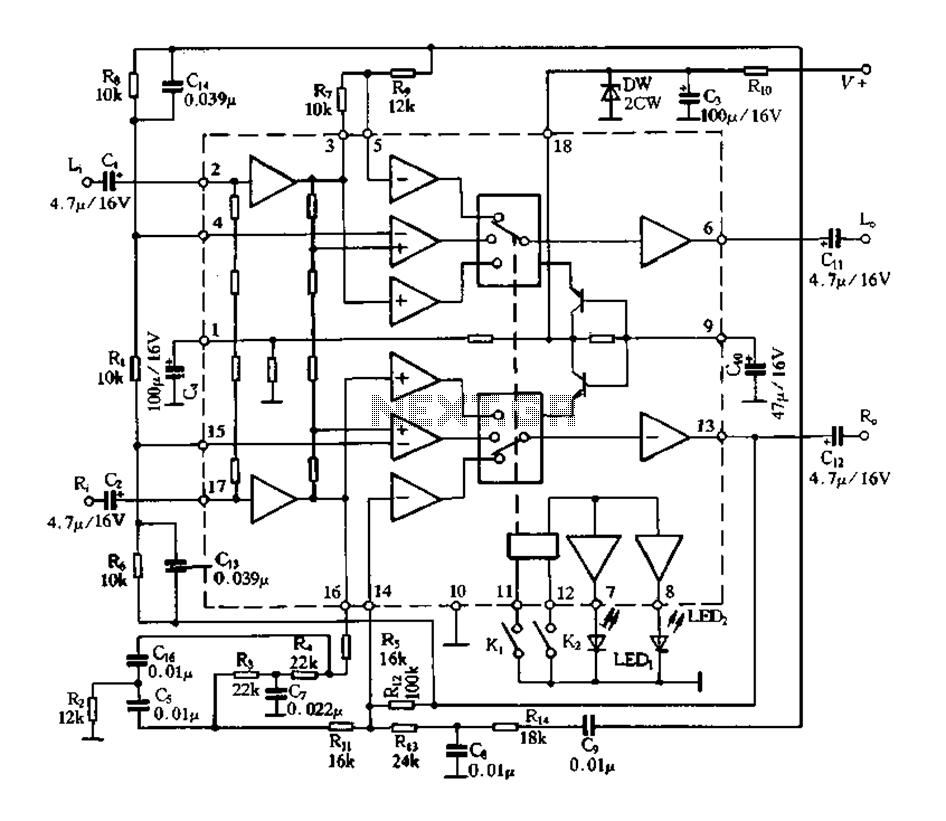
The PC CPU overheating language caution circuit diagram
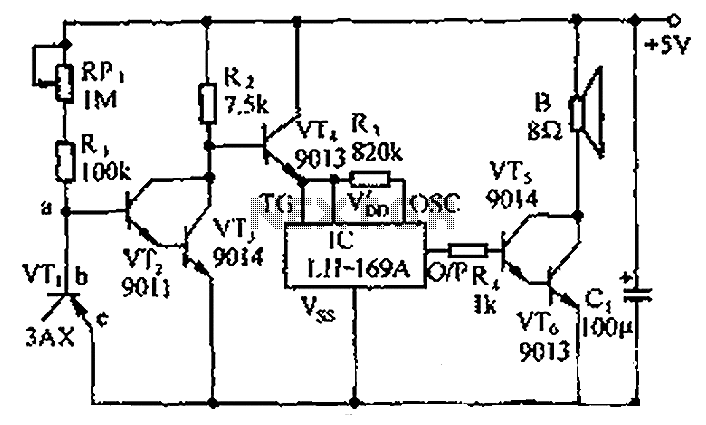
The circuit consists of a temperature sensor, electronic switches for temperature control, and a vocal language output system. During hot summer months, the central processing unit (CPU) of PCs frequently experiences overheating. The circuit, with VT1 positioned near the CPU chip radiator, will issue a temperature caution alert when the CPU overheats, notifying personnel to take necessary cooling measures.
The described circuit is designed to monitor the temperature of a CPU and provide alerts when overheating occurs. It incorporates a temperature sensor that continuously measures the CPU's temperature. The sensor's output is connected to a control circuit that includes electronic switches, which can activate cooling mechanisms, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, when the temperature exceeds a predefined threshold.
The vocal language output system is integrated into the circuit to provide audible alerts. This system can be configured to deliver pre-recorded messages or synthesized speech, ensuring that personnel are promptly informed of the overheating condition. The circuit utilizes VT1, which serves as a critical component in detecting the temperature and triggering the alert mechanism.
In operation, when the CPU temperature rises above the safe operating limit, the temperature sensor sends a signal to the control circuit. This signal activates VT1, which can engage the electronic switches responsible for turning on cooling devices. Simultaneously, the vocal output system generates a warning message, effectively communicating the need for immediate action to prevent potential damage to the CPU.
To enhance the reliability of the circuit, it may include additional features such as a delay timer to prevent false alarms due to momentary temperature spikes and a reset mechanism to silence the alert once corrective actions have been taken. Overall, this circuit plays a vital role in maintaining CPU health and ensuring the longevity of computing systems in high-temperature environments. Circuit is shown. It consists of a temperature sensor, temperature control of electronic switches and circuits composed vocal language. In the hot summer season, PCs central pr ocessing unit CPU often overheating, the circuit VT1 die close to the CPU chip radiator, once the CPU overheating, the circuit will issue a Notice that temperature caution statement, alert personnel to take measures to cool down.
The described circuit is designed to monitor the temperature of a CPU and provide alerts when overheating occurs. It incorporates a temperature sensor that continuously measures the CPU's temperature. The sensor's output is connected to a control circuit that includes electronic switches, which can activate cooling mechanisms, such as fans or liquid cooling systems, when the temperature exceeds a predefined threshold.
The vocal language output system is integrated into the circuit to provide audible alerts. This system can be configured to deliver pre-recorded messages or synthesized speech, ensuring that personnel are promptly informed of the overheating condition. The circuit utilizes VT1, which serves as a critical component in detecting the temperature and triggering the alert mechanism.
In operation, when the CPU temperature rises above the safe operating limit, the temperature sensor sends a signal to the control circuit. This signal activates VT1, which can engage the electronic switches responsible for turning on cooling devices. Simultaneously, the vocal output system generates a warning message, effectively communicating the need for immediate action to prevent potential damage to the CPU.
To enhance the reliability of the circuit, it may include additional features such as a delay timer to prevent false alarms due to momentary temperature spikes and a reset mechanism to silence the alert once corrective actions have been taken. Overall, this circuit plays a vital role in maintaining CPU health and ensuring the longevity of computing systems in high-temperature environments. Circuit is shown. It consists of a temperature sensor, temperature control of electronic switches and circuits composed vocal language. In the hot summer season, PCs central pr ocessing unit CPU often overheating, the circuit VT1 die close to the CPU chip radiator, once the CPU overheating, the circuit will issue a Notice that temperature caution statement, alert personnel to take measures to cool down.