Thermistors As Accurate Temperature Sensors Part 1: Introduction and Methods
This two-part article explains the utilization of a simple voltage divider circuit incorporating a thermistor to obtain high-accuracy temperature readings across a wide range of measurements. The first part focuses on the circuit design and explores various methods for temperature estimation.
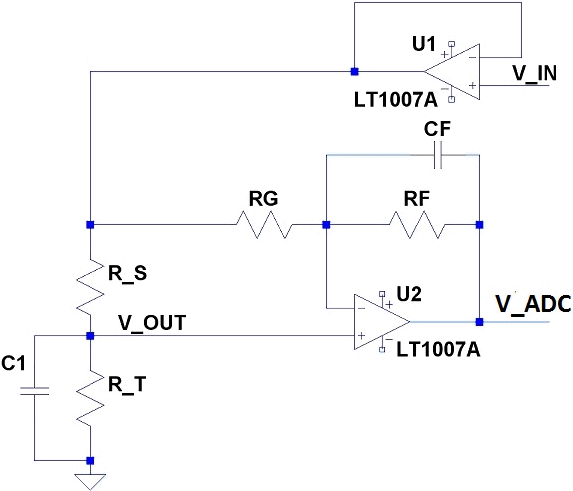
The voltage divider circuit is a fundamental electronic configuration that allows for the measurement of voltage levels in relation to a reference voltage. In this application, the thermistor, a temperature-sensitive resistor, is used to provide a variable resistance that changes with temperature fluctuations. The circuit typically consists of two resistors arranged in series, with the thermistor acting as one of these resistors.
When a voltage is applied across the series combination, the output voltage can be taken from the junction between the two resistors. This output voltage varies as the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature, allowing for the calculation of the temperature based on the output voltage. The accuracy of the temperature readings can be enhanced by employing calibration techniques and compensating for non-linear characteristics of the thermistor.
Various temperature estimation methods can be implemented with this setup, including linear approximation, polynomial fitting, and look-up tables, which can improve the precision of the readings over the desired temperature range. The implementation of filtering techniques may also be beneficial to minimize noise and improve the stability of the measurements.
In summary, the combination of a voltage divider circuit and a thermistor provides an effective means for achieving accurate temperature measurements, making it suitable for a variety of applications in electronics and environmental monitoring.This two-part article describes how to use a simple voltage divider circuit with a thermistor to achieve high-accuracy temperature readings over broad measurement ranges. Part one discusses the circuit and various temperature estimation methods.. 🔗 External reference
The voltage divider circuit is a fundamental electronic configuration that allows for the measurement of voltage levels in relation to a reference voltage. In this application, the thermistor, a temperature-sensitive resistor, is used to provide a variable resistance that changes with temperature fluctuations. The circuit typically consists of two resistors arranged in series, with the thermistor acting as one of these resistors.
When a voltage is applied across the series combination, the output voltage can be taken from the junction between the two resistors. This output voltage varies as the resistance of the thermistor changes with temperature, allowing for the calculation of the temperature based on the output voltage. The accuracy of the temperature readings can be enhanced by employing calibration techniques and compensating for non-linear characteristics of the thermistor.
Various temperature estimation methods can be implemented with this setup, including linear approximation, polynomial fitting, and look-up tables, which can improve the precision of the readings over the desired temperature range. The implementation of filtering techniques may also be beneficial to minimize noise and improve the stability of the measurements.
In summary, the combination of a voltage divider circuit and a thermistor provides an effective means for achieving accurate temperature measurements, making it suitable for a variety of applications in electronics and environmental monitoring.This two-part article describes how to use a simple voltage divider circuit with a thermistor to achieve high-accuracy temperature readings over broad measurement ranges. Part one discusses the circuit and various temperature estimation methods.. 🔗 External reference