Thyristor overcurrent protection circuit 2
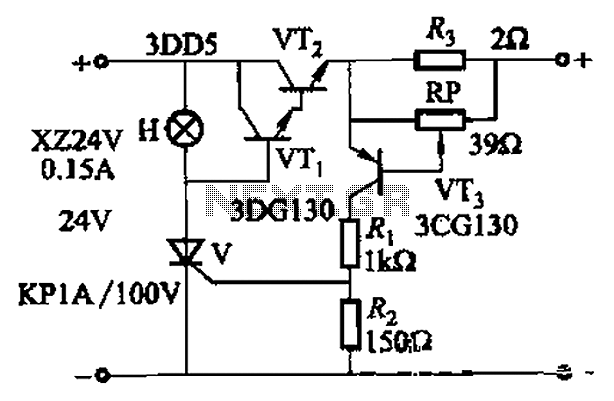
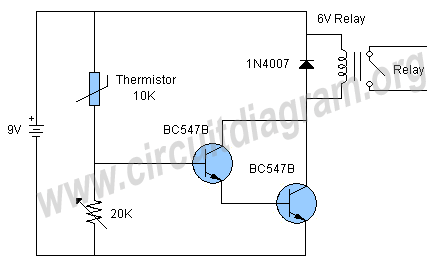
By adjusting Ro or RP, the current setpoint can be modified. The circuit illustrated in Figure 14-98 features overcurrent protection using a thyristor and transistors VTi and VT2, which immediately cut off the power when an overcurrent condition is detected, indicated by the illumination of indicator H. The adjustment potentiometer RP allows for the alteration of the current setpoint.
This circuit utilizes a thyristor for overcurrent protection, which is a crucial component in safeguarding electronic systems from damage due to excessive current. The thyristor operates by remaining in a conducting state until the current flowing through it falls below a certain threshold. In this configuration, transistors VTi and VT2 are employed to monitor the current level. When the current exceeds the predefined setpoint, the circuit triggers the thyristor to turn off, effectively disconnecting the load and preventing potential damage.
The inclusion of an adjustment potentiometer (RP) provides flexibility in setting the desired current threshold. This allows for customization based on the specific requirements of the application. The adjustment can be made by rotating the potentiometer, which modifies the resistance in the circuit, thus changing the voltage at the trigger input of the thyristor.
The indicator H serves as a visual alert, illuminating when an overcurrent condition has been detected. This feature is essential for operators to quickly identify issues within the system and take necessary actions to mitigate risks.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes rapid response to overcurrent situations, ensuring that the electronic system remains protected while allowing for user-defined current settings through the adjustable potentiometer. The integration of these elements makes the circuit a reliable solution for managing current levels in various electronic applications.Adjusting Ro or RP, you can change over the current setpoint. Circuit shown in Figure 14-98. Overcurrent, V conduction thyristor, transistor VTi, VT2 off immediately cut off th e power play fast protection, the indicator H lights. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change over the current setpoint.
This circuit utilizes a thyristor for overcurrent protection, which is a crucial component in safeguarding electronic systems from damage due to excessive current. The thyristor operates by remaining in a conducting state until the current flowing through it falls below a certain threshold. In this configuration, transistors VTi and VT2 are employed to monitor the current level. When the current exceeds the predefined setpoint, the circuit triggers the thyristor to turn off, effectively disconnecting the load and preventing potential damage.
The inclusion of an adjustment potentiometer (RP) provides flexibility in setting the desired current threshold. This allows for customization based on the specific requirements of the application. The adjustment can be made by rotating the potentiometer, which modifies the resistance in the circuit, thus changing the voltage at the trigger input of the thyristor.
The indicator H serves as a visual alert, illuminating when an overcurrent condition has been detected. This feature is essential for operators to quickly identify issues within the system and take necessary actions to mitigate risks.
Overall, the circuit design emphasizes rapid response to overcurrent situations, ensuring that the electronic system remains protected while allowing for user-defined current settings through the adjustable potentiometer. The integration of these elements makes the circuit a reliable solution for managing current levels in various electronic applications.Adjusting Ro or RP, you can change over the current setpoint. Circuit shown in Figure 14-98. Overcurrent, V conduction thyristor, transistor VTi, VT2 off immediately cut off th e power play fast protection, the indicator H lights. Adjustment potentiometer RP, can change over the current setpoint.