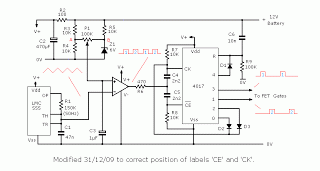
Tilt Sensor Alarm Circuit
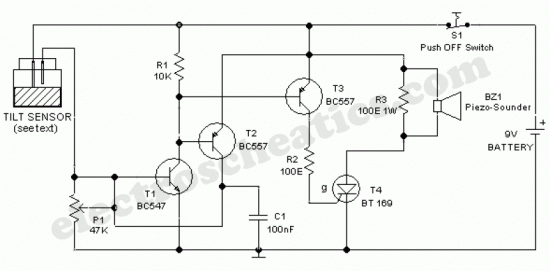
An ultra-simple circuit of the tilt sensor alarm can be fabricated using readily available, inexpensive components. The circuit operates as a true transistor-based design.
The tilt sensor alarm circuit utilizes a tilt sensor, which is a device that detects the orientation of an object. When the object tilts beyond a certain angle, the sensor triggers the alarm circuit. The primary components of this circuit include a tilt sensor, a transistor, a resistor, and a power supply.
The tilt sensor typically consists of a conductive ball within a sealed enclosure that connects two conductive contacts. When the sensor tilts, the ball rolls and completes the circuit, allowing current to flow. This current is directed to the base of the transistor, which acts as a switch.
When the transistor is activated, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which can be used to drive an alarm or indicator, such as a buzzer or LED. The resistor is used to limit the current flowing into the base of the transistor, ensuring it operates within safe parameters.
The power supply for the circuit can be a standard battery, ensuring portability and ease of use. The circuit can be assembled on a breadboard for prototyping or soldered onto a printed circuit board (PCB) for a more permanent solution.
This simple tilt sensor alarm circuit is ideal for applications such as security systems, where it can alert users to unauthorized movement or tampering of objects. Its low cost and ease of assembly make it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike.Ultra simple circuit of the tilt sensor alarm presented here can be fabricated using readily available inexpensive components. The circuit is a true transi. 🔗 External reference
The tilt sensor alarm circuit utilizes a tilt sensor, which is a device that detects the orientation of an object. When the object tilts beyond a certain angle, the sensor triggers the alarm circuit. The primary components of this circuit include a tilt sensor, a transistor, a resistor, and a power supply.
The tilt sensor typically consists of a conductive ball within a sealed enclosure that connects two conductive contacts. When the sensor tilts, the ball rolls and completes the circuit, allowing current to flow. This current is directed to the base of the transistor, which acts as a switch.
When the transistor is activated, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, which can be used to drive an alarm or indicator, such as a buzzer or LED. The resistor is used to limit the current flowing into the base of the transistor, ensuring it operates within safe parameters.
The power supply for the circuit can be a standard battery, ensuring portability and ease of use. The circuit can be assembled on a breadboard for prototyping or soldered onto a printed circuit board (PCB) for a more permanent solution.
This simple tilt sensor alarm circuit is ideal for applications such as security systems, where it can alert users to unauthorized movement or tampering of objects. Its low cost and ease of assembly make it accessible for hobbyists and professionals alike.Ultra simple circuit of the tilt sensor alarm presented here can be fabricated using readily available inexpensive components. The circuit is a true transi. 🔗 External reference