TMP01 Celsius Scale Temperature Sensor
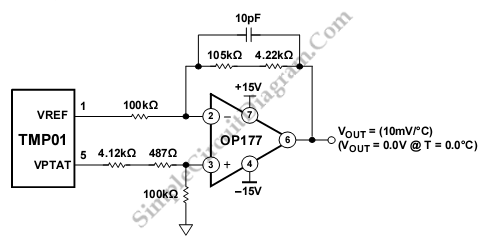
The schematic diagram described here is a TMP01 Celsius Scale Temperature Sensor circuit. This circuit is used to convert the VPTAT output voltage that is...
The TMP01 is a precision temperature sensor that outputs a voltage proportional to temperature. It operates on the principle of measuring the voltage across a temperature-sensitive resistor, which varies with temperature changes. The TMP01 provides a linear output voltage that can be easily interpreted by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or used directly in voltage-based applications.
In the schematic, the TMP01 is typically powered by a stable DC supply, often within the range of 2.7V to 5.5V. The output of the TMP01 is a voltage that corresponds linearly to the temperature in degrees Celsius, with a scale factor of 20 mV/°C. This means that at 0°C, the output voltage is 0V, and it increases by 20 mV for each degree Celsius increase in temperature.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors for biasing, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly an operational amplifier to enhance the output signal if needed. The output voltage can be connected to a microcontroller or a display device for real-time temperature monitoring.
In applications where precise temperature measurement is critical, the TMP01 can be integrated into systems for HVAC control, environmental monitoring, or industrial process control, ensuring accurate temperature readings for effective system management. The design should account for proper layout techniques to minimize noise and ensure signal integrity, particularly when interfacing with sensitive analog components.The schematic diagram described here is a TMP01 Celsius Scale Temperature Sensor circuit. This circuit is used to convert the VPTAT output voltage that is.. 🔗 External reference
The TMP01 is a precision temperature sensor that outputs a voltage proportional to temperature. It operates on the principle of measuring the voltage across a temperature-sensitive resistor, which varies with temperature changes. The TMP01 provides a linear output voltage that can be easily interpreted by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or used directly in voltage-based applications.
In the schematic, the TMP01 is typically powered by a stable DC supply, often within the range of 2.7V to 5.5V. The output of the TMP01 is a voltage that corresponds linearly to the temperature in degrees Celsius, with a scale factor of 20 mV/°C. This means that at 0°C, the output voltage is 0V, and it increases by 20 mV for each degree Celsius increase in temperature.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors for biasing, capacitors for filtering noise, and possibly an operational amplifier to enhance the output signal if needed. The output voltage can be connected to a microcontroller or a display device for real-time temperature monitoring.
In applications where precise temperature measurement is critical, the TMP01 can be integrated into systems for HVAC control, environmental monitoring, or industrial process control, ensuring accurate temperature readings for effective system management. The design should account for proper layout techniques to minimize noise and ensure signal integrity, particularly when interfacing with sensitive analog components.The schematic diagram described here is a TMP01 Celsius Scale Temperature Sensor circuit. This circuit is used to convert the VPTAT output voltage that is.. 🔗 External reference