Tone-burst oscillator and decoder

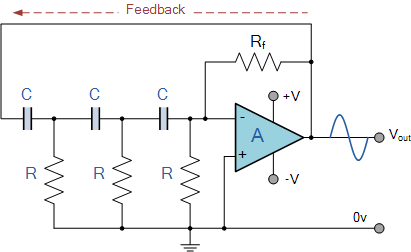
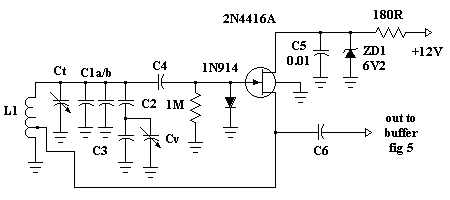
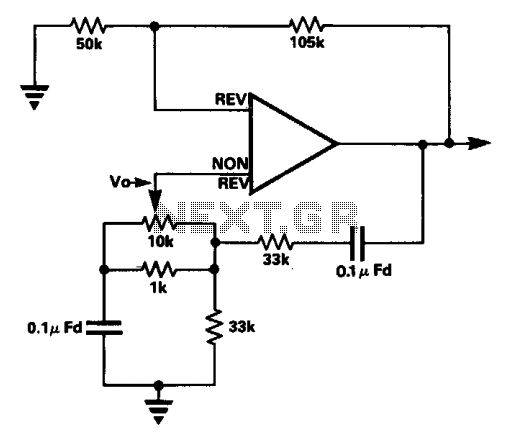
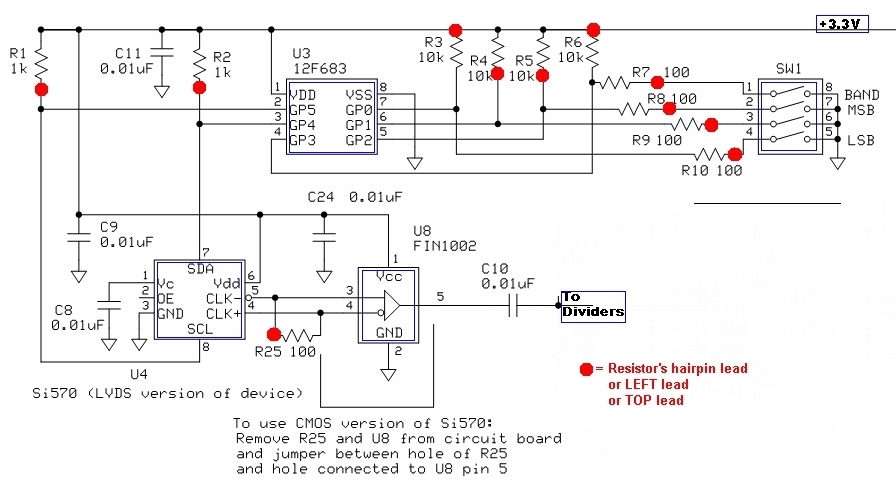
A tone burst sent at the beginning of each transmission is decoded at the receiver by a phase-locked loop (PLL), resulting in an output from pin 3 of a logic gate that activates a carrier-operated switch (COS).
In this circuit, the tone burst serves as a synchronization signal that facilitates the establishment of communication between the transmitter and receiver. The phase-locked loop (PLL) is a crucial component in this setup, as it is responsible for demodulating the incoming tone burst signal. The PLL locks onto the frequency of the tone burst, ensuring that the receiver can accurately decode the information contained within the signal.
Once the PLL successfully locks onto the tone burst, it produces a corresponding output signal at pin 3 of the logic gate. This output is typically a digital signal that transitions from a low to a high state, indicating that the tone burst has been successfully detected. The logic gate processes this signal and generates a control signal that is used to activate the carrier-operated switch (COS).
The COS is designed to control the flow of power to a load or another part of the circuit based on the presence of the tone burst signal. When the output from the logic gate goes high, the COS is turned on, allowing current to flow through the circuit and enabling the connected device to operate. This mechanism is essential for ensuring that the device only activates in response to the correct tone burst, thereby preventing unintended operation due to noise or other signals.
Overall, this configuration is widely used in communication systems where reliable signal detection and control are paramount. The use of a PLL for decoding the tone burst enhances the robustness of the system, making it less susceptible to interference and improving the overall performance of the transmission.A tone burst sent at the beginning of each transmission is decoded (at receiver) by a PLL causing output from pin 3 of logic gate to turn on carrier-operated switch (COS).
In this circuit, the tone burst serves as a synchronization signal that facilitates the establishment of communication between the transmitter and receiver. The phase-locked loop (PLL) is a crucial component in this setup, as it is responsible for demodulating the incoming tone burst signal. The PLL locks onto the frequency of the tone burst, ensuring that the receiver can accurately decode the information contained within the signal.
Once the PLL successfully locks onto the tone burst, it produces a corresponding output signal at pin 3 of the logic gate. This output is typically a digital signal that transitions from a low to a high state, indicating that the tone burst has been successfully detected. The logic gate processes this signal and generates a control signal that is used to activate the carrier-operated switch (COS).
The COS is designed to control the flow of power to a load or another part of the circuit based on the presence of the tone burst signal. When the output from the logic gate goes high, the COS is turned on, allowing current to flow through the circuit and enabling the connected device to operate. This mechanism is essential for ensuring that the device only activates in response to the correct tone burst, thereby preventing unintended operation due to noise or other signals.
Overall, this configuration is widely used in communication systems where reliable signal detection and control are paramount. The use of a PLL for decoding the tone burst enhances the robustness of the system, making it less susceptible to interference and improving the overall performance of the transmission.A tone burst sent at the beginning of each transmission is decoded (at receiver) by a PLL causing output from pin 3 of logic gate to turn on carrier-operated switch (COS).