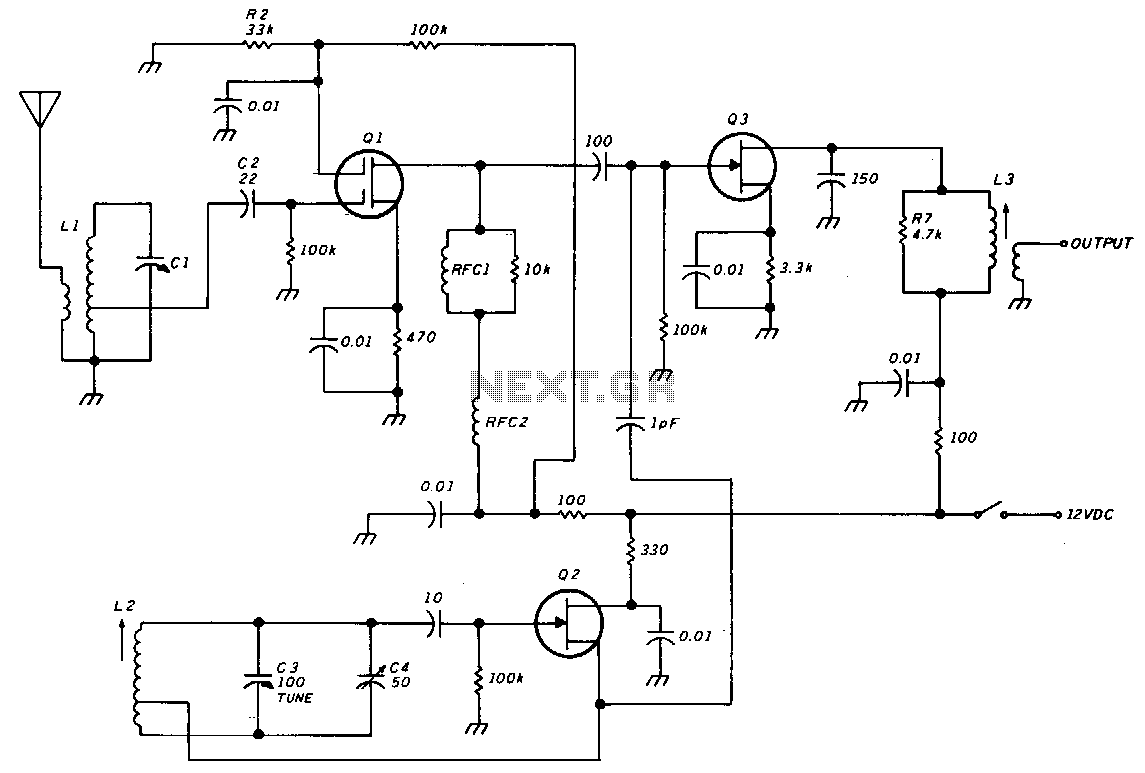
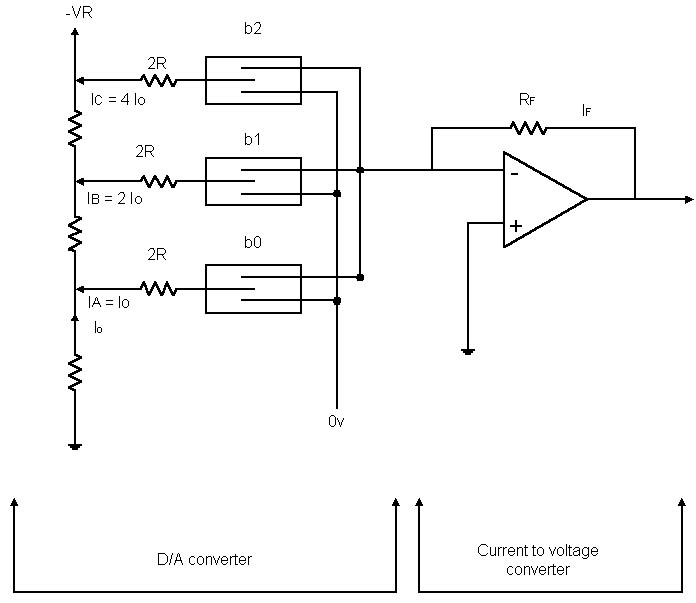
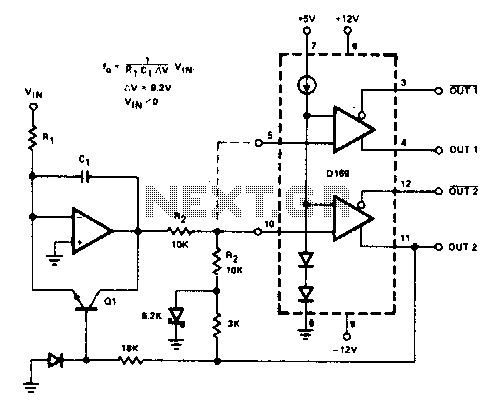
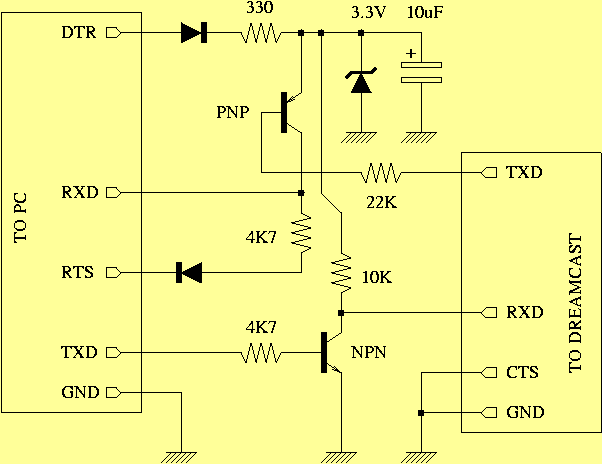
Transformerless Dc -To- Symmetric DC Converter
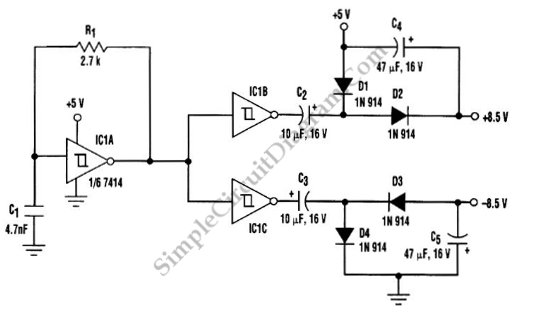
A DC to DC converter is required for a circuit board that operates solely on a +5V supply but needs to deliver dual-polarity outputs for several devices, such as operational amplifiers (op-amps) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs).
To achieve dual-polarity supplies, a DC to DC converter will typically utilize a topology that can efficiently generate both positive and negative voltage rails from the single +5V input. One common approach is to use a charge pump or a buck-boost converter.
In a charge pump configuration, capacitors are switched in and out of the circuit to create the necessary voltage levels. This method is advantageous due to its simplicity and compact size. It can provide the required negative voltage by inverting the input voltage, allowing for the generation of both +5V and -5V outputs.
Alternatively, a buck-boost converter can also be employed, which can step down or step up the input voltage. This type of converter typically involves an inductor, a switch (usually a MOSFET), and diodes to control the flow of energy. The buck-boost topology can efficiently provide the desired dual-polarity supplies while maintaining regulation under varying load conditions.
When designing the circuit, it is crucial to consider the load requirements of the op-amps and DACs to ensure that the converter can supply adequate current and maintain voltage stability. Additionally, filtering capacitors should be included on the output to minimize voltage ripple and noise, which is particularly important for analog devices.
Protection features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and input/output voltage clamping may also be integrated into the design to enhance reliability and performance. Proper PCB layout techniques should be employed to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure stable operation of the DC to DC converter.A DC to DC converter is needed for a board that only has +5V supply but have to provide dual-polarity supplies for few device such as op-amp or some DAC. Using.. 🔗 External reference
To achieve dual-polarity supplies, a DC to DC converter will typically utilize a topology that can efficiently generate both positive and negative voltage rails from the single +5V input. One common approach is to use a charge pump or a buck-boost converter.
In a charge pump configuration, capacitors are switched in and out of the circuit to create the necessary voltage levels. This method is advantageous due to its simplicity and compact size. It can provide the required negative voltage by inverting the input voltage, allowing for the generation of both +5V and -5V outputs.
Alternatively, a buck-boost converter can also be employed, which can step down or step up the input voltage. This type of converter typically involves an inductor, a switch (usually a MOSFET), and diodes to control the flow of energy. The buck-boost topology can efficiently provide the desired dual-polarity supplies while maintaining regulation under varying load conditions.
When designing the circuit, it is crucial to consider the load requirements of the op-amps and DACs to ensure that the converter can supply adequate current and maintain voltage stability. Additionally, filtering capacitors should be included on the output to minimize voltage ripple and noise, which is particularly important for analog devices.
Protection features such as overcurrent protection, thermal shutdown, and input/output voltage clamping may also be integrated into the design to enhance reliability and performance. Proper PCB layout techniques should be employed to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure stable operation of the DC to DC converter.A DC to DC converter is needed for a board that only has +5V supply but have to provide dual-polarity supplies for few device such as op-amp or some DAC. Using.. 🔗 External reference