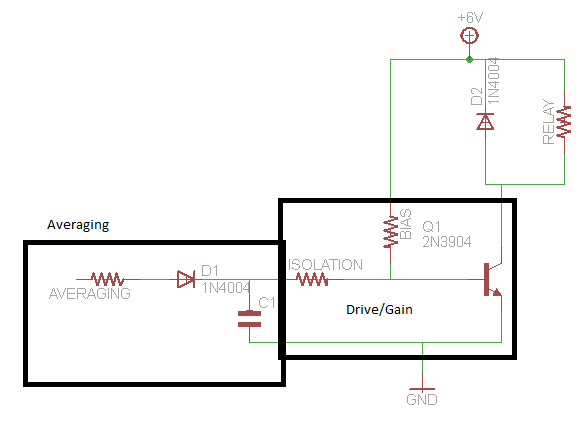
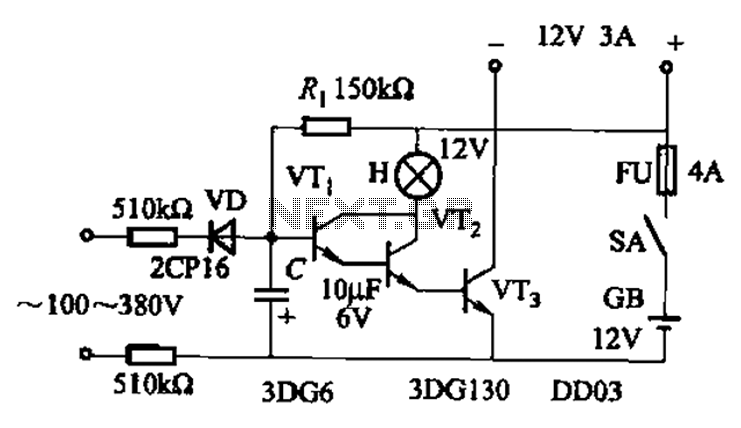
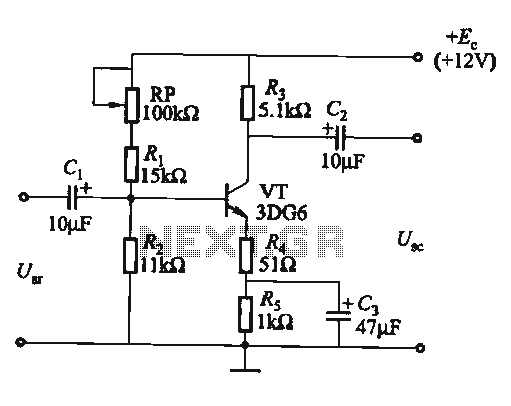
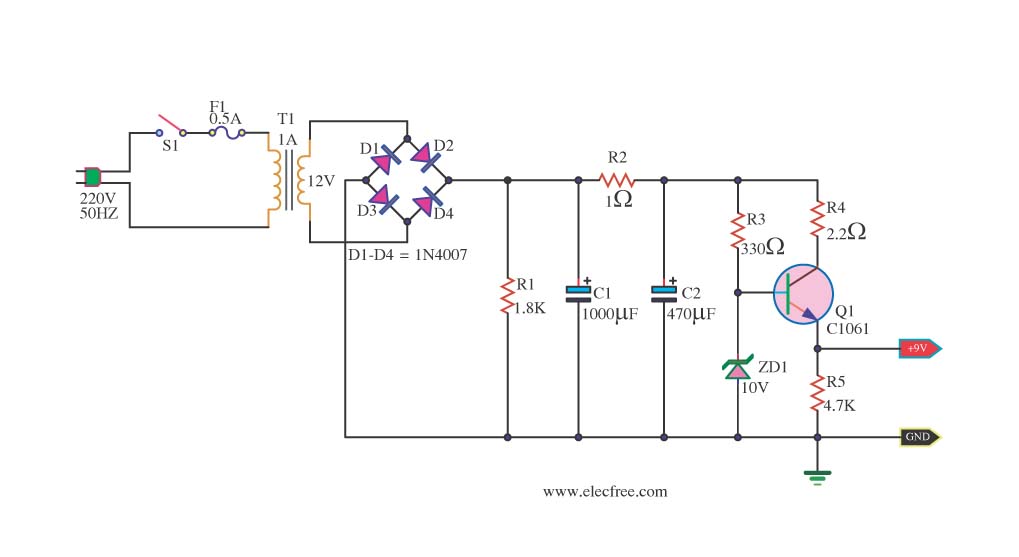
Transistor Tester
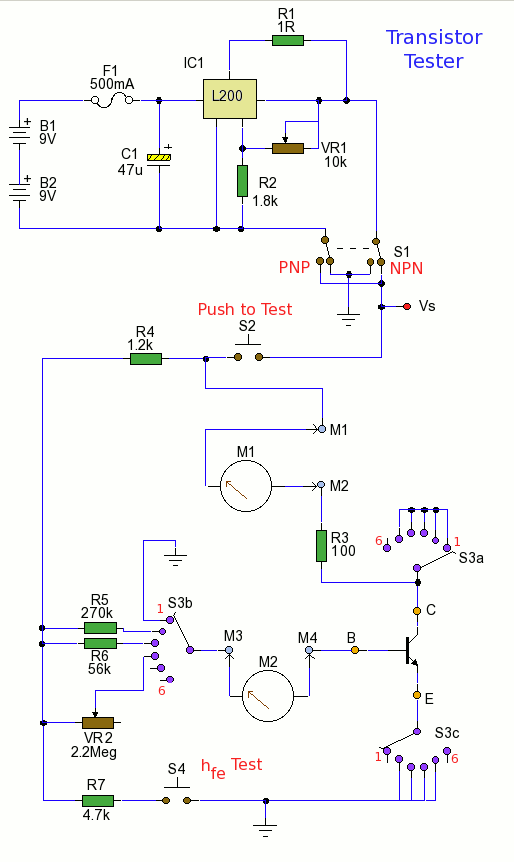
This circuit can measure both small signal hfe and DC current gain hFE of a low to medium power transistor.
The circuit is designed to evaluate the current gain characteristics of low to medium power transistors by measuring both the small signal hfe and the DC current gain hFE. The hfe, or small-signal current gain, is defined as the ratio of the output current to the input current in the active region of a transistor, while hFE represents the DC current gain in a specific operating condition.
The measurement setup typically includes a transistor under test, a variable resistor to set the base current, and a multimeter to measure the collector current. The circuit operates by applying a known base current to the transistor and measuring the resulting collector current, allowing for the calculation of both hfe and hFE.
To perform the measurement, the following steps are generally taken:
1. Connect the transistor to the circuit, ensuring that the emitter, base, and collector terminals are correctly identified and connected.
2. Adjust the variable resistor to establish a specific base current, which can be varied to observe the transistor's response.
3. Measure the collector current using the multimeter, ensuring that it is set to the appropriate current range for accurate readings.
4. Calculate the hfe using the formula: hfe = Ic/Ib, where Ic is the collector current and Ib is the base current.
5. For hFE, the measurement is taken under DC conditions, typically at a fixed collector-emitter voltage, allowing for a different operational perspective of the transistor's gain characteristics.
This circuit is beneficial for testing and characterizing transistors in various applications, ensuring that they meet the required specifications for integration into electronic designs. Proper understanding and measurement of these parameters are crucial for optimizing circuit performance and reliability.This circuit can measure both small signal hfe and DC current gain hFE of a low to medium power power transistor.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed to evaluate the current gain characteristics of low to medium power transistors by measuring both the small signal hfe and the DC current gain hFE. The hfe, or small-signal current gain, is defined as the ratio of the output current to the input current in the active region of a transistor, while hFE represents the DC current gain in a specific operating condition.
The measurement setup typically includes a transistor under test, a variable resistor to set the base current, and a multimeter to measure the collector current. The circuit operates by applying a known base current to the transistor and measuring the resulting collector current, allowing for the calculation of both hfe and hFE.
To perform the measurement, the following steps are generally taken:
1. Connect the transistor to the circuit, ensuring that the emitter, base, and collector terminals are correctly identified and connected.
2. Adjust the variable resistor to establish a specific base current, which can be varied to observe the transistor's response.
3. Measure the collector current using the multimeter, ensuring that it is set to the appropriate current range for accurate readings.
4. Calculate the hfe using the formula: hfe = Ic/Ib, where Ic is the collector current and Ib is the base current.
5. For hFE, the measurement is taken under DC conditions, typically at a fixed collector-emitter voltage, allowing for a different operational perspective of the transistor's gain characteristics.
This circuit is beneficial for testing and characterizing transistors in various applications, ensuring that they meet the required specifications for integration into electronic designs. Proper understanding and measurement of these parameters are crucial for optimizing circuit performance and reliability.This circuit can measure both small signal hfe and DC current gain hFE of a low to medium power power transistor.. 🔗 External reference