TRIAC Dimmer LED Driver Reference Design
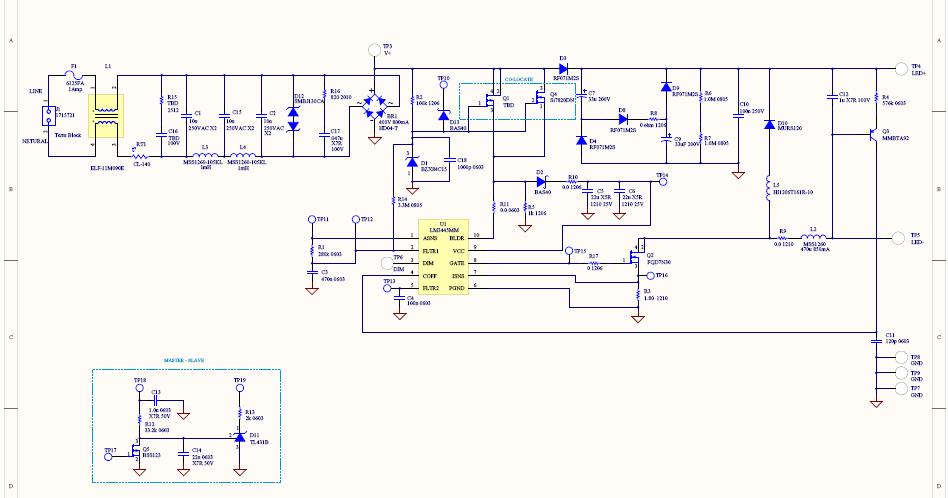
This reference design converts 90V AC to 135V AC input and drives seven or eight series-connected LEDs with an average current ranging from 300 to 600 mA. The LM3445 operates at a nominal switching frequency of 225 kHz. This design is implemented on a four-layer board, utilizing the top and bottom layers for component placement.
The design features a power conversion circuit that efficiently transforms high-voltage AC input to a suitable output for driving multiple LEDs. The input voltage range of 90V to 135V AC allows for flexibility in various applications, particularly in lighting systems where high voltage is prevalent. The LM3445 is a highly integrated LED driver IC that includes features such as current regulation, which is essential for maintaining consistent brightness across the series-connected LEDs.
The average current of 300 to 600 mA is adjustable, allowing for customization based on the specific LED characteristics and desired luminosity. The switching frequency of 225 kHz is optimal for minimizing electromagnetic interference while ensuring efficient operation. The four-layer PCB design enhances thermal management and reduces the overall footprint of the circuit, making it suitable for applications with space constraints.
The top and bottom layers of the PCB are primarily dedicated to component placement, which facilitates easier assembly and maintenance. The inner layers can be utilized for power and ground planes, providing robust connections and minimizing voltage drop across the circuit. This design approach ensures reliability and longevity in demanding environments.
In summary, this reference design provides a comprehensive solution for converting high-voltage AC to a controlled output suitable for LED applications, with a focus on efficiency, flexibility, and reliability in its construction and operation.This reference design converts 90V AC to 135V AC input, and drives seven, or eight series connected LED s from 300 to 600 mA average current. The LM3445 switching frequency is set at a nominal 225 kHz. This is a four layer board using the bottom and top layer for component placement 🔗 External reference
The design features a power conversion circuit that efficiently transforms high-voltage AC input to a suitable output for driving multiple LEDs. The input voltage range of 90V to 135V AC allows for flexibility in various applications, particularly in lighting systems where high voltage is prevalent. The LM3445 is a highly integrated LED driver IC that includes features such as current regulation, which is essential for maintaining consistent brightness across the series-connected LEDs.
The average current of 300 to 600 mA is adjustable, allowing for customization based on the specific LED characteristics and desired luminosity. The switching frequency of 225 kHz is optimal for minimizing electromagnetic interference while ensuring efficient operation. The four-layer PCB design enhances thermal management and reduces the overall footprint of the circuit, making it suitable for applications with space constraints.
The top and bottom layers of the PCB are primarily dedicated to component placement, which facilitates easier assembly and maintenance. The inner layers can be utilized for power and ground planes, providing robust connections and minimizing voltage drop across the circuit. This design approach ensures reliability and longevity in demanding environments.
In summary, this reference design provides a comprehensive solution for converting high-voltage AC to a controlled output suitable for LED applications, with a focus on efficiency, flexibility, and reliability in its construction and operation.This reference design converts 90V AC to 135V AC input, and drives seven, or eight series connected LED s from 300 to 600 mA average current. The LM3445 switching frequency is set at a nominal 225 kHz. This is a four layer board using the bottom and top layer for component placement 🔗 External reference