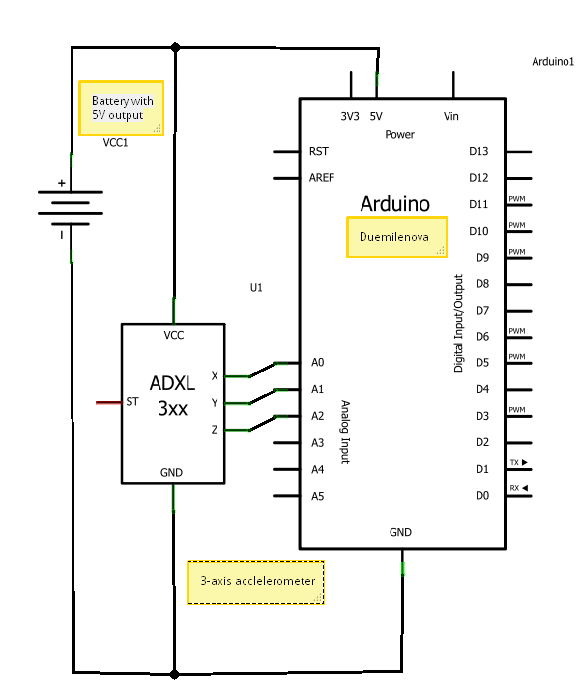
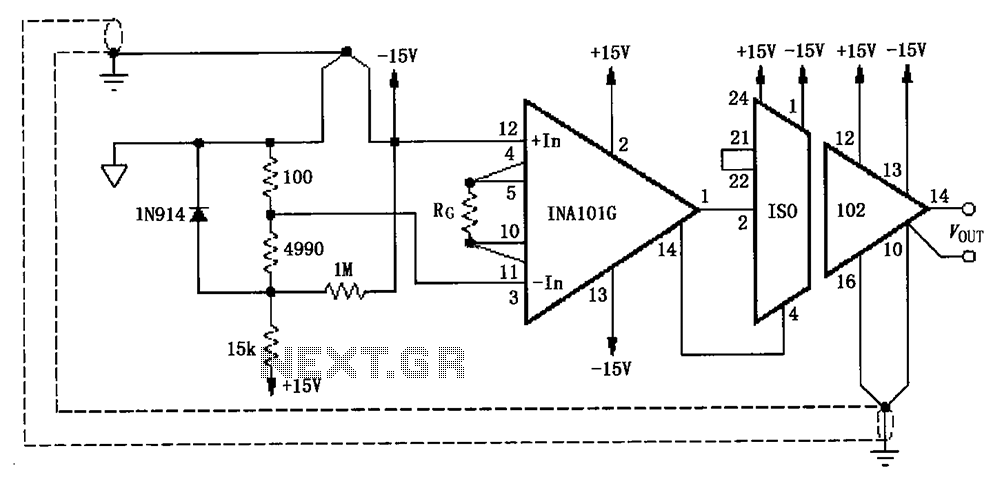
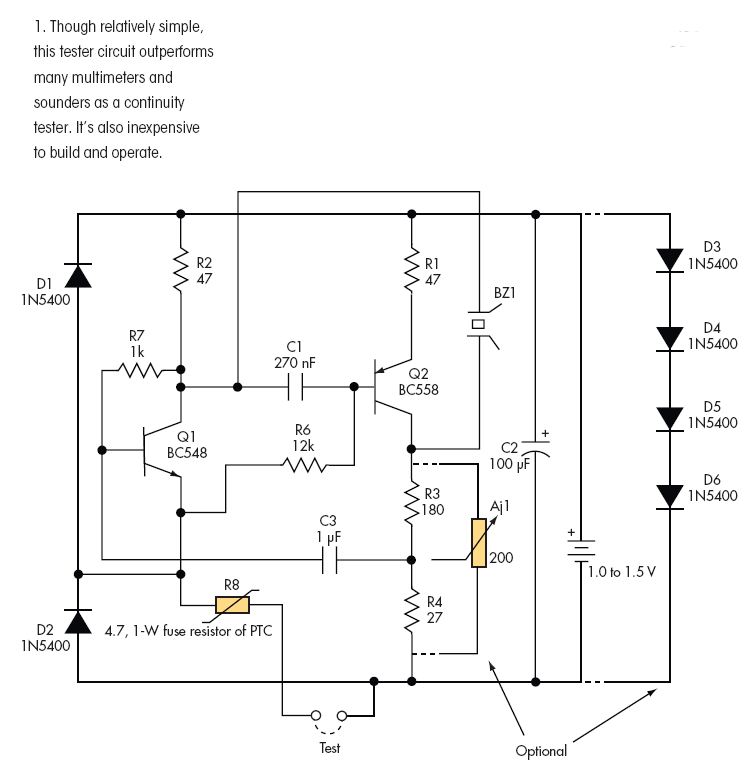
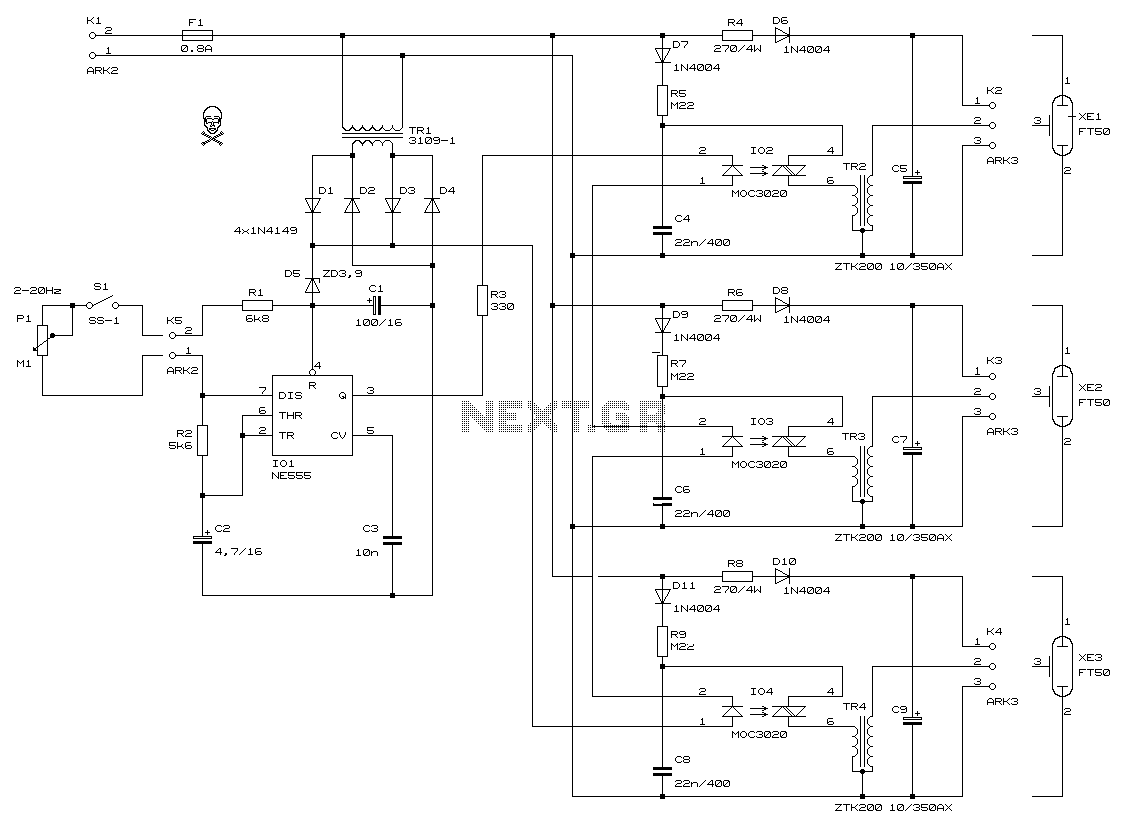
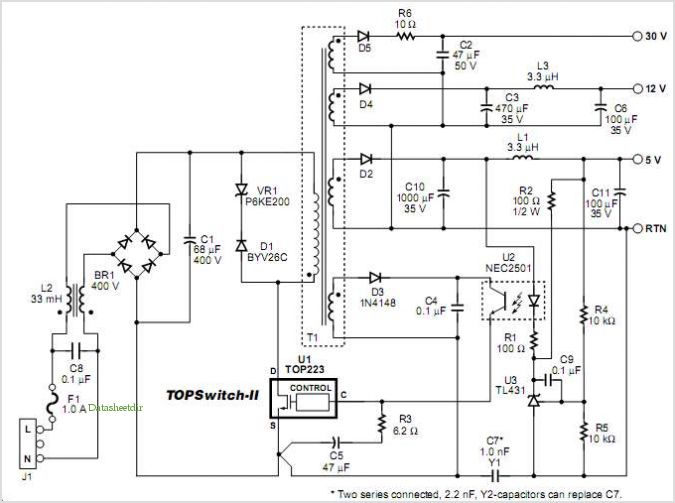
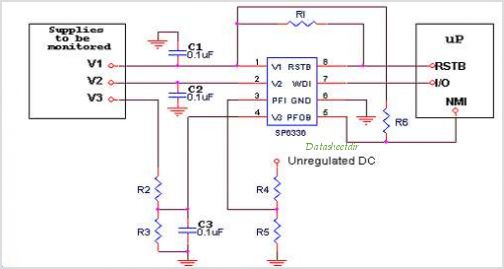
Triple Emitter-Follower as OPS for the Aikido
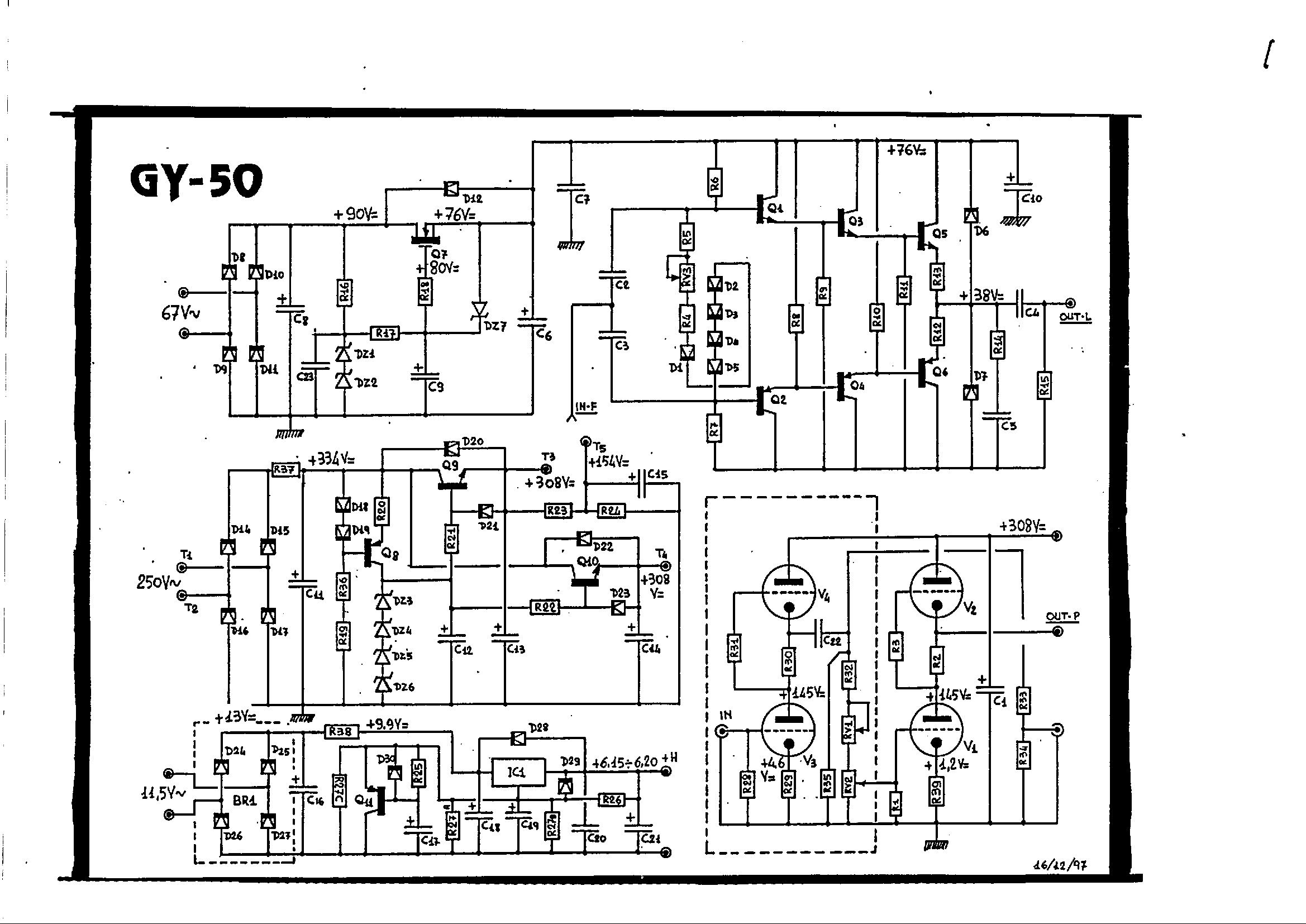
A hybrid amplifier is being developed, utilizing an Aikido configuration for the voltage amplification stage (VAS) and an emitter-follower variation for the output stage (OPS).
The hybrid amplifier design integrates two distinct amplification stages to achieve high performance and efficiency. The Aikido topology, known for its low distortion and high linearity, serves as the voltage amplification stage. This configuration typically employs a differential amplifier followed by a push-pull output stage, which helps in maintaining a balanced operation and reducing common-mode noise.
The output stage, implemented as an emitter-follower, is chosen for its high current drive capability and low output impedance. This configuration allows the amplifier to effectively drive loads while maintaining signal integrity. The emitter-follower stage provides voltage buffering, which is crucial for interfacing with subsequent stages or speakers without significant signal degradation.
In designing this hybrid amplifier, careful consideration must be given to the biasing of the Aikido stage to ensure optimal performance. The use of feedback mechanisms can further enhance linearity and stability across varying load conditions. Additionally, the power supply design should accommodate the requirements of both stages, ensuring that adequate voltage and current are supplied without introducing noise into the system.
Thermal management is another critical aspect, as both the Aikido and emitter-follower stages can generate heat during operation. Implementing proper heat sinking and ventilation strategies will help maintain the reliability and longevity of the amplifier.
Overall, this hybrid amplifier design aims to combine the strengths of both the Aikido and emitter-follower configurations, resulting in a high-fidelity audio amplification solution suitable for various applications.Hi, I`m working towards an hybrid amplifier where the VAS will be the Aikido, where the OPS is some Emitter-Follower variation. Unfortunately my.. 🔗 External reference
The hybrid amplifier design integrates two distinct amplification stages to achieve high performance and efficiency. The Aikido topology, known for its low distortion and high linearity, serves as the voltage amplification stage. This configuration typically employs a differential amplifier followed by a push-pull output stage, which helps in maintaining a balanced operation and reducing common-mode noise.
The output stage, implemented as an emitter-follower, is chosen for its high current drive capability and low output impedance. This configuration allows the amplifier to effectively drive loads while maintaining signal integrity. The emitter-follower stage provides voltage buffering, which is crucial for interfacing with subsequent stages or speakers without significant signal degradation.
In designing this hybrid amplifier, careful consideration must be given to the biasing of the Aikido stage to ensure optimal performance. The use of feedback mechanisms can further enhance linearity and stability across varying load conditions. Additionally, the power supply design should accommodate the requirements of both stages, ensuring that adequate voltage and current are supplied without introducing noise into the system.
Thermal management is another critical aspect, as both the Aikido and emitter-follower stages can generate heat during operation. Implementing proper heat sinking and ventilation strategies will help maintain the reliability and longevity of the amplifier.
Overall, this hybrid amplifier design aims to combine the strengths of both the Aikido and emitter-follower configurations, resulting in a high-fidelity audio amplification solution suitable for various applications.Hi, I`m working towards an hybrid amplifier where the VAS will be the Aikido, where the OPS is some Emitter-Follower variation. Unfortunately my.. 🔗 External reference