
task 32 triple axis accelerometer
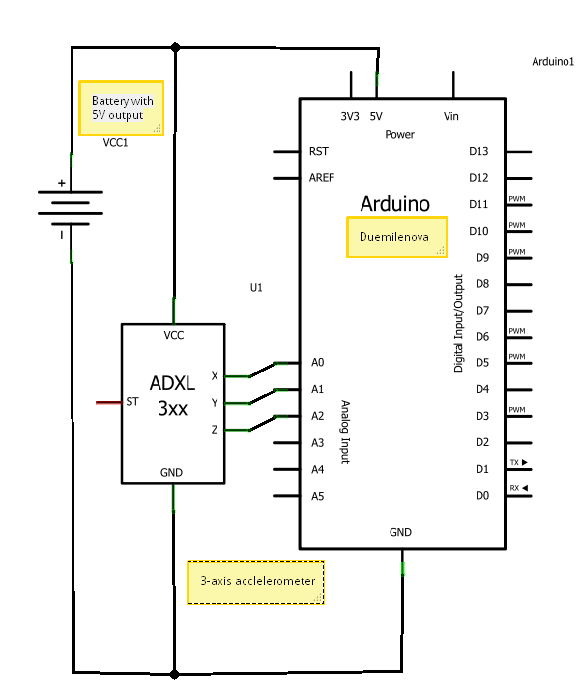
A circuit diagram illustrating the connection of an accelerometer to an Arduino board and an external power source.
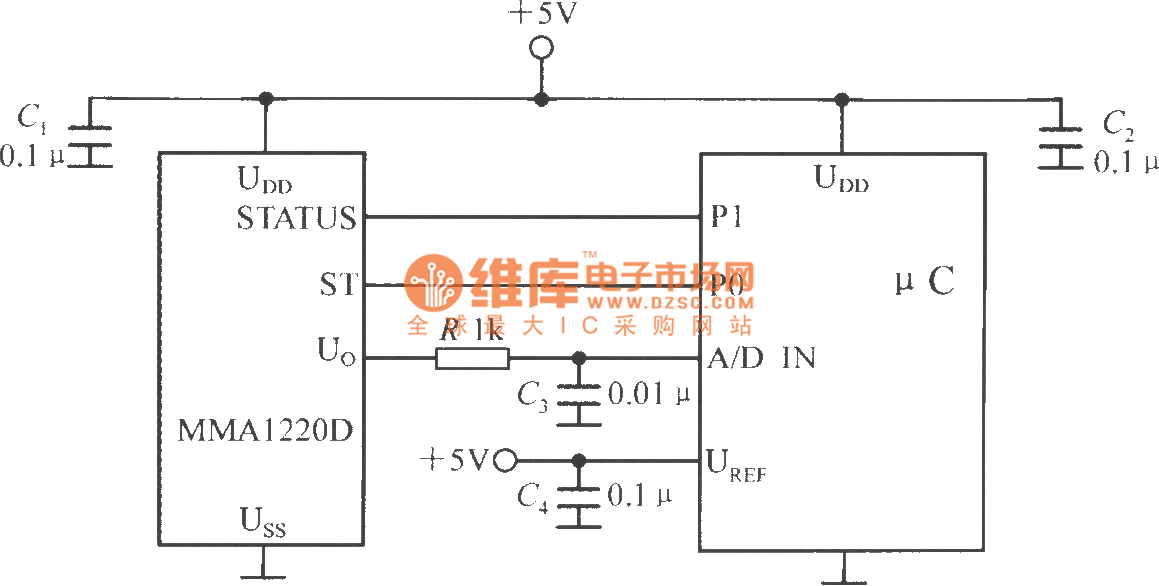
The circuit diagram depicts the integration of an accelerometer with an Arduino microcontroller, providing a clear representation of how these components interact within an electronic system. The accelerometer, a device that measures acceleration forces, is connected to the Arduino board, which serves as the central processing unit for data collection and processing.
In this setup, the accelerometer typically has three output pins corresponding to the X, Y, and Z axes of acceleration. These pins are connected to the analog input pins of the Arduino board, allowing the microcontroller to read the acceleration data. The external power source is essential for powering both the accelerometer and the Arduino, ensuring that the circuit operates efficiently.
The power connections are usually made by connecting the VCC pin of the accelerometer to the positive terminal of the external power source, while the GND pin is connected to the ground. This configuration ensures that the accelerometer receives the necessary voltage for proper operation.
In addition to the basic connections, pull-up or pull-down resistors may be included in the schematic to stabilize the signal levels and prevent floating inputs. Capacitors can also be integrated into the circuit to filter out noise and provide a stable power supply to the components.
Overall, this circuit diagram serves as a fundamental illustration for those looking to utilize an accelerometer with an Arduino platform, facilitating various applications such as motion detection, tilt sensing, and gesture recognition.a circuit diagram showing how the accelerometer is connected to an Arduino board & external power source (not complicated at all, is it) 🔗 External reference
The circuit diagram depicts the integration of an accelerometer with an Arduino microcontroller, providing a clear representation of how these components interact within an electronic system. The accelerometer, a device that measures acceleration forces, is connected to the Arduino board, which serves as the central processing unit for data collection and processing.
In this setup, the accelerometer typically has three output pins corresponding to the X, Y, and Z axes of acceleration. These pins are connected to the analog input pins of the Arduino board, allowing the microcontroller to read the acceleration data. The external power source is essential for powering both the accelerometer and the Arduino, ensuring that the circuit operates efficiently.
The power connections are usually made by connecting the VCC pin of the accelerometer to the positive terminal of the external power source, while the GND pin is connected to the ground. This configuration ensures that the accelerometer receives the necessary voltage for proper operation.
In addition to the basic connections, pull-up or pull-down resistors may be included in the schematic to stabilize the signal levels and prevent floating inputs. Capacitors can also be integrated into the circuit to filter out noise and provide a stable power supply to the components.
Overall, this circuit diagram serves as a fundamental illustration for those looking to utilize an accelerometer with an Arduino platform, facilitating various applications such as motion detection, tilt sensing, and gesture recognition.a circuit diagram showing how the accelerometer is connected to an Arduino board & external power source (not complicated at all, is it) 🔗 External reference
.jpg)