TUNED-COLLECTOR ARMSTRONG OSCILLATOR
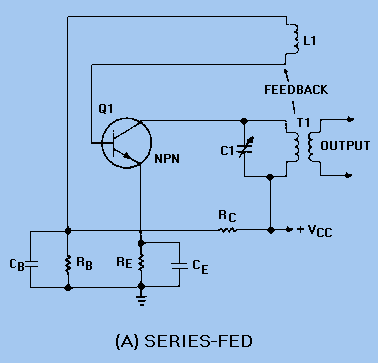
The DC path is established from the negative side (ground) of VCC through RE, Q1, T1, and returns to the positive side of VCC. The figure clearly illustrates that both the AC and DC components flow through the tank circuit. By making slight modifications to the circuit, it can be transformed into a shunt-fed, tuned-collector Armstrong oscillator, as depicted in view (B). The DC component flows from ground through RE to Q1 and then to positive VCC. The DC is blocked from entering the tank circuit by capacitor C2, allowing only the AC component to flow within the tank circuit.
The described circuit presents a fundamental configuration for generating oscillations through the use of an Armstrong oscillator. In this arrangement, the DC path is critical for biasing the transistor Q1, which acts as the active component of the oscillator. The resistor RE serves as an emitter resistor, providing stability and setting the operating point of Q1.
The tank circuit, which consists of an inductor and a capacitor, is crucial for determining the oscillation frequency. The AC component generated by the transistor Q1 is fed into the tank circuit, where it resonates at a specific frequency determined by the values of the inductor and capacitor. This resonance is essential for sustaining oscillations.
The modification to create a shunt-fed, tuned-collector configuration involves routing the output from the collector of the transistor back into the tank circuit while ensuring that the DC component is effectively blocked by capacitor C2. This capacitor acts as a coupling device, allowing only the alternating current (AC) signals to pass through to the tank circuit while preventing any DC bias from affecting the oscillation process.
In summary, the circuit operates by utilizing the transistor's ability to amplify signals, with the tank circuit providing the necessary conditions for oscillation. The careful arrangement of components ensures that the oscillator functions effectively, producing a stable output signal characterized by its frequency and amplitude. Proper selection of the inductor and capacitor values, alongside the biasing of the transistor, is essential for achieving optimal performance in this configuration.The dc path is from the negative side (ground) of VCC through RE, Q1, T1, and back to the positive side of VCC. The figure clearly illustrates that both the ac and dc components flow through the tank circuit. By modifying the circuit slightly, it becomes a SHUNT-FED, TUNED-COLLECTOR ARMSTRONG OSCILLATOR as shown in view (B). The dc component flows from ground through RE to Q1 to positive VCC. The dc is blocked from the tank circuit by capacitor C2. Only the ac component flows in the tank circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit presents a fundamental configuration for generating oscillations through the use of an Armstrong oscillator. In this arrangement, the DC path is critical for biasing the transistor Q1, which acts as the active component of the oscillator. The resistor RE serves as an emitter resistor, providing stability and setting the operating point of Q1.
The tank circuit, which consists of an inductor and a capacitor, is crucial for determining the oscillation frequency. The AC component generated by the transistor Q1 is fed into the tank circuit, where it resonates at a specific frequency determined by the values of the inductor and capacitor. This resonance is essential for sustaining oscillations.
The modification to create a shunt-fed, tuned-collector configuration involves routing the output from the collector of the transistor back into the tank circuit while ensuring that the DC component is effectively blocked by capacitor C2. This capacitor acts as a coupling device, allowing only the alternating current (AC) signals to pass through to the tank circuit while preventing any DC bias from affecting the oscillation process.
In summary, the circuit operates by utilizing the transistor's ability to amplify signals, with the tank circuit providing the necessary conditions for oscillation. The careful arrangement of components ensures that the oscillator functions effectively, producing a stable output signal characterized by its frequency and amplitude. Proper selection of the inductor and capacitor values, alongside the biasing of the transistor, is essential for achieving optimal performance in this configuration.The dc path is from the negative side (ground) of VCC through RE, Q1, T1, and back to the positive side of VCC. The figure clearly illustrates that both the ac and dc components flow through the tank circuit. By modifying the circuit slightly, it becomes a SHUNT-FED, TUNED-COLLECTOR ARMSTRONG OSCILLATOR as shown in view (B). The dc component flows from ground through RE to Q1 to positive VCC. The dc is blocked from the tank circuit by capacitor C2. Only the ac component flows in the tank circuit. 🔗 External reference