Two channel panning circuit
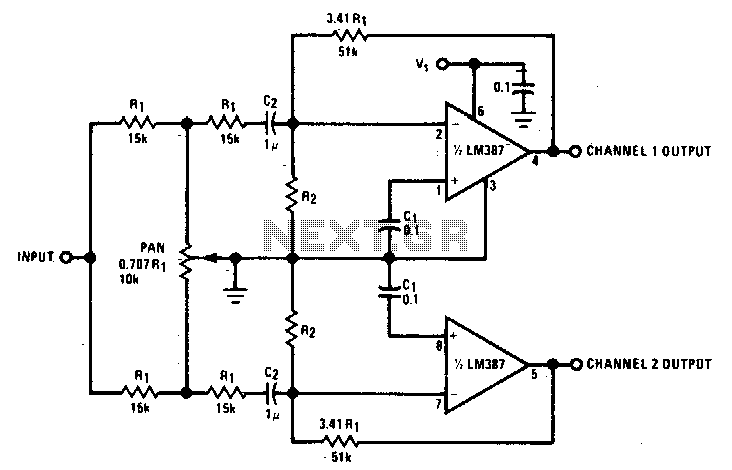
This panning circuit, also known as a panoramic control circuit, allows for the adjustment of the perceived position of a microphone's input across two output channels. This effect is frequently utilized in mixing consoles within recording studios. Panning enables recording engineers to create a spatial audio experience, such as positioning the sound of a pianist to appear as if it is moving from one side of the stage to the other.
The panning circuit typically consists of a potentiometer or a variable resistor that adjusts the level of the audio signal sent to each output channel. The circuit can be designed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) to ensure low noise and high fidelity. The input signal from the microphone is fed into the circuit, where it is split into two paths. Each path is then attenuated based on the position of the potentiometer, allowing the engineer to control the balance between the left and right output channels.
In a basic schematic, the microphone input connects to a differential amplifier configuration, which processes the audio signal. Following this, the signal is routed through two separate gain stages, each associated with one of the output channels. The potentiometer is placed in a way that alters the gain of each channel proportionally, enabling smooth transitions in the panning effect.
Additional components may include capacitors for filtering and resistors for setting the gain levels. To enhance the functionality, the circuit can incorporate features such as a mute switch or LED indicators to denote active channels. The overall design should prioritize minimal signal degradation and maintain the integrity of the audio quality throughout the panning process. This circuit is essential for achieving dynamic and immersive soundscapes in both live and recorded audio environments.This panning circuit (short for panoramic control circuit) provides the ability to move the apparent position of one microphone"s input between two output channels. This effect is often required in recording studio mixing consoles Panning is how recording engineers manage to pick up your favorite pianist and "float" the sound over to the other side of the stage and back again. 🔗 External reference
The panning circuit typically consists of a potentiometer or a variable resistor that adjusts the level of the audio signal sent to each output channel. The circuit can be designed using operational amplifiers (op-amps) to ensure low noise and high fidelity. The input signal from the microphone is fed into the circuit, where it is split into two paths. Each path is then attenuated based on the position of the potentiometer, allowing the engineer to control the balance between the left and right output channels.
In a basic schematic, the microphone input connects to a differential amplifier configuration, which processes the audio signal. Following this, the signal is routed through two separate gain stages, each associated with one of the output channels. The potentiometer is placed in a way that alters the gain of each channel proportionally, enabling smooth transitions in the panning effect.
Additional components may include capacitors for filtering and resistors for setting the gain levels. To enhance the functionality, the circuit can incorporate features such as a mute switch or LED indicators to denote active channels. The overall design should prioritize minimal signal degradation and maintain the integrity of the audio quality throughout the panning process. This circuit is essential for achieving dynamic and immersive soundscapes in both live and recorded audio environments.This panning circuit (short for panoramic control circuit) provides the ability to move the apparent position of one microphone"s input between two output channels. This effect is often required in recording studio mixing consoles Panning is how recording engineers manage to pick up your favorite pianist and "float" the sound over to the other side of the stage and back again. 🔗 External reference