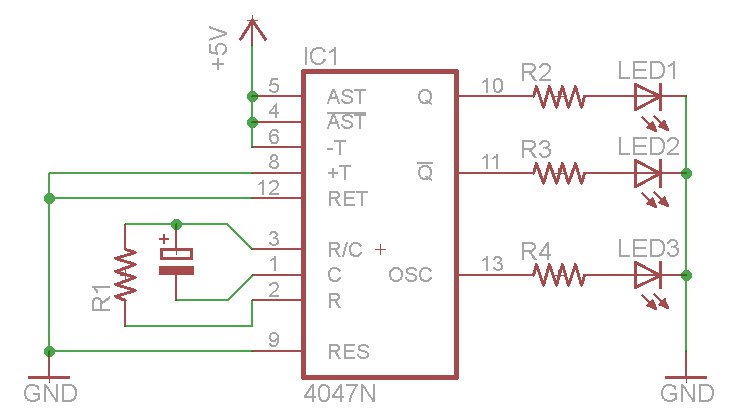
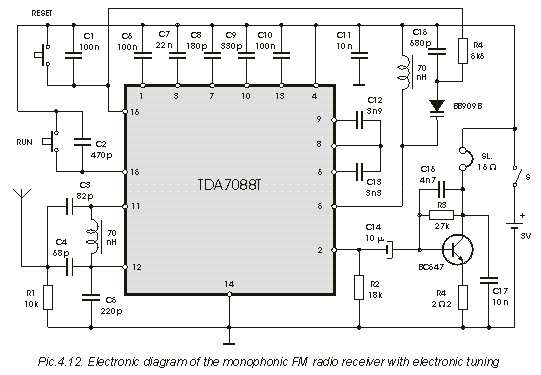
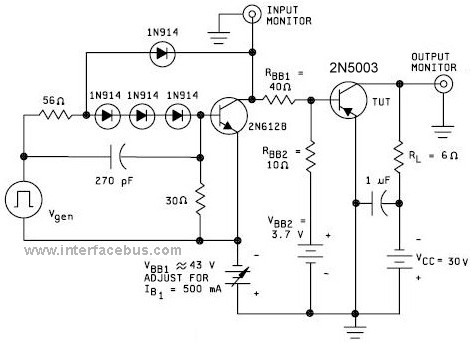
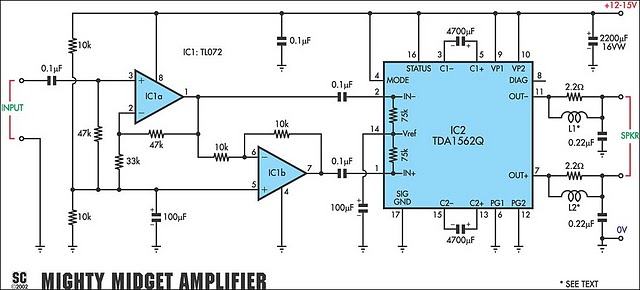
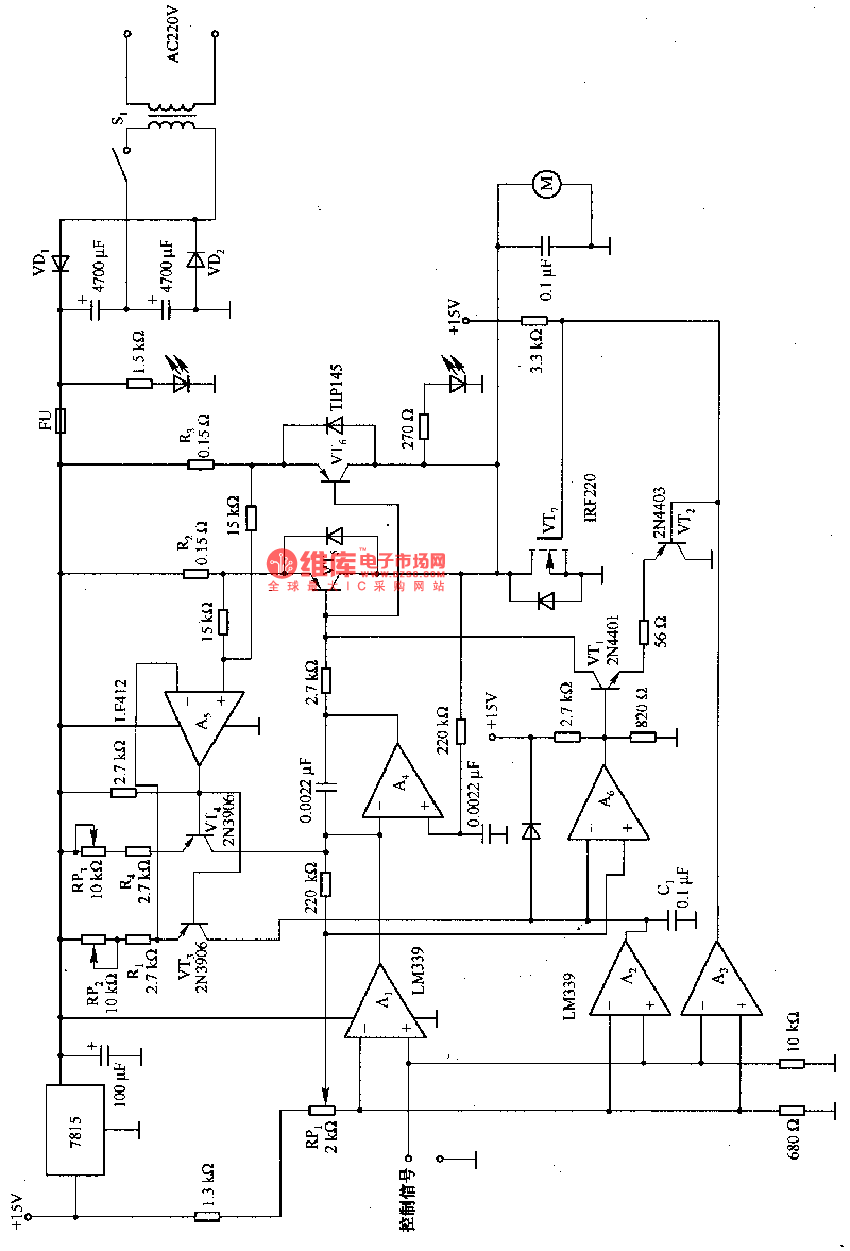
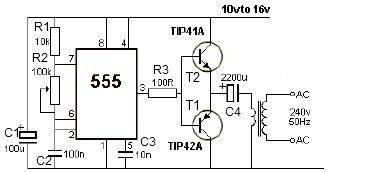
Two-Transistor DC Motor DriverCircuit Using The TIP32 Transistor
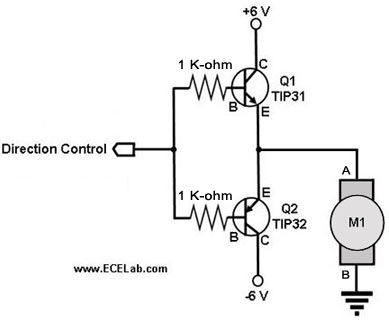
The following circuit illustrates a two-transistor DC motor driver circuit diagram. This circuit utilizes the TIP32 transistor. Features: operates in...
The two-transistor DC motor driver circuit is designed to control the operation of a DC motor using two NPN transistors, which function as switches. The TIP32, a PNP transistor, is often employed in this configuration due to its capability to handle higher currents and voltages, making it suitable for driving motors.
In this circuit, the two NPN transistors are connected in a complementary push-pull configuration. When a control signal is applied to the base of the first NPN transistor, it turns on, allowing current to flow from the power supply through the motor and into the collector of the first transistor. This action causes the motor to rotate in one direction. Simultaneously, the second NPN transistor remains off, preventing current from flowing through it.
When the control signal is switched to the second transistor, it turns on, redirecting the current flow through the motor in the opposite direction, effectively reversing its rotation. This capability provides bidirectional control of the motor, which is essential for applications requiring precise movement, such as robotics or automated systems.
The circuit typically includes additional components, such as diodes for flyback protection, which safeguard the transistors from voltage spikes generated when the motor is switched off. Capacitors may also be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply.
Overall, this two-transistor DC motor driver circuit is a robust solution for controlling DC motors, offering simplicity in design while providing effective control over the motor's direction and speed.The following circuit shows about Two-Transistor DC Motor Driver Circuit Diagram . This circuit using the TIP32 Transistor. Features: runs in .. 🔗 External reference
The two-transistor DC motor driver circuit is designed to control the operation of a DC motor using two NPN transistors, which function as switches. The TIP32, a PNP transistor, is often employed in this configuration due to its capability to handle higher currents and voltages, making it suitable for driving motors.
In this circuit, the two NPN transistors are connected in a complementary push-pull configuration. When a control signal is applied to the base of the first NPN transistor, it turns on, allowing current to flow from the power supply through the motor and into the collector of the first transistor. This action causes the motor to rotate in one direction. Simultaneously, the second NPN transistor remains off, preventing current from flowing through it.
When the control signal is switched to the second transistor, it turns on, redirecting the current flow through the motor in the opposite direction, effectively reversing its rotation. This capability provides bidirectional control of the motor, which is essential for applications requiring precise movement, such as robotics or automated systems.
The circuit typically includes additional components, such as diodes for flyback protection, which safeguard the transistors from voltage spikes generated when the motor is switched off. Capacitors may also be included to filter out noise and stabilize the power supply.
Overall, this two-transistor DC motor driver circuit is a robust solution for controlling DC motors, offering simplicity in design while providing effective control over the motor's direction and speed.The following circuit shows about Two-Transistor DC Motor Driver Circuit Diagram . This circuit using the TIP32 Transistor. Features: runs in .. 🔗 External reference