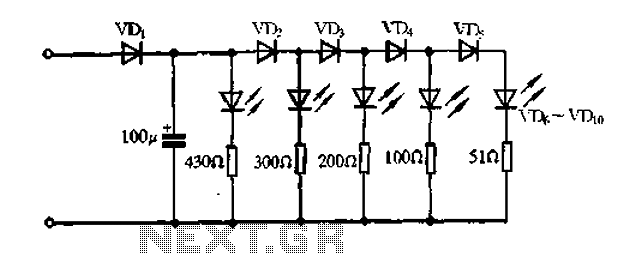
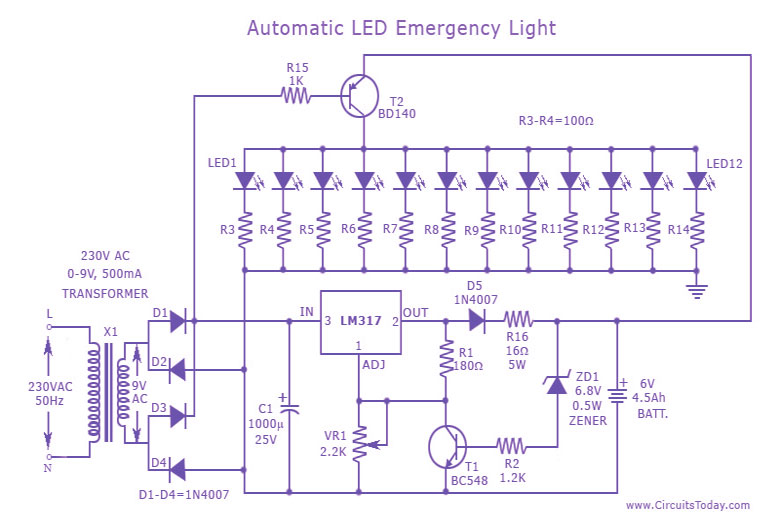
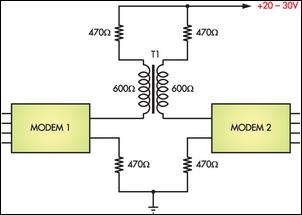
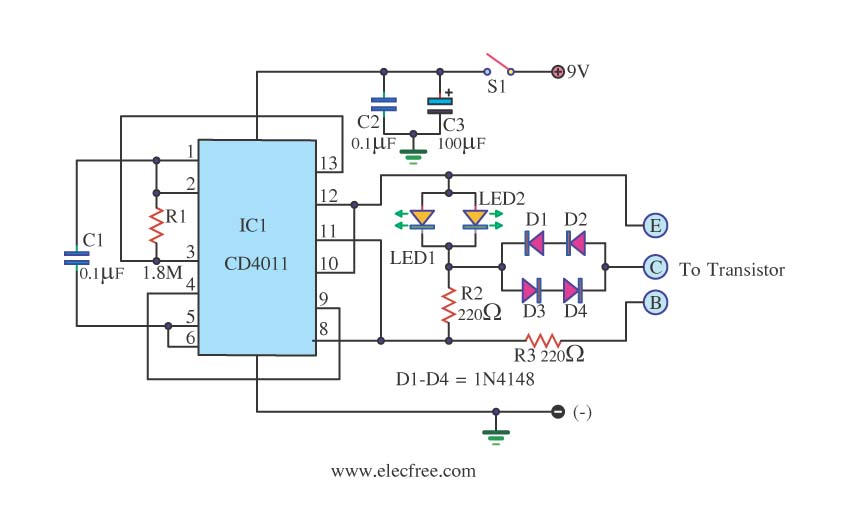
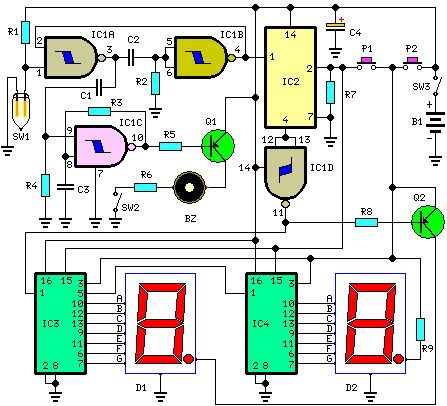
Two way intercom circuit diagram using transistors and UM66 as ringer
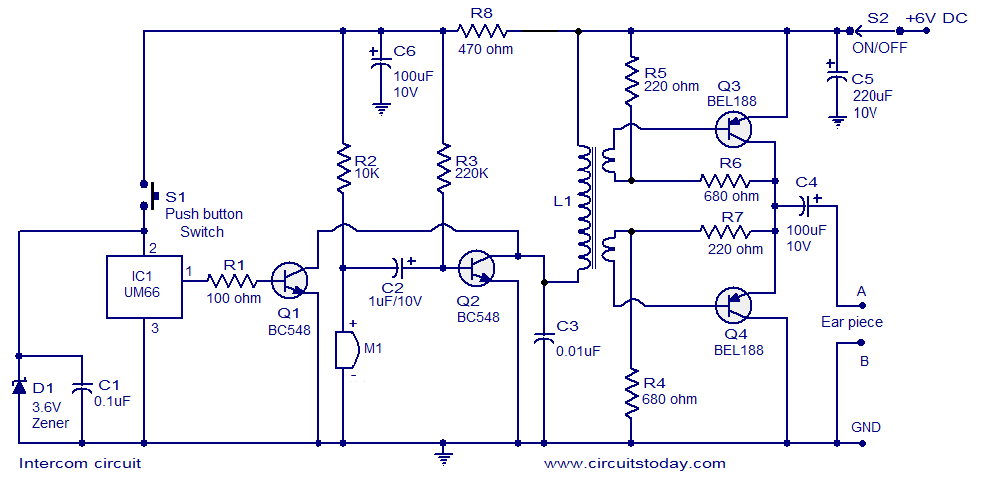
A straightforward intercom circuit designed using transistors. It does not require a changeover switch and can be used similarly to a telephone.
This intercom circuit utilizes transistors to facilitate communication between two or more stations without the need for complex switching mechanisms. The design typically consists of a transmitter and a receiver unit, where each unit is equipped with a transistor amplifier to enhance audio signals.
The circuit operates by converting the audio input from a microphone into an electrical signal, which is then amplified by the transistor. The amplified signal is transmitted through the wiring to the receiving unit, where another transistor amplifies the signal further before it is output through a speaker.
Key components of the circuit include:
1. **Transistors**: These serve as the main amplifying devices and are crucial for boosting the audio signals for clear communication.
2. **Microphone**: A standard electret or dynamic microphone can be used to capture the user's voice.
3. **Speaker**: A small speaker or piezo buzzer is employed to reproduce the audio signal at the receiving end.
4. **Resistors and Capacitors**: These passive components are used for biasing the transistors, filtering, and ensuring stability in the circuit operation.
5. **Power Supply**: A simple DC power supply (typically 9V or 12V) is required to power the circuit.
The simplicity of this intercom circuit makes it an excellent choice for basic communication needs, such as in homes or small offices. Its reliance on transistors allows for a compact design, making it easier to integrate into various environments without the need for extensive wiring or additional switching components. This circuit can also be modified or expanded by adding more units, allowing for multi-station communication.A very simple intercom circuit designed based on transistors. No need for a changeover switch and you can use it just like a telephone.. 🔗 External reference
This intercom circuit utilizes transistors to facilitate communication between two or more stations without the need for complex switching mechanisms. The design typically consists of a transmitter and a receiver unit, where each unit is equipped with a transistor amplifier to enhance audio signals.
The circuit operates by converting the audio input from a microphone into an electrical signal, which is then amplified by the transistor. The amplified signal is transmitted through the wiring to the receiving unit, where another transistor amplifies the signal further before it is output through a speaker.
Key components of the circuit include:
1. **Transistors**: These serve as the main amplifying devices and are crucial for boosting the audio signals for clear communication.
2. **Microphone**: A standard electret or dynamic microphone can be used to capture the user's voice.
3. **Speaker**: A small speaker or piezo buzzer is employed to reproduce the audio signal at the receiving end.
4. **Resistors and Capacitors**: These passive components are used for biasing the transistors, filtering, and ensuring stability in the circuit operation.
5. **Power Supply**: A simple DC power supply (typically 9V or 12V) is required to power the circuit.
The simplicity of this intercom circuit makes it an excellent choice for basic communication needs, such as in homes or small offices. Its reliance on transistors allows for a compact design, making it easier to integrate into various environments without the need for extensive wiring or additional switching components. This circuit can also be modified or expanded by adding more units, allowing for multi-station communication.A very simple intercom circuit designed based on transistors. No need for a changeover switch and you can use it just like a telephone.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713