1972 Ford V8 alternator wiring diagram and voltage regulator
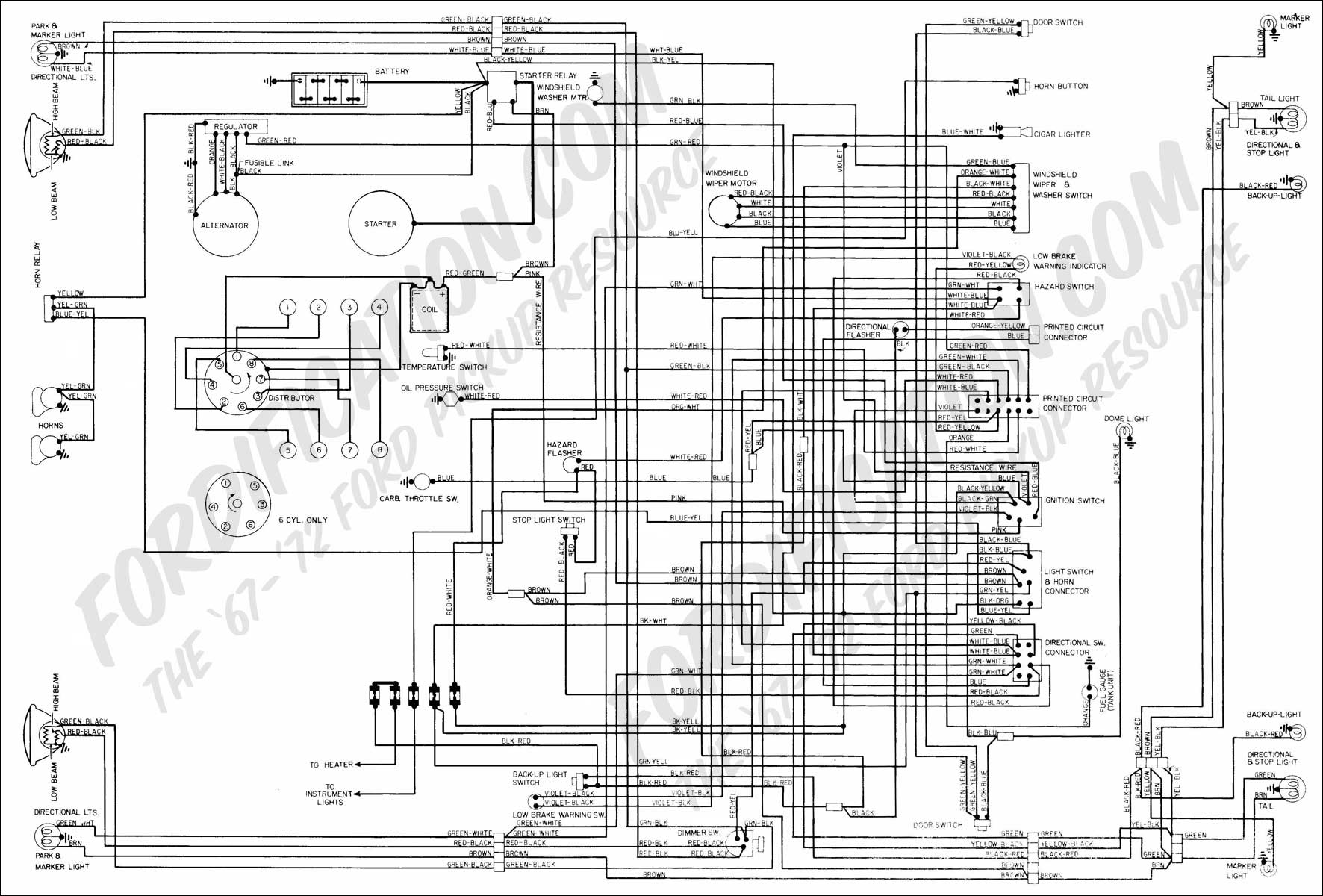
The vehicle is a 1968 Ford equipped with a 1972 engine. The original alternator has been replaced with a new unit. It has been suggested that reversing the polarity of the voltage regulator is necessary for the alternator to start functioning correctly. A wiring diagram for both the voltage regulator and the alternator is requested to assist with the installation.
To create a functional electrical system in this 1968 Ford with a 1972 engine, it is essential to understand the interaction between the alternator and the voltage regulator. The alternator generates electrical power, which is then regulated by the voltage regulator to ensure a consistent voltage output to the vehicle's electrical system and battery.
In this scenario, the new alternator may be designed for a different polarity than the original setup. Typically, older systems, such as those in a 1968 Ford, operate on positive ground, while many modern alternators are negative ground. To accommodate this, the voltage regulator's polarity must be reversed. This adjustment allows the alternator to charge the battery effectively.
The wiring connections for the alternator typically include:
1. **B+ Terminal**: This terminal connects to the battery positive terminal, providing the alternator with the necessary voltage to charge the battery.
2. **Field Terminal (F)**: This terminal connects to the voltage regulator, controlling the alternator's output based on the battery's charge level.
3. **Ground Terminal (G)**: This terminal must be connected to the vehicle's chassis ground to complete the circuit.
For the voltage regulator, the connections are as follows:
1. **Battery Terminal (B)**: This terminal connects to the positive side of the battery to receive voltage input from the alternator.
2. **Field Terminal (F)**: This terminal connects to the alternator's field terminal, allowing the regulator to control the alternator's output.
3. **Ground Terminal (G)**: This terminal is connected to the vehicle's ground to ensure proper operation of the regulator.
A detailed wiring diagram should illustrate these connections clearly, showing the alternator's B+ terminal connecting to the battery, the field terminal connecting to the voltage regulator, and the ground connections to the chassis. It is also important to ensure that the voltage regulator is correctly oriented to reflect the reversed polarity, allowing for proper voltage regulation and safe operation of the new alternator.
In conclusion, careful attention to the wiring and polarity adjustments is crucial for the successful integration of the new alternator into the 1968 Ford with a 1972 engine. The provided wiring diagram will serve as a valuable resource for ensuring all connections are made correctly, facilitating reliable vehicle operation.I have 1968 Ford and the motor identification is now a 1972 engine. Alternator was gone and I have a new one. Was told that I need to reverse the polarity of voltage regulator to make alternator start charging. A diagram of wiring to both voltage regulator and alternator would help. 🔗 External reference
To create a functional electrical system in this 1968 Ford with a 1972 engine, it is essential to understand the interaction between the alternator and the voltage regulator. The alternator generates electrical power, which is then regulated by the voltage regulator to ensure a consistent voltage output to the vehicle's electrical system and battery.
In this scenario, the new alternator may be designed for a different polarity than the original setup. Typically, older systems, such as those in a 1968 Ford, operate on positive ground, while many modern alternators are negative ground. To accommodate this, the voltage regulator's polarity must be reversed. This adjustment allows the alternator to charge the battery effectively.
The wiring connections for the alternator typically include:
1. **B+ Terminal**: This terminal connects to the battery positive terminal, providing the alternator with the necessary voltage to charge the battery.
2. **Field Terminal (F)**: This terminal connects to the voltage regulator, controlling the alternator's output based on the battery's charge level.
3. **Ground Terminal (G)**: This terminal must be connected to the vehicle's chassis ground to complete the circuit.
For the voltage regulator, the connections are as follows:
1. **Battery Terminal (B)**: This terminal connects to the positive side of the battery to receive voltage input from the alternator.
2. **Field Terminal (F)**: This terminal connects to the alternator's field terminal, allowing the regulator to control the alternator's output.
3. **Ground Terminal (G)**: This terminal is connected to the vehicle's ground to ensure proper operation of the regulator.
A detailed wiring diagram should illustrate these connections clearly, showing the alternator's B+ terminal connecting to the battery, the field terminal connecting to the voltage regulator, and the ground connections to the chassis. It is also important to ensure that the voltage regulator is correctly oriented to reflect the reversed polarity, allowing for proper voltage regulation and safe operation of the new alternator.
In conclusion, careful attention to the wiring and polarity adjustments is crucial for the successful integration of the new alternator into the 1968 Ford with a 1972 engine. The provided wiring diagram will serve as a valuable resource for ensuring all connections are made correctly, facilitating reliable vehicle operation.I have 1968 Ford and the motor identification is now a 1972 engine. Alternator was gone and I have a new one. Was told that I need to reverse the polarity of voltage regulator to make alternator start charging. A diagram of wiring to both voltage regulator and alternator would help. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713