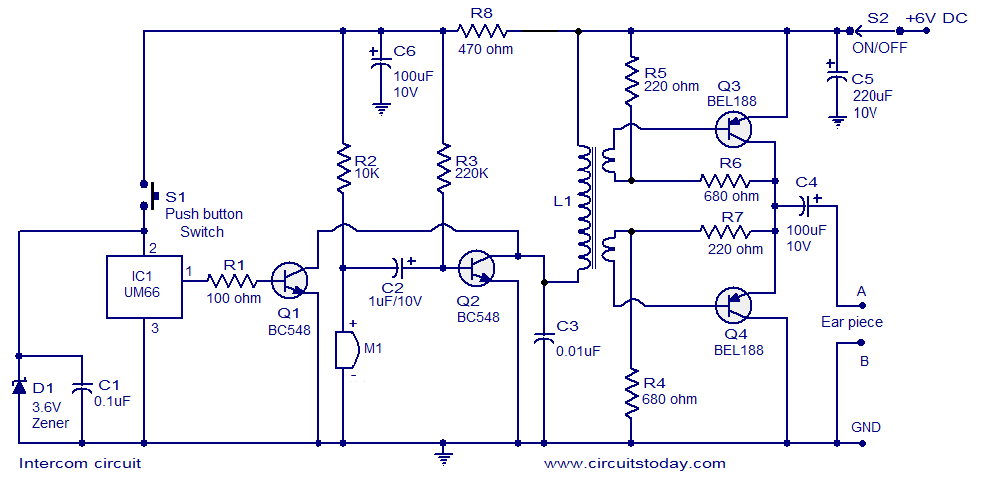
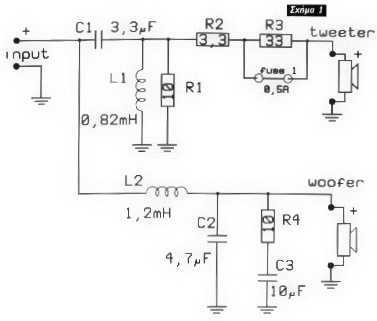
Two way Loudspeaker cross-over
The resistance of loudspeakers is characterized in a frequency depending on the destination and their press. Loudspeakers are distinguished, as for the destination, in loudspeakers of low frequencies, woofer intermediate, mid-range and high tweeter. Their resistance in Ω is 4Ω, 8Ω and 16Ω. The cross-over that we present is intended for loudspeakers 8Ω. The loudspeakers are distinguished by various characteristics that make them distinguishable. The characteristics of interest for the manufacture are their complex or simple resistance and the diagram that provides the relation of sound attribution as a function of frequency (sensitivity). Cross-overs are typically constructed using passive materials that aim to separate a region of frequencies into smaller segments. The cross-over offered separates the acoustic region into two sub-areas to direct two loudspeakers for high frequencies and low frequencies. Cross-overs are essential for the operation of loudspeaker combinations. Without them, two things happen: on one side, all frequencies are sent simultaneously to different loudspeakers, and on the other side, energy is wasted on loudspeakers that cannot reproduce the frequencies correctly. Cross-overs can be classified based on the number of loudspeakers they drive as two-way, three-way, or even more complex configurations. Each region is figuratively named a "way," through which the corresponding frequency range is directed to the appropriate loudspeaker. The simplest system is that of two ways, where the acoustic region is separated into two sub-areas using two filters: one for low-pass and one for high-pass. The low-pass filter directs the low-frequency loudspeaker, known as a woofer, while the high-pass filter directs the high-frequency loudspeaker, known as a tweeter.
The described loudspeaker system incorporates a passive cross-over network designed specifically for 8Ω loudspeakers. This network is crucial for optimizing sound reproduction by effectively dividing the audio signal into distinct frequency bands, ensuring that each loudspeaker operates within its optimal frequency range. The two-way configuration consists of a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter, which can be implemented using passive components such as inductors and capacitors.
The low-pass filter allows frequencies below a certain cutoff frequency to pass through to the woofer, which is designed to handle bass sounds effectively. The inductor in this filter provides impedance to higher frequencies, effectively blocking them from reaching the woofer. Conversely, the high-pass filter allows frequencies above a specified cutoff to be directed to the tweeter, which is optimized for high-frequency sounds. The capacitor in this filter blocks lower frequencies, preventing them from reaching the tweeter.
To ensure proper functionality, the design of the cross-over network must consider the impedance of the loudspeakers and the desired crossover frequencies. Calculating the values of the inductors and capacitors is essential to achieve the desired performance characteristics, including the slope of the filter and the transition between frequency bands. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize signal loss and interference, which can be achieved by using short, direct connections and ensuring that the components are placed in a manner that reduces inductive and capacitive coupling between them.
In summary, the implementation of a two-way passive cross-over network for 8Ω loudspeakers enhances the overall audio experience by allowing for efficient frequency separation, thus optimizing the performance of both woofers and tweeters. This design approach not only improves sound quality but also extends the lifespan of the loudspeakers by preventing them from operating outside their specified frequency ranges.The resistance of loudspeakers is characterized in a frequency depending on the destination and their press. Loudspeakers are distinguished, as for the destination, in loudspeakers of low frequencies, woofer intermediate, mid-range and high tweeter.
Their resistance in W is 4W, 8W and 16W. Cross-over that we present it is intended for loudspeakers 8W. The loudspeakers are distinguished by various characteristics that him make distinguish between them. That characteristics that us interest for the manufacture that we make, are their complex or more simply resistance and diagram that us gives the relation of attribution of sound as for frequency (sensitivity).
Cross-over they are netting usually with passive materials that have aim to separate a region of frequencies in smaller. Cross-over the manufacture that to you we offer it separates the acoustic region in two sub areas in order to we lead two loudspeakers for the high frequencies and for low.
Cross-over they are essentially for the operation of combination of loudspeakers. Without them, two things happen: on one side are led all the frequencies simultaneously to different loudspeakers and otherwise is consumed pointlessly force in loudspeakers that cannot him attribute rightly. Cross-over depending on the number of loudspeakers that leads they are distinguished in two streets and three streets, even if they can result also complexes.
The each region is figuratively named street, through which will pass the corresponding region of frequencies in order to it leads the corresponding loudspeaker. The simpler system is that of two streets. In that acoustic region it is separated in two sub areas with two filters: one of low passage and one high.
The filter of low passage leads the loudspeaker for the low frequencies and the filter of high frequencies the loudspeaker for the high frequencies. The loudspeaker for the low frequencies is known as woofer and the loudspeaker for the high frequencies as tweeter.
🔗 External reference
The described loudspeaker system incorporates a passive cross-over network designed specifically for 8Ω loudspeakers. This network is crucial for optimizing sound reproduction by effectively dividing the audio signal into distinct frequency bands, ensuring that each loudspeaker operates within its optimal frequency range. The two-way configuration consists of a low-pass filter and a high-pass filter, which can be implemented using passive components such as inductors and capacitors.
The low-pass filter allows frequencies below a certain cutoff frequency to pass through to the woofer, which is designed to handle bass sounds effectively. The inductor in this filter provides impedance to higher frequencies, effectively blocking them from reaching the woofer. Conversely, the high-pass filter allows frequencies above a specified cutoff to be directed to the tweeter, which is optimized for high-frequency sounds. The capacitor in this filter blocks lower frequencies, preventing them from reaching the tweeter.
To ensure proper functionality, the design of the cross-over network must consider the impedance of the loudspeakers and the desired crossover frequencies. Calculating the values of the inductors and capacitors is essential to achieve the desired performance characteristics, including the slope of the filter and the transition between frequency bands. Additionally, the layout of the circuit should minimize signal loss and interference, which can be achieved by using short, direct connections and ensuring that the components are placed in a manner that reduces inductive and capacitive coupling between them.
In summary, the implementation of a two-way passive cross-over network for 8Ω loudspeakers enhances the overall audio experience by allowing for efficient frequency separation, thus optimizing the performance of both woofers and tweeters. This design approach not only improves sound quality but also extends the lifespan of the loudspeakers by preventing them from operating outside their specified frequency ranges.The resistance of loudspeakers is characterized in a frequency depending on the destination and their press. Loudspeakers are distinguished, as for the destination, in loudspeakers of low frequencies, woofer intermediate, mid-range and high tweeter.
Their resistance in W is 4W, 8W and 16W. Cross-over that we present it is intended for loudspeakers 8W. The loudspeakers are distinguished by various characteristics that him make distinguish between them. That characteristics that us interest for the manufacture that we make, are their complex or more simply resistance and diagram that us gives the relation of attribution of sound as for frequency (sensitivity).
Cross-over they are netting usually with passive materials that have aim to separate a region of frequencies in smaller. Cross-over the manufacture that to you we offer it separates the acoustic region in two sub areas in order to we lead two loudspeakers for the high frequencies and for low.
Cross-over they are essentially for the operation of combination of loudspeakers. Without them, two things happen: on one side are led all the frequencies simultaneously to different loudspeakers and otherwise is consumed pointlessly force in loudspeakers that cannot him attribute rightly. Cross-over depending on the number of loudspeakers that leads they are distinguished in two streets and three streets, even if they can result also complexes.
The each region is figuratively named street, through which will pass the corresponding region of frequencies in order to it leads the corresponding loudspeaker. The simpler system is that of two streets. In that acoustic region it is separated in two sub areas with two filters: one of low passage and one high.
The filter of low passage leads the loudspeaker for the low frequencies and the filter of high frequencies the loudspeaker for the high frequencies. The loudspeaker for the low frequencies is known as woofer and the loudspeaker for the high frequencies as tweeter.
🔗 External reference