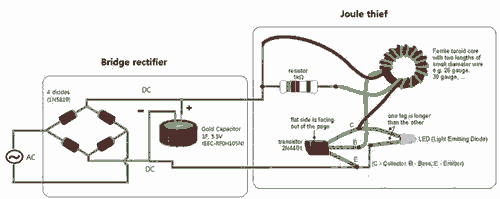
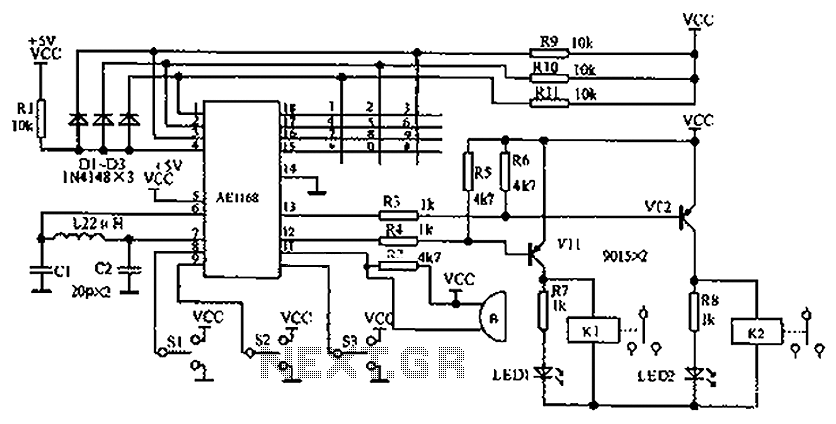
Ultrasonic Pest Repeller Circuit
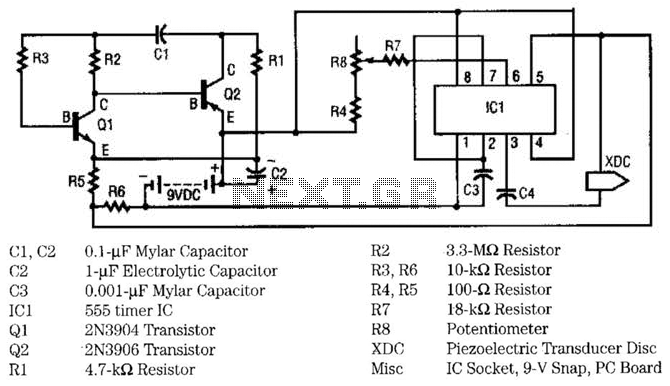
This circuit utilizes two transistors and one integrated circuit (555 timer IC) to generate a pulsating ultrasonic frequency. Transistors Q1 and Q2 are configured in a direct-coupled oscillator arrangement. The frequency of the oscillator is determined by capacitor C1. The output of the oscillator is taken from the emitter of Q2 and fed into pin 7 of IC1. Transistor Q1 is an NPN type, while Q2 is a PNP type. The signal at pin 7 of IC1 modulates the output signal at pin 3, influenced by the audio frequency generated by Q1 and Q2. The IC is configured as a stable multivibrator, with its frequency governed by capacitor C3. Capacitor C3 establishes a base frequency that lies well above the human hearing range, thus producing ultrasonic sound. The combined modulated ultrasonic frequency is available at pin 3 of IC1, where it is coupled through capacitor C4 to a piezoelectric transducer.
The circuit design incorporates a direct-coupled oscillator formed by the complementary transistors Q1 (NPN) and Q2 (PNP). This configuration allows for efficient oscillation, with the frequency being primarily determined by the capacitor C1, which sets the timing characteristics of the oscillator. The emitter of Q2 serves as the output point for this oscillation, providing a signal that is subsequently routed to pin 7 of the 555 timer IC (IC1).
The 555 timer is configured in a stable multivibrator mode, where its operation is influenced by capacitor C3. This capacitor plays a crucial role in determining the frequency of the output signal at pin 3 of the IC. The output signal at pin 3 is modulated by the audio frequency produced by the oscillator, resulting in a composite ultrasonic waveform.
Capacitor C3 ensures that the generated frequency remains in the ultrasonic range, effectively beyond the limits of human hearing. The final output, which combines the modulated ultrasonic frequency, is accessed at pin 3 of the 555 timer. This signal is then coupled to a piezoelectric transducer via capacitor C4, which converts the electrical signal into ultrasonic sound waves.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines the properties of transistors and a 555 timer to create an ultrasonic generator, with careful selection of capacitors to define the operational frequencies, ensuring the output is suitable for applications requiring ultrasonic sound generation. This circuit uses two transistors and one IC (555 timer IC) to produce a pulsating ultrasonic frequency. Transistors Ql and Q2 are connected in a direct-coupled oscillator. The frequency of that oscillator is set by capacitor CI. The oscillator output is taken from the emitter of Q2 to pin 7 of IC1. Transistor Ql is an npn transistor, and Q2 is a pnp transistor. The signal of pin 7 on IC1 causes the output signal appearing on pin 3 to be modulated or varied by the audio frequency developed by Ql and Q2.
The IC itself is connected as a stable multivibrator with a frequency that is determined by C3. Capacitor C3 sets the basic frequency to be well above the human hearing range (ultrasonic). The combined modulated ultrasonic frequency appears on pin 3 of IC1, where it is coupled by capacitor C4 to the piezoelectric transducer.
The circuit design incorporates a direct-coupled oscillator formed by the complementary transistors Q1 (NPN) and Q2 (PNP). This configuration allows for efficient oscillation, with the frequency being primarily determined by the capacitor C1, which sets the timing characteristics of the oscillator. The emitter of Q2 serves as the output point for this oscillation, providing a signal that is subsequently routed to pin 7 of the 555 timer IC (IC1).
The 555 timer is configured in a stable multivibrator mode, where its operation is influenced by capacitor C3. This capacitor plays a crucial role in determining the frequency of the output signal at pin 3 of the IC. The output signal at pin 3 is modulated by the audio frequency produced by the oscillator, resulting in a composite ultrasonic waveform.
Capacitor C3 ensures that the generated frequency remains in the ultrasonic range, effectively beyond the limits of human hearing. The final output, which combines the modulated ultrasonic frequency, is accessed at pin 3 of the 555 timer. This signal is then coupled to a piezoelectric transducer via capacitor C4, which converts the electrical signal into ultrasonic sound waves.
In summary, this circuit effectively combines the properties of transistors and a 555 timer to create an ultrasonic generator, with careful selection of capacitors to define the operational frequencies, ensuring the output is suitable for applications requiring ultrasonic sound generation. This circuit uses two transistors and one IC (555 timer IC) to produce a pulsating ultrasonic frequency. Transistors Ql and Q2 are connected in a direct-coupled oscillator. The frequency of that oscillator is set by capacitor CI. The oscillator output is taken from the emitter of Q2 to pin 7 of IC1. Transistor Ql is an npn transistor, and Q2 is a pnp transistor. The signal of pin 7 on IC1 causes the output signal appearing on pin 3 to be modulated or varied by the audio frequency developed by Ql and Q2.
The IC itself is connected as a stable multivibrator with a frequency that is determined by C3. Capacitor C3 sets the basic frequency to be well above the human hearing range (ultrasonic). The combined modulated ultrasonic frequency appears on pin 3 of IC1, where it is coupled by capacitor C4 to the piezoelectric transducer.