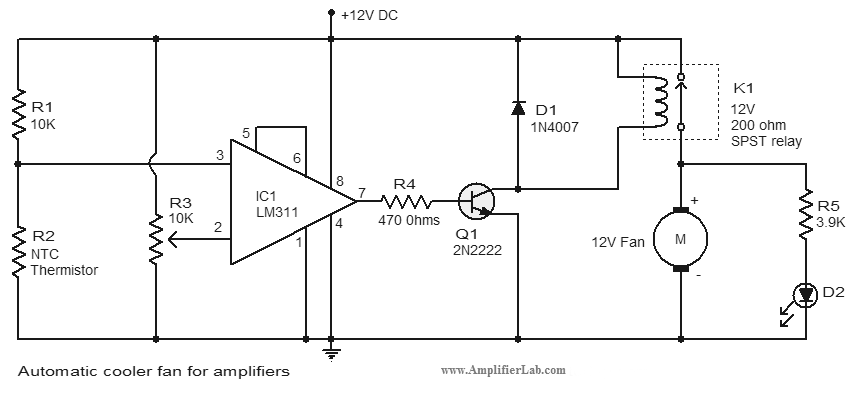
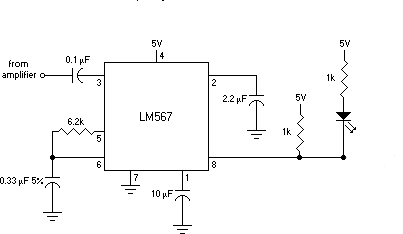
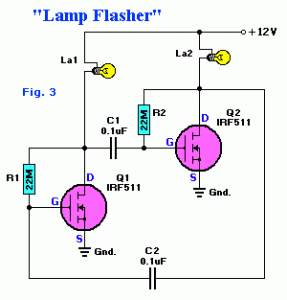
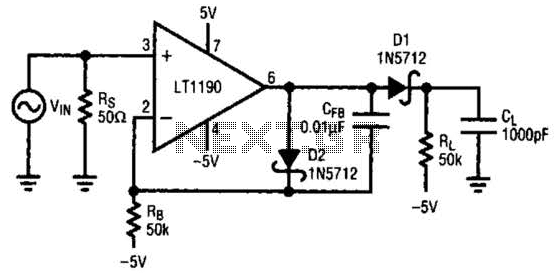
Bright JOULE THIEF flashlight circuit
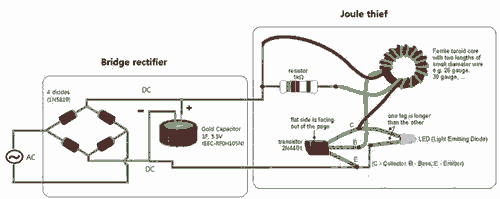
Breathe down and come out on the bright flashlight. In order to promote the voltage, pieces of a highly skilled Joule thief circuit have been used.
The Joule thief circuit is a minimalist, low-power boost converter designed to extract energy from low-voltage sources, such as depleted batteries. This circuit is particularly effective in applications where energy efficiency is critical, allowing for the utilization of energy that would otherwise be wasted.
The core component of the Joule thief is a transistor, which acts as a switch. When the circuit is powered, the transistor rapidly turns on and off, creating a magnetic field in the inductor. This magnetic field stores energy and, when the transistor turns off, the collapsing field induces a voltage spike. This spike is then rectified and smoothed to provide a higher output voltage than the input.
The typical configuration includes a few essential components: a transistor (often a low-threshold NPN type), a resistor, an inductor, and a diode. The resistor is used to limit the base current to the transistor, ensuring it operates within safe limits. The inductor is chosen based on the desired output voltage and current, while the diode prevents backflow of current, protecting the circuit.
In a flashlight application, the Joule thief can significantly extend the life of batteries by allowing them to be fully utilized until they can no longer provide usable power. This is particularly advantageous for LED flashlights, which require higher voltages than what a single AA or AAA battery can provide when nearly depleted.
Overall, the Joule thief circuit exemplifies an efficient solution for low-voltage energy harvesting, making it an ideal choice for portable lighting applications where maximizing battery life is essential.Breathe down and come out on the bright flashlight. In order to promote the voltage, I have used pieces of highly skilled Joule thief circuit 🔗 External reference
The Joule thief circuit is a minimalist, low-power boost converter designed to extract energy from low-voltage sources, such as depleted batteries. This circuit is particularly effective in applications where energy efficiency is critical, allowing for the utilization of energy that would otherwise be wasted.
The core component of the Joule thief is a transistor, which acts as a switch. When the circuit is powered, the transistor rapidly turns on and off, creating a magnetic field in the inductor. This magnetic field stores energy and, when the transistor turns off, the collapsing field induces a voltage spike. This spike is then rectified and smoothed to provide a higher output voltage than the input.
The typical configuration includes a few essential components: a transistor (often a low-threshold NPN type), a resistor, an inductor, and a diode. The resistor is used to limit the base current to the transistor, ensuring it operates within safe limits. The inductor is chosen based on the desired output voltage and current, while the diode prevents backflow of current, protecting the circuit.
In a flashlight application, the Joule thief can significantly extend the life of batteries by allowing them to be fully utilized until they can no longer provide usable power. This is particularly advantageous for LED flashlights, which require higher voltages than what a single AA or AAA battery can provide when nearly depleted.
Overall, the Joule thief circuit exemplifies an efficient solution for low-voltage energy harvesting, making it an ideal choice for portable lighting applications where maximizing battery life is essential.Breathe down and come out on the bright flashlight. In order to promote the voltage, I have used pieces of highly skilled Joule thief circuit 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713