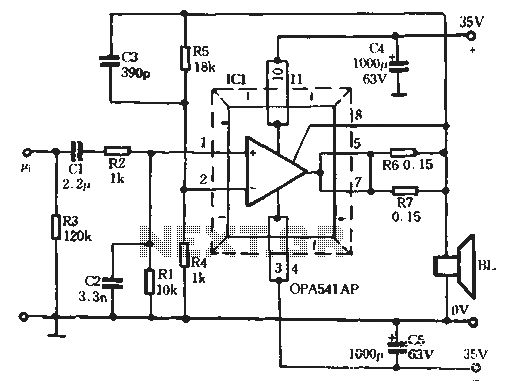
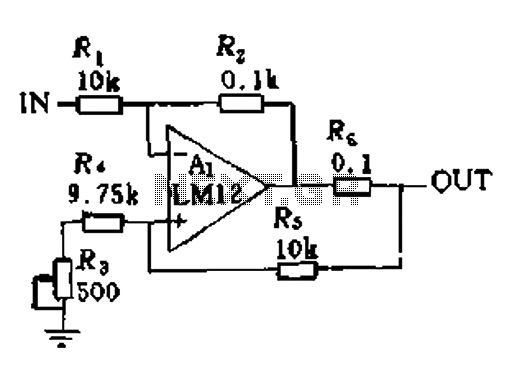
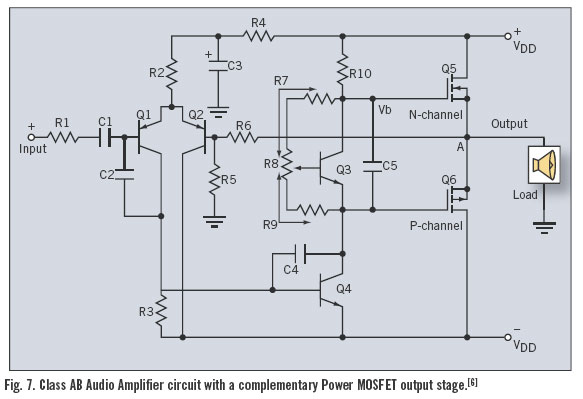
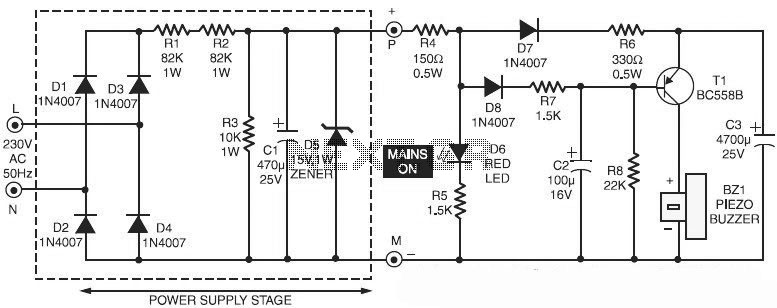
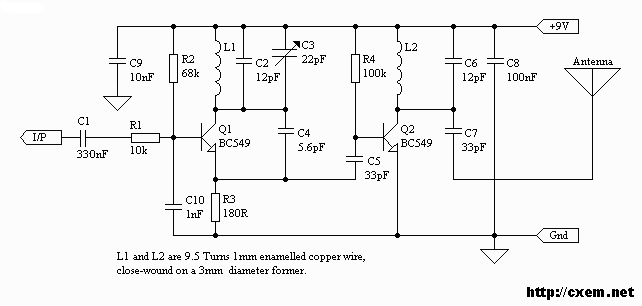
UPS-Uninterruptable Power Supplies
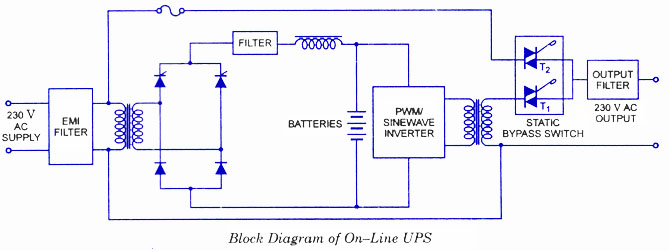
Most individuals take the mains AC supply for granted and use it casually without considering its inherent shortcomings and the potential dangers it poses to sophisticated and sensitive electronic instruments and equipment. For ordinary household appliances such as incandescent lamps, tubes, fans, TVs, and refrigerators, the mains AC supply does not make much difference. However, for computers, medical equipment, and telecommunication systems, a clean, stable, interruption-free power supply is of utmost importance. Among the various devices, processes, and systems that rely on AC power, computers are particularly sensitive to power disturbances and failures. Interruptions in the power supply may result in the loss or corruption of memory contents, system malfunctions or failures, and various component failures, leading to both inconvenience and financial loss. As more personal computers, word processors, and data terminals are integrated into small businesses, UPS systems that meet the power requirements and budget constraints of these organizations are being developed. There are three distinct types of uninterruptible power supplies (UPS): (i) online UPS, (ii) offline UPS, and (iii) electronic generators. In an online UPS, the battery-operated inverter is always on, supplying the AC output voltage whether the mains power is on or off. The UPS will operate until the battery discharges, after which the battery will recharge when the mains power resumes. In offline UPS and electronic generators, the inverter is off when mains power is present, and the output voltage is derived directly from the mains supply. The inverter activates only when the mains power is lost. The increasing reliance on computers in industry and commerce emphasizes the need for high-quality, stable, and interruption-free power supplies. A clean AC power source is essential for the operation of most sensitive electronic equipment, and many new sophisticated circuits are designed to mitigate the effects of disturbances typically found in the mains AC supply. To protect sensitive systems from power losses and blackouts, an alternative power source that can switch into operation immediately during disruptions is necessary. An uninterruptible power supply (UPS) serves as such an alternative source. A UPS typically includes a rectifier, battery charger, battery bank, and inverter circuit, which converts the commercial AC input into DC suitable for the battery bank and inverter. The rectifier should have input protection and be capable of supplying power to the inverter when the commercial supply voltage is slightly below or above normal levels. In the case of an online UPS, the battery-operated inverter functions continuously, regardless of the mains supply status. Triac T1 remains on at all times, while Triac T2 is designed to bypass the UPS inverter only when a fault occurs in the inverter. When the mains supply fails, the UPS provides power until the batteries discharge. Once mains power is restored, the batteries recharge. The switching times for these systems are considered to be zero. Typically, sealed maintenance-free batteries are utilized, and the operational time of the inverter is limited (approximately 10 to 30 minutes). For offline UPS, the inverter remains off when mains power is present, and the output voltage is directly derived from the mains. The inverter activates only when the mains supply fails, with a switching time of less than 5 ms. These UPS systems are generally used with PCs or computers or other appliances where a brief interruption (5 ms or less) in power supply can be tolerated. Sealed batteries are commonly employed in these systems.
To ensure the reliability and efficiency of uninterruptible power supplies, various design considerations must be addressed. The rectifier in the UPS should be designed with adequate protection against voltage surges and spikes, as well as thermal management mechanisms to prevent overheating. The battery charger must be capable of rapid charging to minimize downtime and ensure that the battery bank is ready for use when needed. The inverter circuit should provide a clean sine wave output to avoid introducing noise and harmonics that could affect sensitive electronic equipment.
In an online UPS configuration, the continuous operation of the inverter allows for instantaneous switching, eliminating any transfer time during power interruptions. The use of Triacs in the control circuitry helps manage the switching operations efficiently, providing redundancy and fault tolerance. In contrast, the offline UPS configuration, while simpler and often more cost-effective, requires careful consideration of the switching time to ensure that connected devices can tolerate brief power interruptions.
Overall, the design and implementation of UPS systems are critical for maintaining the operational integrity of sensitive electronic equipment in both commercial and industrial applications, ensuring that power disturbances do not compromise functionality or data integrity.Most of us take the mains ac supply for granted and use it almost casually without giving the slightest thought to its inherent shortcomings and the danger posed to sophisticated and sensitive electronic instruments/equipments. For ordinary household appliances such as incandencent lamps, tubes, fans, TV and fridge, the mains ac supply does not ma
ke much difference, but when used for computers, medical equipments and telecommunica ¬tion systems, a clean, stable interruption free power supply is of the utmost importance. Of the myriad of devices, processes and systems which rely on ac power, computers are probably the most sensitive to power disturbances and failures.
Interruptions in powersupply may cause the contents of a memory to be lost or corrupted, the entire system to malfunction or fail, or even variety of components failures to occur, all of which not only result in inconvenience but also loss of money. As more and more PCs, word processors and data terminals find their way into small business, UPS systems that meet the power requirements and price range needs of even the small business organizations and offices are being manufactured.
There are three distinct types of uninter rupted power supplies, namely, ( £) on-line UPS (ii) off-line UPS, and (Hi) electronic gen erators. In the on-line UPS, whether the mains power is on or off, the battery operated inverter is on all the time and supplies the ac output voltage.
When the mains power supply goes off, the UPS will be on only until the battery gets discharged. When the main power resumes, the battery will get charged again. In off-line UPS and electronic genera tors, ther inverter is off when the mains power is present and the output voltage derived directly from the mains is the same as the mains supply voltage. The inverter turns on only when the mains supply goes off. The ever increasing importance of computers in industry and commerce will increase the need for quality, high stability and interruption free power supplies.
A clean ac power source is the fundamental to the operation of most sensitive elec tronic equipment, and many new and sophisticated circuits are designed to overcome the effects of disturbances normally found in the mains ac supply. In order to protect a sensitive system from power losses and blackouts, an alternative power source is required that can switch into operation immediately when disruption occurs.
An interruptible power supply (UPS) is just such an alternative source. A UPS generally consists of a rectifier, battery charger, a battery bank and inverter circuit which converts the commercial ac input into dc suitable for input to the battery bank and the inverter. The rectifier should have its input protected and should be capable of supplying power to the inverter when the commercial supply is either slightly below the normal voltage or slightly above.
In case of On-line UPS, the battery operated inverter works continuously whether the mains supply is present or not. Triac T1 is on for all the times while Triac T2 has been provided to bypass the UPS inverter, only when a fault develops in the UPS inverter.
When the mains supply fails, the UPS supplies power only until the batteries get dis charged. However, once the mains power resumes, the batteries will get charged again. The switching times of these supplies is considered to be zero. Usually sealed maintenance free batteries are used and the running time of the inverter is low (approximately 10 to 30 minutes). In the case of Off-Line UPS, the inverter is off when the mains power is on and the output voltage is derived directly from the mains.
The inverter turns on only when the mains supply fails. Its switching time is less than 5 ms. These UPS are generally used with PCs or computers or other appliances where a small duration (5 ms or less) interrup tion in power supply can be tolerated. Usually, sealed batteries 🔗 External reference
To ensure the reliability and efficiency of uninterruptible power supplies, various design considerations must be addressed. The rectifier in the UPS should be designed with adequate protection against voltage surges and spikes, as well as thermal management mechanisms to prevent overheating. The battery charger must be capable of rapid charging to minimize downtime and ensure that the battery bank is ready for use when needed. The inverter circuit should provide a clean sine wave output to avoid introducing noise and harmonics that could affect sensitive electronic equipment.
In an online UPS configuration, the continuous operation of the inverter allows for instantaneous switching, eliminating any transfer time during power interruptions. The use of Triacs in the control circuitry helps manage the switching operations efficiently, providing redundancy and fault tolerance. In contrast, the offline UPS configuration, while simpler and often more cost-effective, requires careful consideration of the switching time to ensure that connected devices can tolerate brief power interruptions.
Overall, the design and implementation of UPS systems are critical for maintaining the operational integrity of sensitive electronic equipment in both commercial and industrial applications, ensuring that power disturbances do not compromise functionality or data integrity.Most of us take the mains ac supply for granted and use it almost casually without giving the slightest thought to its inherent shortcomings and the danger posed to sophisticated and sensitive electronic instruments/equipments. For ordinary household appliances such as incandencent lamps, tubes, fans, TV and fridge, the mains ac supply does not ma
ke much difference, but when used for computers, medical equipments and telecommunica ¬tion systems, a clean, stable interruption free power supply is of the utmost importance. Of the myriad of devices, processes and systems which rely on ac power, computers are probably the most sensitive to power disturbances and failures.
Interruptions in powersupply may cause the contents of a memory to be lost or corrupted, the entire system to malfunction or fail, or even variety of components failures to occur, all of which not only result in inconvenience but also loss of money. As more and more PCs, word processors and data terminals find their way into small business, UPS systems that meet the power requirements and price range needs of even the small business organizations and offices are being manufactured.
There are three distinct types of uninter rupted power supplies, namely, ( £) on-line UPS (ii) off-line UPS, and (Hi) electronic gen erators. In the on-line UPS, whether the mains power is on or off, the battery operated inverter is on all the time and supplies the ac output voltage.
When the mains power supply goes off, the UPS will be on only until the battery gets discharged. When the main power resumes, the battery will get charged again. In off-line UPS and electronic genera tors, ther inverter is off when the mains power is present and the output voltage derived directly from the mains is the same as the mains supply voltage. The inverter turns on only when the mains supply goes off. The ever increasing importance of computers in industry and commerce will increase the need for quality, high stability and interruption free power supplies.
A clean ac power source is the fundamental to the operation of most sensitive elec tronic equipment, and many new and sophisticated circuits are designed to overcome the effects of disturbances normally found in the mains ac supply. In order to protect a sensitive system from power losses and blackouts, an alternative power source is required that can switch into operation immediately when disruption occurs.
An interruptible power supply (UPS) is just such an alternative source. A UPS generally consists of a rectifier, battery charger, a battery bank and inverter circuit which converts the commercial ac input into dc suitable for input to the battery bank and the inverter. The rectifier should have its input protected and should be capable of supplying power to the inverter when the commercial supply is either slightly below the normal voltage or slightly above.
In case of On-line UPS, the battery operated inverter works continuously whether the mains supply is present or not. Triac T1 is on for all the times while Triac T2 has been provided to bypass the UPS inverter, only when a fault develops in the UPS inverter.
When the mains supply fails, the UPS supplies power only until the batteries get dis charged. However, once the mains power resumes, the batteries will get charged again. The switching times of these supplies is considered to be zero. Usually sealed maintenance free batteries are used and the running time of the inverter is low (approximately 10 to 30 minutes). In the case of Off-Line UPS, the inverter is off when the mains power is on and the output voltage is derived directly from the mains.
The inverter turns on only when the mains supply fails. Its switching time is less than 5 ms. These UPS are generally used with PCs or computers or other appliances where a small duration (5 ms or less) interrup tion in power supply can be tolerated. Usually, sealed batteries 🔗 External reference