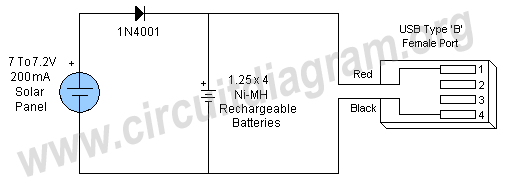
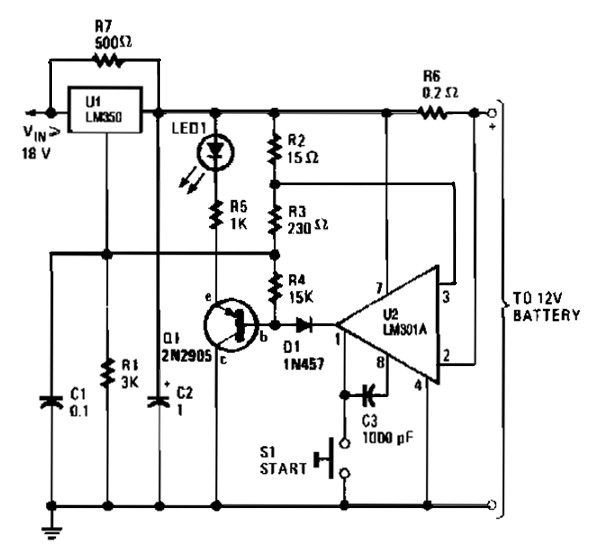
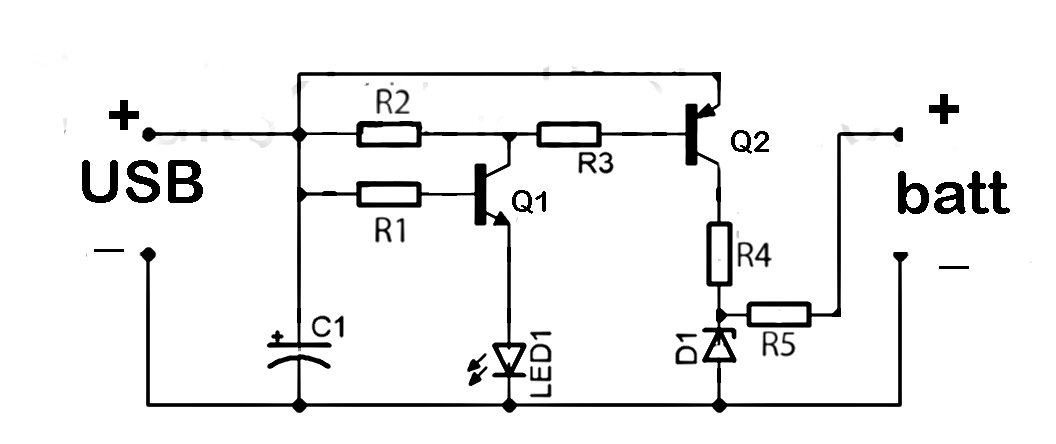
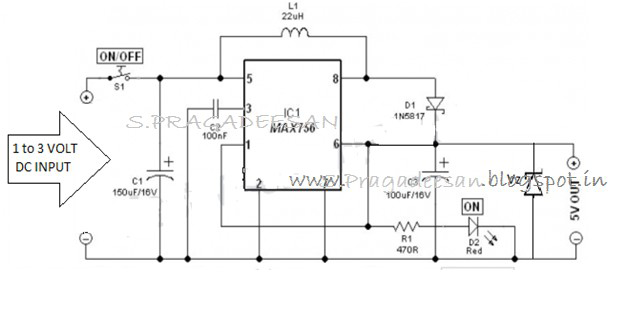
USB Charge PCB
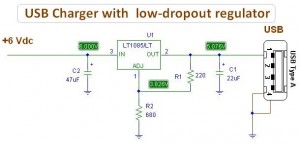
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) specification provides both connectivity and power. This advancement emphasizes the transition from series and parallel connections of the past, enabling an increased number of devices to interface with a personal computer. A basic circuit USB charger utilizing a low-dropout regulator (LDO) employs the LT1085 integrated circuit (IC). One application of USB power is in battery charging. Many mobile devices, such as MP3 players and PDAs, benefit from the convenience of simultaneous data exchange and charging via a USB cable. The integration of USB functionality with battery charging allows for a variety of autonomous devices, such as webcams, to connect to a PC or operate independently. In many instances, the need for cumbersome adapters or wall chargers is eliminated. The complexity of a USB battery charger can vary, as it is not bound by stringent requirements typical of USB devices.
The USB specification has revolutionized the way electronic devices are powered and connected, allowing for a standardized method of data transfer and power supply. The LT1085 is a popular choice for implementing a low-dropout regulator in USB charger circuits. This IC is capable of providing a stable output voltage with minimal voltage drop, making it ideal for battery charging applications where efficiency is crucial.
In a typical USB charger circuit using the LT1085, the input voltage is derived from a USB port, which supplies 5V. The LT1085 can regulate this voltage to a lower level, suitable for charging batteries of various chemistries, such as lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride. The circuit design generally includes input and output capacitors to stabilize voltage levels and reduce noise, ensuring smooth operation.
The architecture of the circuit allows for simultaneous data transfer while charging, which is particularly beneficial for mobile devices. The USB interface facilitates communication between the device and the host computer, enabling functionalities such as file transfer and device management. The ability to charge while exchanging data eliminates the need for separate charging devices, enhancing user convenience.
Furthermore, the design of the USB charger can be adapted to support various charging protocols, such as USB Power Delivery (USB PD), which allows for higher power levels and faster charging times. This adaptability is essential as the demand for faster charging solutions continues to grow in the consumer electronics market.
In summary, the integration of USB technology with battery charging capabilities, exemplified by the use of the LT1085 low-dropout regulator, represents a significant advancement in electronic design, providing efficient power management and enhanced user experience across a wide range of devices.The USB(Universal Serial Bus) specification provides the ability and energy. This change highlights series and parallel connections of the past, allowing an increase in the number of devices that can use a Personal computer. This simple circuit USB charger low-dropout regulator (LDO) has use IC LT1085. One way to use the USB power is the battery . Since many mobile devices such as MP3 players and PDAs to exchange information with computers, peripherals convenience is significant when the battery and the exchange of data takes place simultaneously on cable. The combination of USB and battery function leads to a series of autonomous from devices such as webcams lid, all connected to a PC or not.
In many cases, it is no longer required, a clumsy adapter or wall wart. The battery charger from the USB can be complex or simple as you are exempt from the requirements of the USB device. 🔗 External reference
The USB specification has revolutionized the way electronic devices are powered and connected, allowing for a standardized method of data transfer and power supply. The LT1085 is a popular choice for implementing a low-dropout regulator in USB charger circuits. This IC is capable of providing a stable output voltage with minimal voltage drop, making it ideal for battery charging applications where efficiency is crucial.
In a typical USB charger circuit using the LT1085, the input voltage is derived from a USB port, which supplies 5V. The LT1085 can regulate this voltage to a lower level, suitable for charging batteries of various chemistries, such as lithium-ion or nickel-metal hydride. The circuit design generally includes input and output capacitors to stabilize voltage levels and reduce noise, ensuring smooth operation.
The architecture of the circuit allows for simultaneous data transfer while charging, which is particularly beneficial for mobile devices. The USB interface facilitates communication between the device and the host computer, enabling functionalities such as file transfer and device management. The ability to charge while exchanging data eliminates the need for separate charging devices, enhancing user convenience.
Furthermore, the design of the USB charger can be adapted to support various charging protocols, such as USB Power Delivery (USB PD), which allows for higher power levels and faster charging times. This adaptability is essential as the demand for faster charging solutions continues to grow in the consumer electronics market.
In summary, the integration of USB technology with battery charging capabilities, exemplified by the use of the LT1085 low-dropout regulator, represents a significant advancement in electronic design, providing efficient power management and enhanced user experience across a wide range of devices.The USB(Universal Serial Bus) specification provides the ability and energy. This change highlights series and parallel connections of the past, allowing an increase in the number of devices that can use a Personal computer. This simple circuit USB charger low-dropout regulator (LDO) has use IC LT1085. One way to use the USB power is the battery . Since many mobile devices such as MP3 players and PDAs to exchange information with computers, peripherals convenience is significant when the battery and the exchange of data takes place simultaneously on cable. The combination of USB and battery function leads to a series of autonomous from devices such as webcams lid, all connected to a PC or not.
In many cases, it is no longer required, a clumsy adapter or wall wart. The battery charger from the USB can be complex or simple as you are exempt from the requirements of the USB device. 🔗 External reference