Variable (Adjustable) Current Limiter Circuit
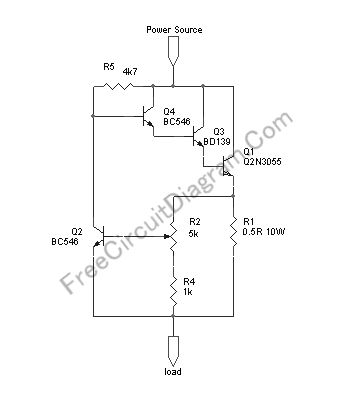
This circuit provides automatic current limiting up to 8.4 A. Unlike current limiters that use only a resistor, this current limiting circuit does not drop the voltage significantly or keeps the voltage drop to a minimum until a specific current threshold is exceeded. The current limit is adjustable from 1.4 A to 8.4 A using a potentiometer. Component values can be modified to achieve different current limiting ranges. The schematic diagram of the circuit is as follows: Resistor R1 is used to sense the current. With the R2 potentiometer set to minimum resistance (the center tap connected to R1), when the current drawn by the load reaches 1.2 A, the voltage across R1 reaches 0.6 V, and Q2 begins conducting. This action shorts the base voltage of Q4 to ground, reducing the base current and consequently lowering the output voltage sensed by the load, which prevents further current flow. To limit the current at a lower threshold, R1 can be changed to 1Ω, providing an adjustment range of approximately 0.7 A to 4.2 A. Due to the power dissipation capability of the 2N3055 transistor, in the worst-case scenario where the load is shorted to ground (zero resistance), limiting the current to 8.4 A allows the circuit to handle a maximum source voltage of 14 V. If the current is limited to 4.2 A, the circuit can handle up to 27 V source voltage. The maximum voltage that this circuit can handle is 60 V, but at this maximum voltage, the current limit can only be safely set to 1.9 A under extreme conditions when the load is shorted to ground. It is essential to ensure that the Q1 transistor has an adequate heat sink.
The automatic current limiting circuit described operates on the principle of feedback control to prevent excessive current flow, thus protecting both the circuit and the load. The operational mechanism involves the use of a current sensing resistor (R1), which generates a voltage proportional to the current flowing through it. This voltage is monitored by the transistor Q2, which acts as a switch that responds to the sensed current.
The potentiometer R2 allows for fine-tuning of the current limit. By adjusting its resistance, the user can set the desired threshold at which the circuit will begin to limit the current. When the load current exceeds the set limit, the voltage across R1 increases, causing Q2 to conduct. This conduction effectively pulls the base voltage of transistor Q4 to ground, reducing its output to the load and thereby limiting the current.
The circuit is designed to handle a range of input voltages, with the 2N3055 transistor providing sufficient power dissipation capacity. The transistor must be adequately heat-sinked to manage the thermal load generated during operation, especially at high current limits. The circuit's ability to handle a maximum voltage of 60 V, while maintaining a current limit of 1.9 A, showcases its versatility in various applications where current regulation is critical.
In summary, this automatic current limiting circuit is a robust solution for applications requiring precise current control, offering adjustable limits and high voltage handling capabilities while ensuring the safety and longevity of both the circuit and connected components.This circuit provide automatic current limiting up to 8. 4A. Unlike current limiter that uses only a resistor, this current limiting circuit doesn`t drop the voltage, or at least keep the voltage drop at minimum, until a certain current amount is exceeded. This current amount limit is adjustable from 1. 4 A to 8. 4A using a potentiometer. You can mod ify the component value to give different current limiting range. Here is the circuit`s schematic diagram: The resistor R1 is there to sense the current. At R2 potentiometer at minimum resistance (the center tap connected to R1), if the current drawn by the load reach 1. 2A then the voltage across R1 reach 0. 6V and Q2 begin conducting, thus shorting the base voltage of Q4 to ground. This shorting action reduce the base current and therefore reduce the output voltage sensed by the load, and prevent the current to flow further.
If you need the current limiter to limit at lower threshold range, you can change the R1 to 1R and you`ll get about 0. 7A to 4. 2A adjustment range. Because of the power dissipation capability of 2N3055 transistor, at the worst case that the load is shorted to ground (zero resistance), if you limit the current to 8.
4 A then the circuit can handle maximum source voltage of 14V, while limiting the current at 4. 2A can handle up to 27V source voltage. The maximum voltage can be handled by this circuit is 60 volt, but at that maximum voltage you can only safely set the current limit at 1. 9A in the extreme condition, when the load is shorted to ground. Please make sure the Q1 transistor has sufficient heat sink. [Circuit Schematic Source: Designed by FreeCircuitDiagram. Com] 🔗 External reference
The automatic current limiting circuit described operates on the principle of feedback control to prevent excessive current flow, thus protecting both the circuit and the load. The operational mechanism involves the use of a current sensing resistor (R1), which generates a voltage proportional to the current flowing through it. This voltage is monitored by the transistor Q2, which acts as a switch that responds to the sensed current.
The potentiometer R2 allows for fine-tuning of the current limit. By adjusting its resistance, the user can set the desired threshold at which the circuit will begin to limit the current. When the load current exceeds the set limit, the voltage across R1 increases, causing Q2 to conduct. This conduction effectively pulls the base voltage of transistor Q4 to ground, reducing its output to the load and thereby limiting the current.
The circuit is designed to handle a range of input voltages, with the 2N3055 transistor providing sufficient power dissipation capacity. The transistor must be adequately heat-sinked to manage the thermal load generated during operation, especially at high current limits. The circuit's ability to handle a maximum voltage of 60 V, while maintaining a current limit of 1.9 A, showcases its versatility in various applications where current regulation is critical.
In summary, this automatic current limiting circuit is a robust solution for applications requiring precise current control, offering adjustable limits and high voltage handling capabilities while ensuring the safety and longevity of both the circuit and connected components.This circuit provide automatic current limiting up to 8. 4A. Unlike current limiter that uses only a resistor, this current limiting circuit doesn`t drop the voltage, or at least keep the voltage drop at minimum, until a certain current amount is exceeded. This current amount limit is adjustable from 1. 4 A to 8. 4A using a potentiometer. You can mod ify the component value to give different current limiting range. Here is the circuit`s schematic diagram: The resistor R1 is there to sense the current. At R2 potentiometer at minimum resistance (the center tap connected to R1), if the current drawn by the load reach 1. 2A then the voltage across R1 reach 0. 6V and Q2 begin conducting, thus shorting the base voltage of Q4 to ground. This shorting action reduce the base current and therefore reduce the output voltage sensed by the load, and prevent the current to flow further.
If you need the current limiter to limit at lower threshold range, you can change the R1 to 1R and you`ll get about 0. 7A to 4. 2A adjustment range. Because of the power dissipation capability of 2N3055 transistor, at the worst case that the load is shorted to ground (zero resistance), if you limit the current to 8.
4 A then the circuit can handle maximum source voltage of 14V, while limiting the current at 4. 2A can handle up to 27V source voltage. The maximum voltage can be handled by this circuit is 60 volt, but at that maximum voltage you can only safely set the current limit at 1. 9A in the extreme condition, when the load is shorted to ground. Please make sure the Q1 transistor has sufficient heat sink. [Circuit Schematic Source: Designed by FreeCircuitDiagram. Com] 🔗 External reference