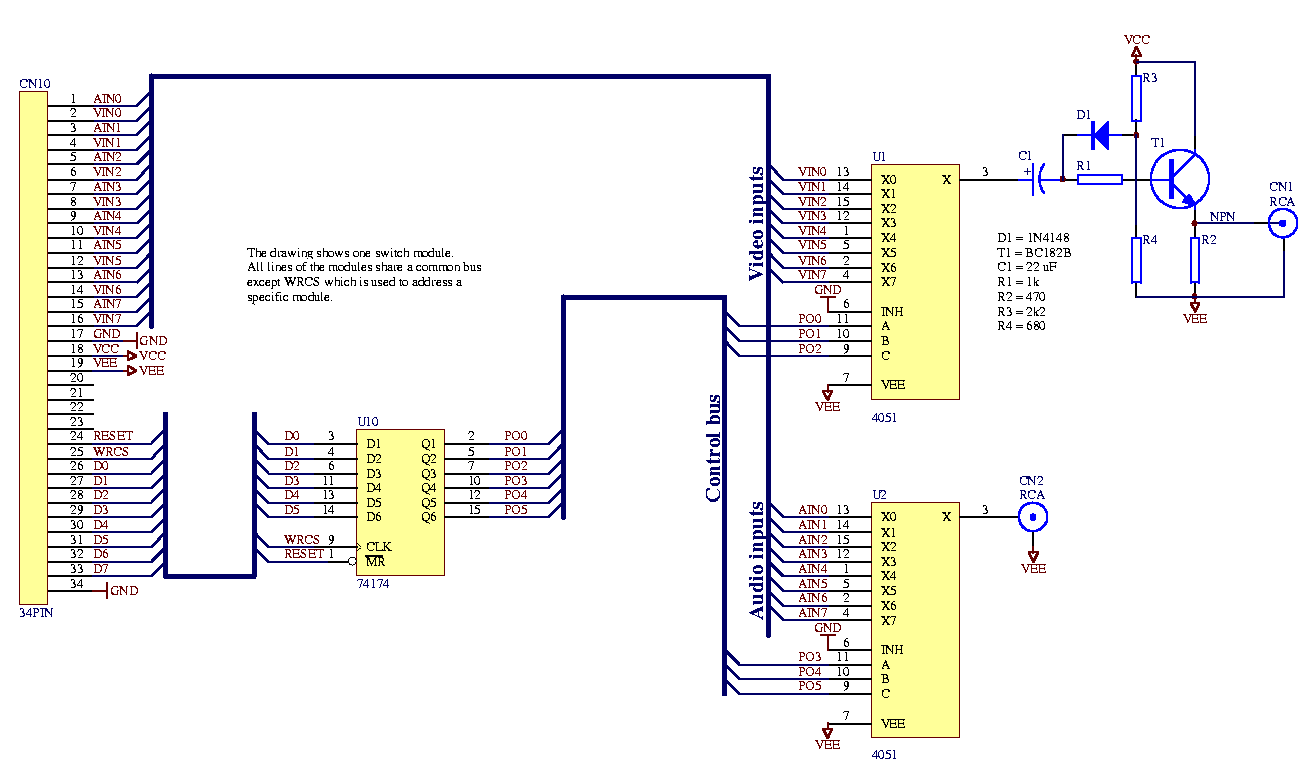
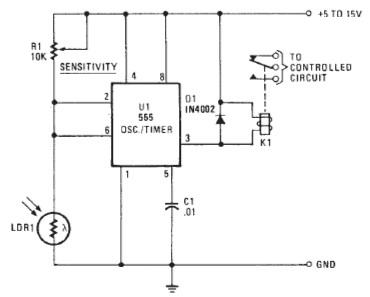
Video Fader Circuit
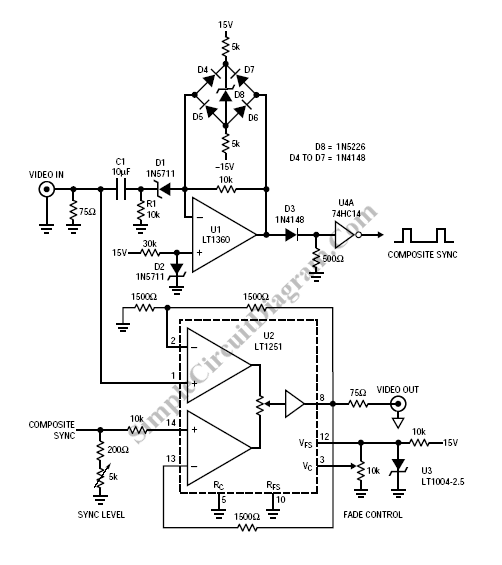
Fading a video signal cannot be achieved merely by attenuating the composite signal, as this may cause the synchronization signal to fall below an unacceptable level.
To effectively fade a video signal while maintaining the integrity of the synchronization components, a more sophisticated approach is required. This can be achieved through the implementation of a dedicated fading circuit that selectively attenuates the luminance (Y) and chrominance (C) components of the video signal, while preserving the timing information.
A common method involves the use of a voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) for the luminance signal and a separate VCA for the chrominance signal. These components can be controlled by a common control voltage that dictates the fade level. The synchronization pulses, which are embedded within the composite signal, must be extracted and treated separately to ensure they remain at an acceptable amplitude throughout the fading process.
The circuit can be designed using operational amplifiers configured as inverting or non-inverting amplifiers, where the gain can be adjusted based on the control voltage. A low-pass filter may also be integrated to smooth out any abrupt changes in the signal, which can lead to visual artifacts.
In addition, a feedback mechanism can be implemented to monitor the output levels of the synchronization signals, ensuring they do not drop below the required thresholds. This can be achieved using comparators that trigger an alarm or adjust the control voltage dynamically if the sync pulses approach critical levels.
In summary, fading a video signal requires careful handling of both the luminance and chrominance components, as well as the synchronization signals, to ensure a seamless transition without degradation of the signal quality. Proper circuit design, including the use of VCAs and feedback mechanisms, is essential to achieve the desired result.Fading a video signal can`t be done simply by attenuating the composite signal, since the synchronization signal may drop below unacceptable level. Here a . 🔗 External reference
To effectively fade a video signal while maintaining the integrity of the synchronization components, a more sophisticated approach is required. This can be achieved through the implementation of a dedicated fading circuit that selectively attenuates the luminance (Y) and chrominance (C) components of the video signal, while preserving the timing information.
A common method involves the use of a voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) for the luminance signal and a separate VCA for the chrominance signal. These components can be controlled by a common control voltage that dictates the fade level. The synchronization pulses, which are embedded within the composite signal, must be extracted and treated separately to ensure they remain at an acceptable amplitude throughout the fading process.
The circuit can be designed using operational amplifiers configured as inverting or non-inverting amplifiers, where the gain can be adjusted based on the control voltage. A low-pass filter may also be integrated to smooth out any abrupt changes in the signal, which can lead to visual artifacts.
In addition, a feedback mechanism can be implemented to monitor the output levels of the synchronization signals, ensuring they do not drop below the required thresholds. This can be achieved using comparators that trigger an alarm or adjust the control voltage dynamically if the sync pulses approach critical levels.
In summary, fading a video signal requires careful handling of both the luminance and chrominance components, as well as the synchronization signals, to ensure a seamless transition without degradation of the signal quality. Proper circuit design, including the use of VCAs and feedback mechanisms, is essential to achieve the desired result.Fading a video signal can`t be done simply by attenuating the composite signal, since the synchronization signal may drop below unacceptable level. Here a . 🔗 External reference